Semiconductor Fab Financial Model
This 20-Year, 3-Statement Excel Semiconductor Fab Financial Model includes 10 sales revenue streams from Microprocessors to Radio Frequency (RF) Chips, cost structures, financial statements, DCF (Discounted Cash Flow), WACC (Weighted Average Cost of Capital), Sensitivity Analysis, to forecast the financial health of your Semiconductor Fab.
20-year Financial Model for a Semiconductor Fab
This very extensive 20 Year Semiconductor Fabrication Plant Model involves detailed revenue projections, cost structures, capital expenditures, and financing needs. This model provides a thorough understanding of the financial viability, profitability, and cash flow position of the fab. Including: 20x Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, Balance Sheets, CAPEX sheets, OPEX Sheets, Statement Summary Sheets, and Revenue Forecasting Charts with the specified revenue streams, BEA charts, sales summary charts, employee salary tabs and expenses sheets. Over 120 spreadsheets in one Excel Workbook.
A. Capex and Ramp-Up
Ramp-up capacity (% utilization over time)
Cleanroom capacity
Equipment depreciation life (5–7 years)
B. Operating Metrics
Capacity (wafers per month)
ASP (average selling price per wafer or die)
Yield
Utilization rate
Production cost per wafer (variable costs)
Maintenance and upgrades
C. Financing Assumptions
Debt/equity mix
Interest rate
Loan term
Government grants or subsidies
Tax incentives and depreciation schedules
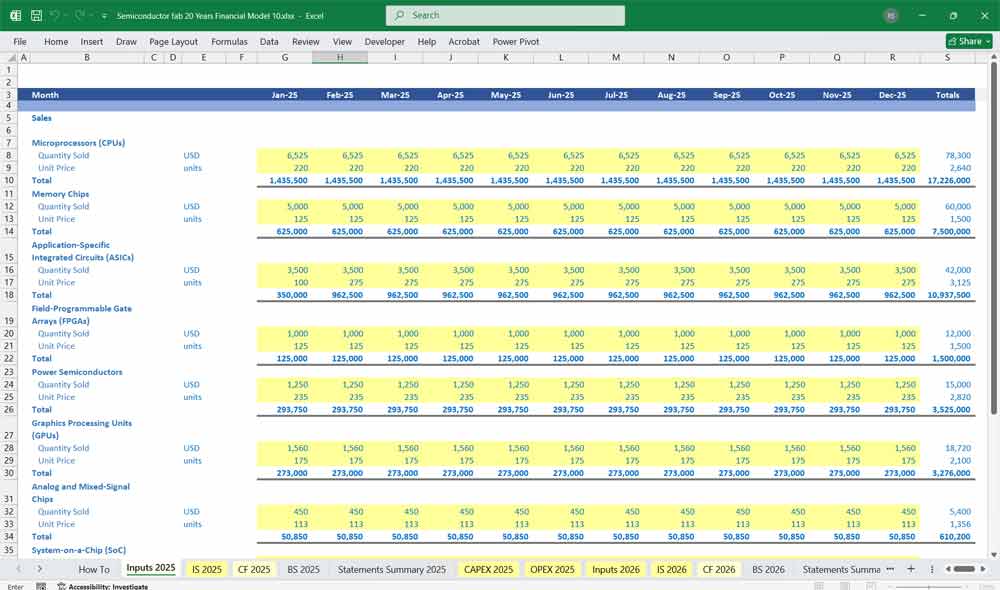
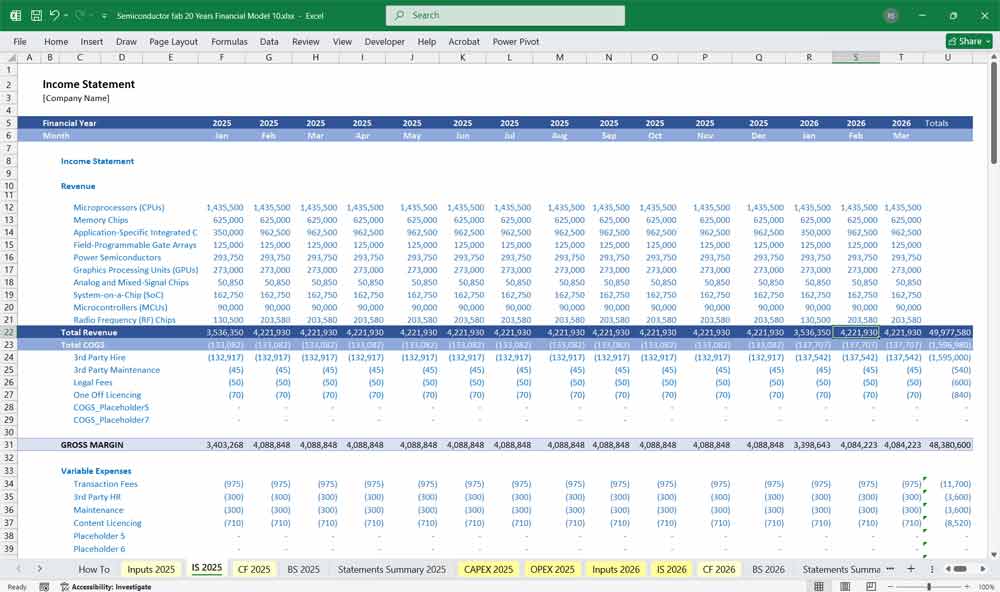
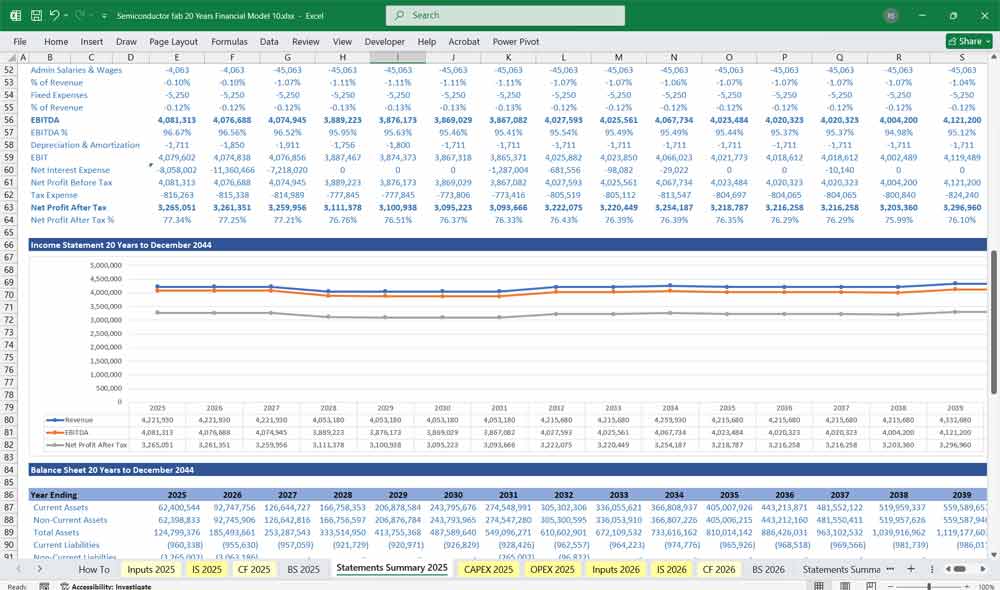
Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
The Income Statement tracks revenue, costs, and profitability over a given period (monthly over 20 years).
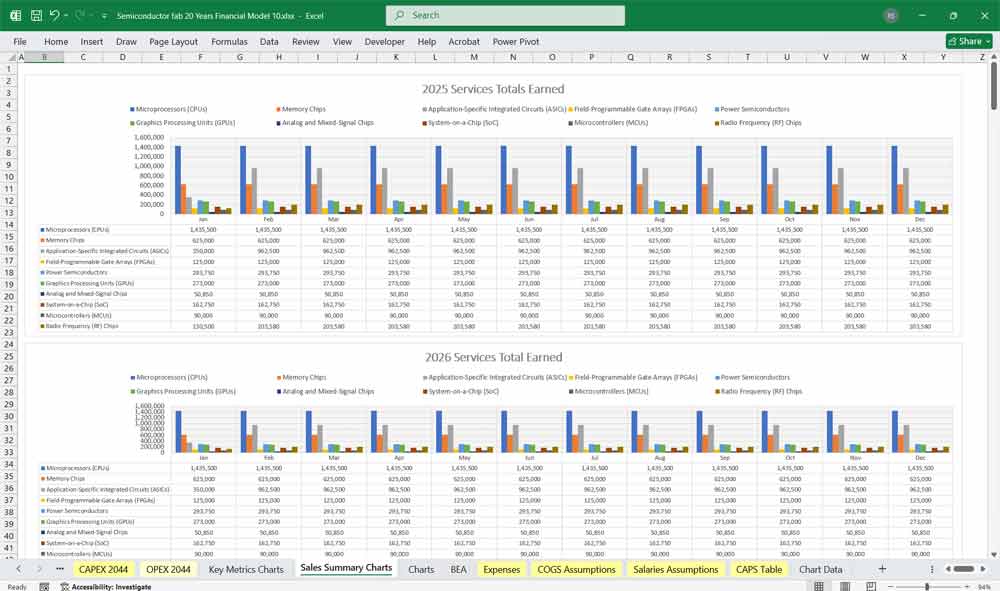
A. Revenue
Wafer Sales Revenue
Volume (wafers/month) × Average Selling Price (ASP) per wafer
Differentiated by node (e.g., 28nm, 14nm, 7nm, 5nm)
Long-term contracts vs. spot market pricing
Licensing & Royalties
IP licensing fees from design partners
Technology transfer agreements
Engineering Services
Custom process development for clients
B. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Direct Manufacturing Costs
Materials: Silicon wafers, chemicals, gases, photomasks
Labor: Technicians, engineers, fab operators
Utilities: High electricity, water, and gas consumption
Depreciation: Equipment (lifespan: 5-10 years)
Indirect Costs
Facility maintenance
Equipment servicing & spare parts
Yield loss (defective wafers)
C. Gross Profit
Revenue – COGS = Gross Profit
Gross Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Revenue) × 100
D. Operating Expenses (OpEx)
Research & Development (R&D)
Process technology development
New node R&D (e.g., moving from 5nm to 3nm)
Sales & Marketing
Customer acquisition costs
Trade shows, technical support
General & Administrative (G&A)
Salaries for management, legal, HR
Insurance, compliance, IT infrastructure
E. EBITDA & Net Profit
EBITDA = Gross Profit – OpEx
EBIT = EBITDA – Depreciation & Amortization
Net Profit = EBIT – Interest – Taxes
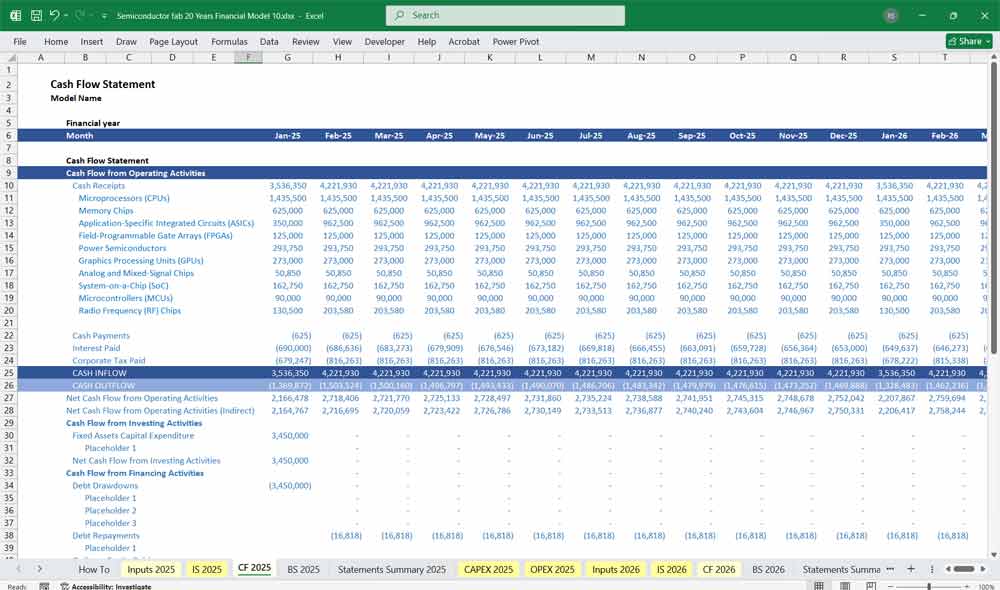
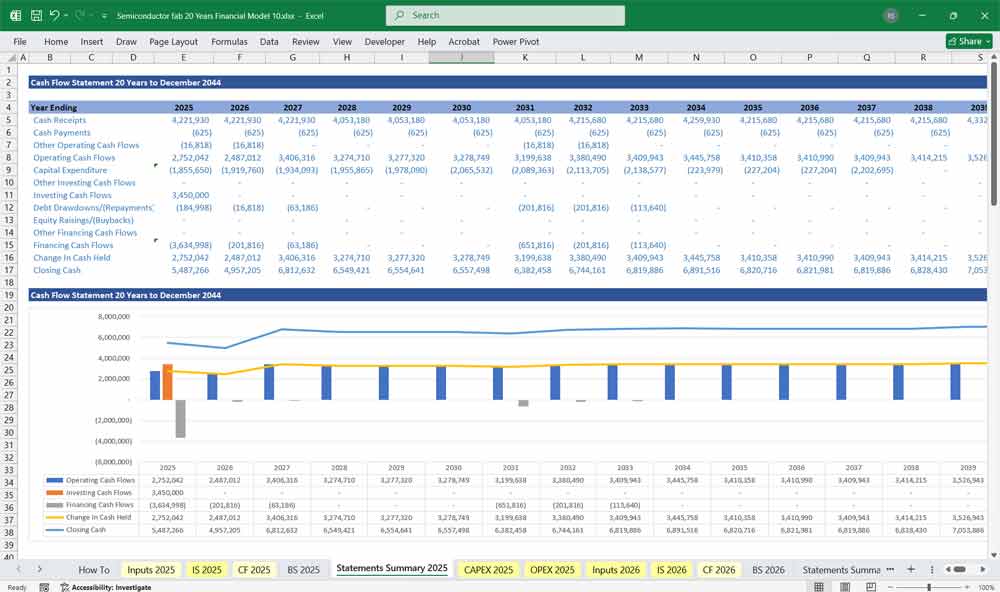
Semiconductor Fab Cash Flow Statement
Tracks cash inflows and outflows across Operating, Investing, and Financing Activities.
A. Cash Flow from Operations (CFO)
Net Income (from Income Statement)
Adjustments for Non-Cash Items
Depreciation & Amortization (added back)
Changes in Working Capital:
Inventory (silicon wafers, raw materials)
Accounts Receivable (customer payments)
Accounts Payable (supplier payments)
B. Cash Flow from Investing (CFI)
Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
Equipment Purchases: Lithography (EUV/DUV), etching, deposition tools
Facility Expansion: Cleanroom construction, utility upgrades
Technology Upgrades: Moving to next-gen nodes
Other Investments
Joint ventures, acquisitions
C. Cash Flow from Financing (CFF)
Debt Financing
Loans for CapEx (long-term debt issuance)
Interest payments
Equity Financing
Venture capital, IPO proceeds
Share buybacks or dividends (rare in early-stage fabs)
D. Net Cash Flow
CFO + CFI + CFF = Net Change in Cash
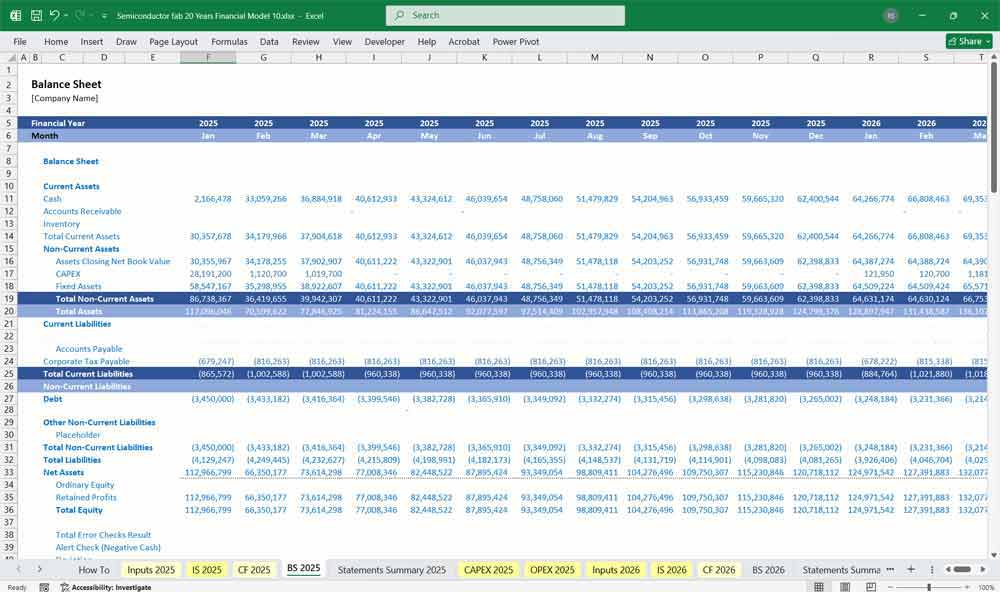
Semiconductor Fab Balance Sheet
A snapshot of the company’s financial position at a given time.
A. Assets
Current Assets
Cash & Equivalents
Accounts Receivable (unpaid wafer sales)
Inventory (raw wafers, work-in-progress, finished goods)
Non-Current Assets
Property, Plant & Equipment (PP&E):
Cleanroom facilities
Semiconductor tools (lithography, etching, deposition)
Intangible Assets: Patents, IP licenses
B. Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable (suppliers, contractors)
Short-term debt (working capital loans)
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-term debt (equipment financing)
Lease obligations (facilities, equipment)
C. Shareholders’ Equity
Common Stock
Retained Earnings (accumulated profits)
Additional Semiconductor Fab Model Sections
Note: because of the number of variances in the services offered for revenues, we cannot cover every scenario within a sensitivity analysis, so the user will require some additional inputs through the use of the Ribbon.
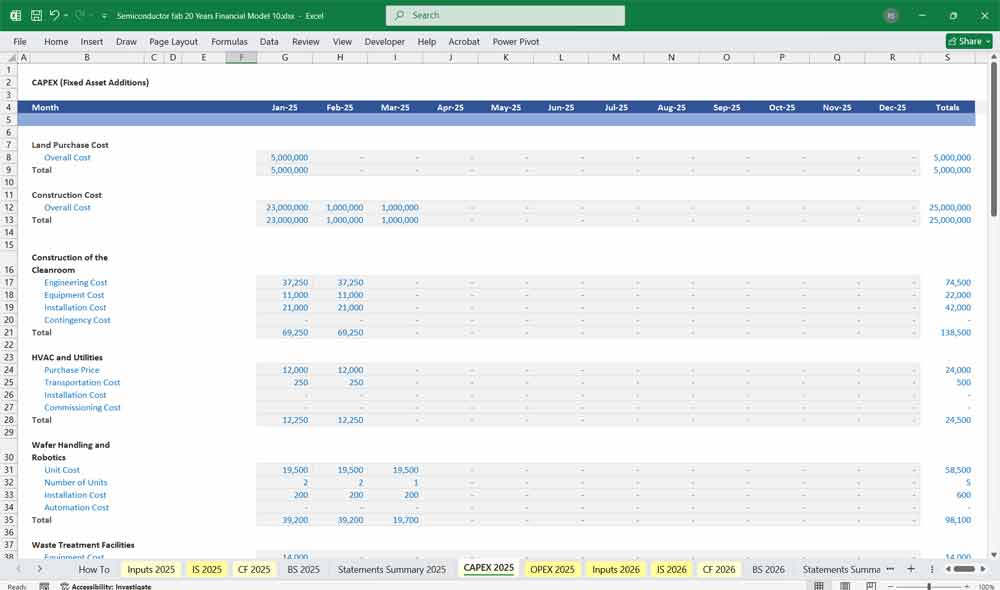
1. CapEx Schedule
Multi-year schedule broken down by:
Building
Equipment (depreciable)
Upgrades
Replacement capex
2. Depreciation Schedule
Based on capex and asset class
3. Debt Schedule
Term loan or bond
Interest calculations
Amortization of principal
Covenants, if any
4. Working Capital Schedule
DSO, assumptions
Drives receivables, payables
5. Scenario and Sensitivity Analysis
Volatility
Capex overruns
Output Metrics & KPIs
Gross Margin %
EBITDA Margin %
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC)
Payback Period (for fab investment)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Net Present Value (NPV) of project
Free Cash Flow (FCF)
Debt/Equity ratio
Interest Coverage Ratio
Fab Utilization Rate
Cost per wafer
Benefits of a 20-year Semiconductor Fab Model
A 20-year semiconductor fab financial model provides a comprehensive view of long-term capital deployment, profitability, and risk. Given the immense upfront investment and long development cycle of a semiconductor fabrication facility, short-term models are insufficient to capture the full return on investment. A 20-year horizon allows stakeholders to evaluate the entire lifecycle—from site construction and ramp-up to peak production and eventual technology obsolescence or repurposing.
Semiconductor Fab Long Term Perspective
Such a model enables more accurate forecasting of revenue streams and cost structures over time. It captures the evolving dynamics of wafer pricing, technology migration (e.g., from 7nm to 3nm), utilization rates, and maintenance capex. This long-range perspective is critical for planning major reinvestments, technology upgrades, and equipment replacements—each of which can significantly impact cash flow and competitiveness.
20-year Semiconductor Fab Model Risk Management and Strategy
For investors, lenders, and policymakers, a 20-year Semiconductor fab financial model is an essential tool for risk management and strategic decision-making. It helps assess debt servicing ability, funding gaps, and potential returns under different market and operational scenarios. It also supports justification for public incentives, tax abatements, and infrastructure development by demonstrating long-term economic impact and job creation potential.
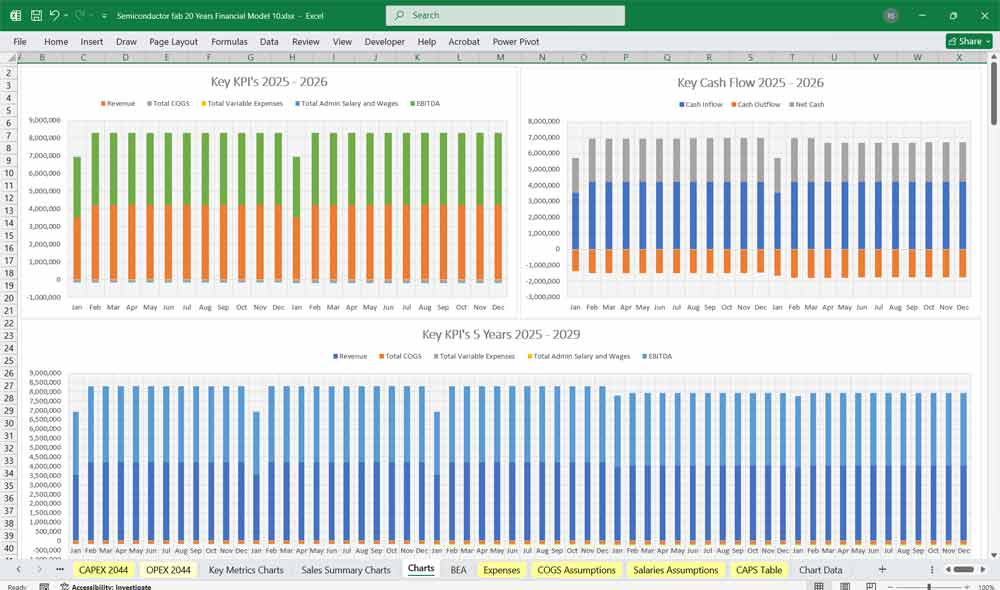
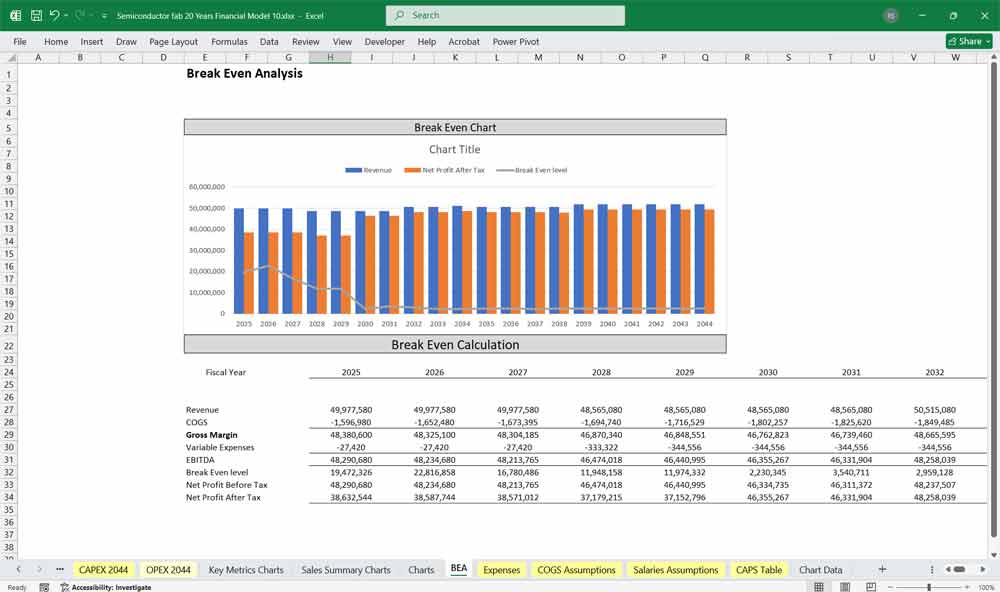
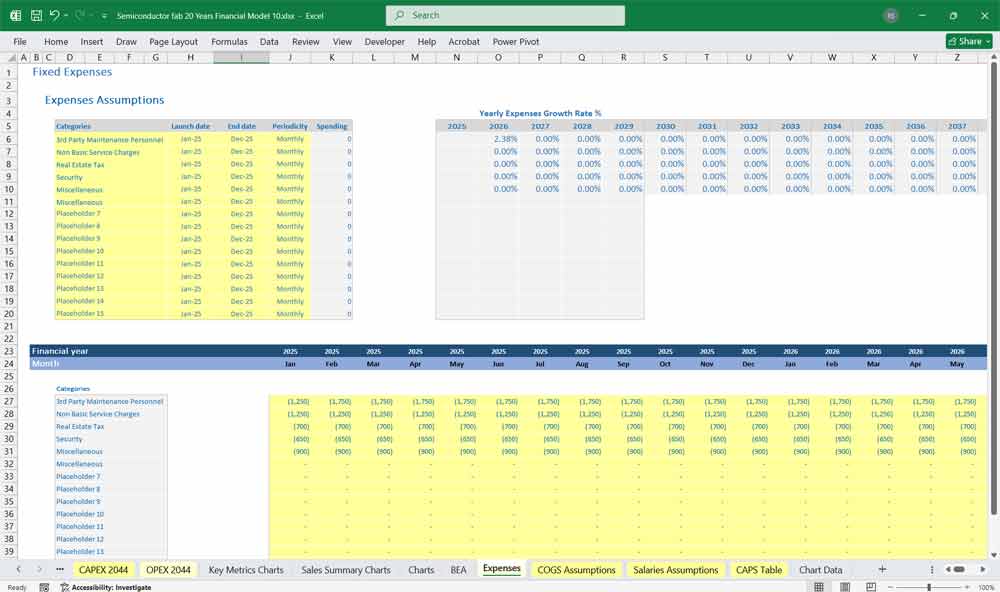
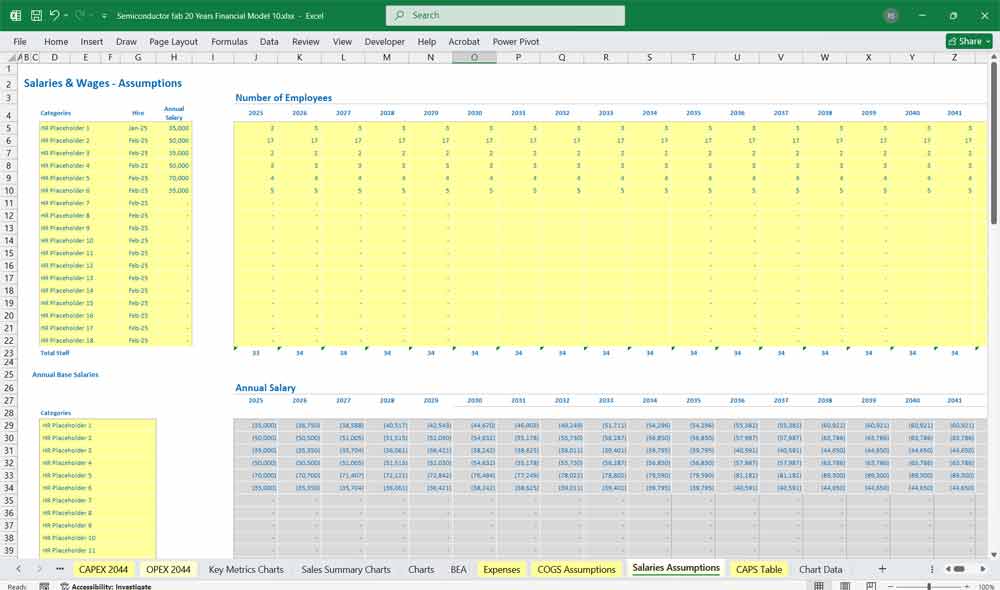
Semiconductor Fab Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) with Terminal Value, Sensitivity Analysis, and WACC
DCF: Modeling Extreme Capital Intensity and Rapid Cycles
A Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis for a semiconductor fab estimates the facility’s value based on projected future cash flows generated from chip production. These cash flows depend on factors such as wafer capacity utilization, pricing per wafer, yield rates, technology node competitiveness, and long-term customer contracts. Given the capital-intensive nature of semiconductor manufacturing, significant upfront capital expenditures and ongoing reinvestment are incorporated into the forecast. The projected free cash flows over a defined period, along with a terminal value reflecting the fab’s long-term earning potential, are discounted to determine the asset’s intrinsic value.
WACC: Pricing Tech Obsolescence and Geopolitical Risk
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) is used as the discount rate in valuing a semiconductor fab because it reflects the blended cost of debt and equity financing for such a high-capex, technology-driven asset. Semiconductor fabs face cyclical demand, rapid technological obsolescence, and pricing volatility, which influence their risk profile and required returns. The WACC incorporates investors’ expected returns, the company’s capital structure, and the tax shield on debt, representing the minimum return needed to justify the substantial investment.
Sensitivity Analysis: Stress-Testing Yields and Utilization
For a semiconductor fab, Sensitivity Analysis is the pulse check for profitability, centered primarily on wafer yields and capacity utilization. Because fixed costs are so high, a mere 5% drop in “prime yield” (the percentage of functional chips per wafer) can swing a project from a multi-billion dollar profit to a massive loss. Analysts use sensitivity tables to stress-test the model against fluctuating “average selling prices” (ASPs) for chips and potential delays in equipment delivery from lithography suppliers. By testing the impact of a cyclical downturn in consumer electronics or automotive demand, the analysis reveals how much “margin of safety” the fab has during the inevitable periods of global oversupply.
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This 20 Year Semiconductor Fab Financial Model must focus on balancing capital expenditures with steady revenue growth from the vast array of wafer sales. By optimizing operational costs, power efficiency, and maximizing high-margin services like Microprocessor, Memory Chip, and GPU sales, the model ensures sustainable profitability and cash flow stability.
Download Link On Next Page
Download Link On Next Page
