SaaS Startup Financial Model
5 Year 3 Statement SaaS Startup Financial Model in Excel is a comprehensive financial planning tool designed to help business owners, investors, and financial model analysts evaluate the financial feasibility and profitability of your SaaS Startup.
Financial Model for a SaaS Startup (Start up)
These financial models for a SaaS startup provide a structured framework to forecast revenue, expenses, cash flow, and financial health. They each span 5 years and include key metrics such as MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue), CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost), LTV (Customer Lifetime Value), Churn Rate, and Gross Margins.
What Do You Get? Two 5-year 3 statement versions in 1 Zip File
Version 1: 10 project-based inputs for SaaS services
Version 2: 6 Tier subscription and 5 PAYG project-based inputs
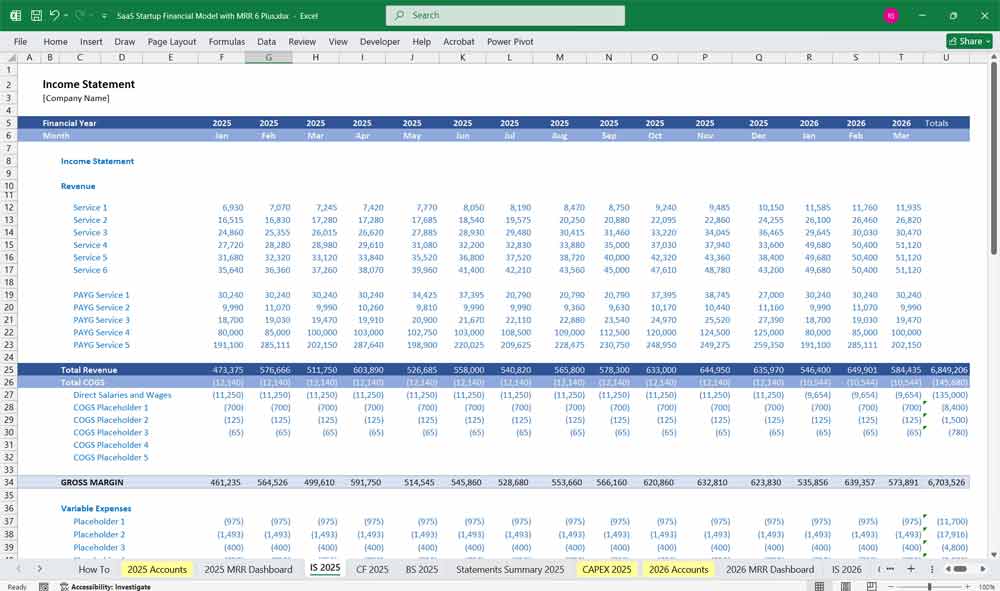
1. Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
The Income Statement tracks revenue, expenses, and profitability over a period (monthly, quarterly, or annually).
Revenue Section
- Recurring Revenue (MRR/ARR)
- Subscription revenue from customers on a monthly/annual basis.
- MRR = Number of customers × Average Revenue per User (ARPU).
- One-Time Revenue
- Setup fees, consultation fees, or one-time software licensing fees.
- Expansion Revenue
- Upsells, cross-sells, and upgrades by existing customers.
- Churn Impact
- Lost revenue from customer cancellations.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Hosting and Infrastructure Costs
- AWS, Google Cloud, or other cloud hosting expenses.
- Customer Support & Success
- Salaries of support teams, onboarding costs.
- Third-Party API & Software Costs
- Payment gateway fees, third-party integrations.
- Data Storage & Security
- Costs related to databases and compliance measures.
Gross Profit & Gross Margin
- Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
- Gross Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Revenue) × 100
- SaaS companies typically have 60-80% gross margins.
Operating Expenses (OPEX)
- Sales & Marketing
- Paid ads, content marketing, SEO, sales team salaries, commissions.
- Product Development (R&D)
- Engineering salaries, UI/UX design, product management.
- General & Administrative (G&A)
- Legal, accounting, HR, rent, office expenses.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Total marketing & sales expenses / New customers acquired.
EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization)
- EBITDA = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Net Income (Profit or Loss)
- Net Income = EBITDA – Interest – Taxes – Depreciation & Amortization
- If positive, the company is profitable. If negative, it indicates a loss.
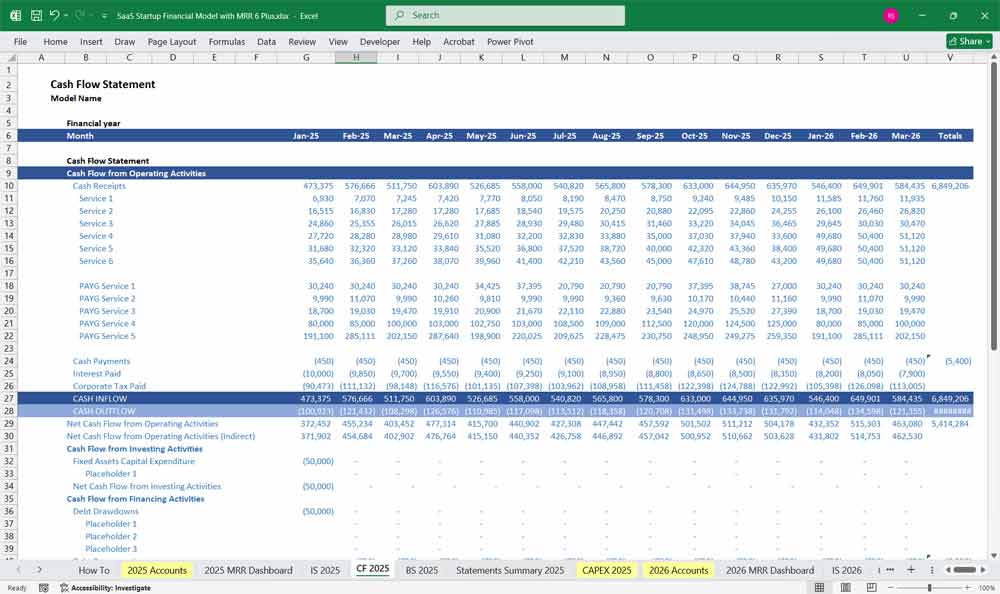
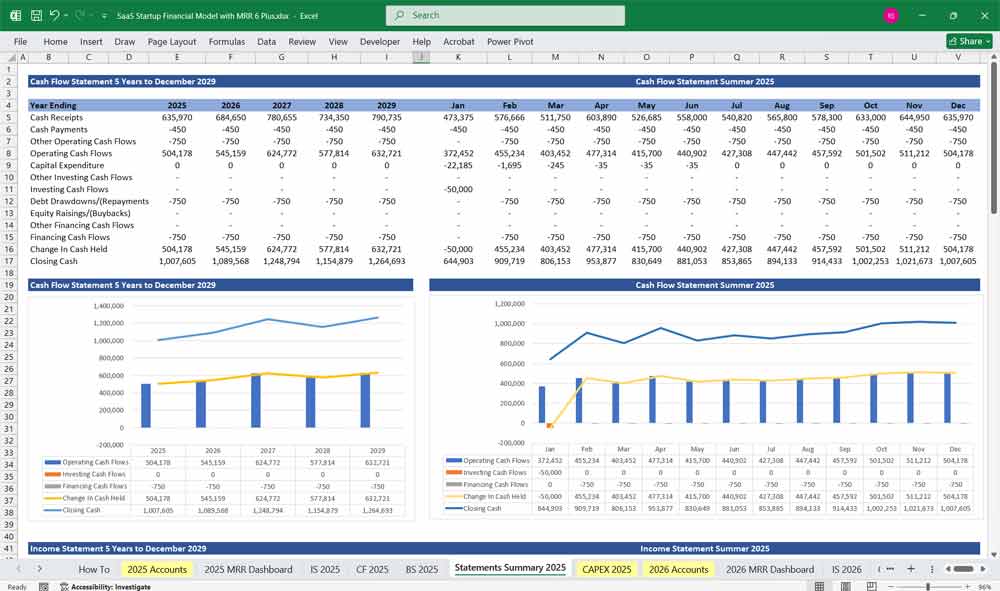
SaaS Startup Financial Model Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement tracks cash inflows and outflows, categorizing them into Operating, Investing, and Financing Activities.
Operating Cash Flow (OCF)
- Cash Inflows:
- Customer payments (subscription revenue).
- One-time service payments.
- Interest income (if applicable).
- Cash Outflows:
- Salaries, rent, and office expenses.
- Cloud hosting costs.
- Marketing expenses.
- Customer support costs.
Investing Cash Flow (ICF)
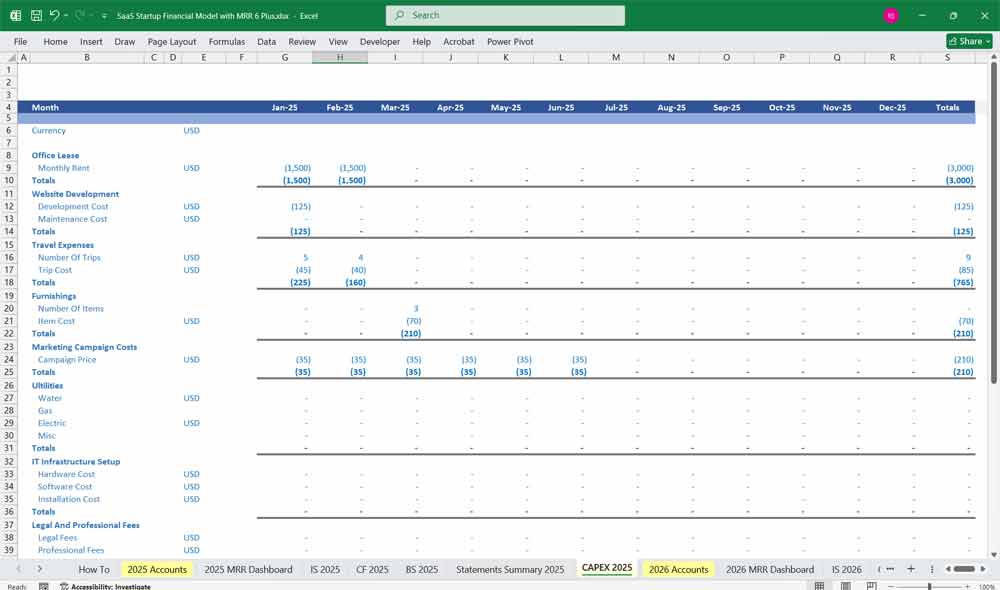
- Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
- Purchase of servers, office equipment, or software tools.
- Investment in Product Development
- R&D costs for long-term product improvements.
- Acquisitions or Mergers
- Cash spent on acquiring other companies or technologies.
Financing Cash Flow (FCF)
- Cash Inflows:
- Equity Financing (VC funding, Angel investments).
- Debt Financing (Loans, Convertible Notes).
- Cash Outflows:
- Loan repayments.
- Dividends (if applicable).
Net Change in Cash
- Net Cash Flow = Operating Cash Flow + Investing Cash Flow + Financing Cash Flow
- This determines whether the startup is cash-positive or burning cash.
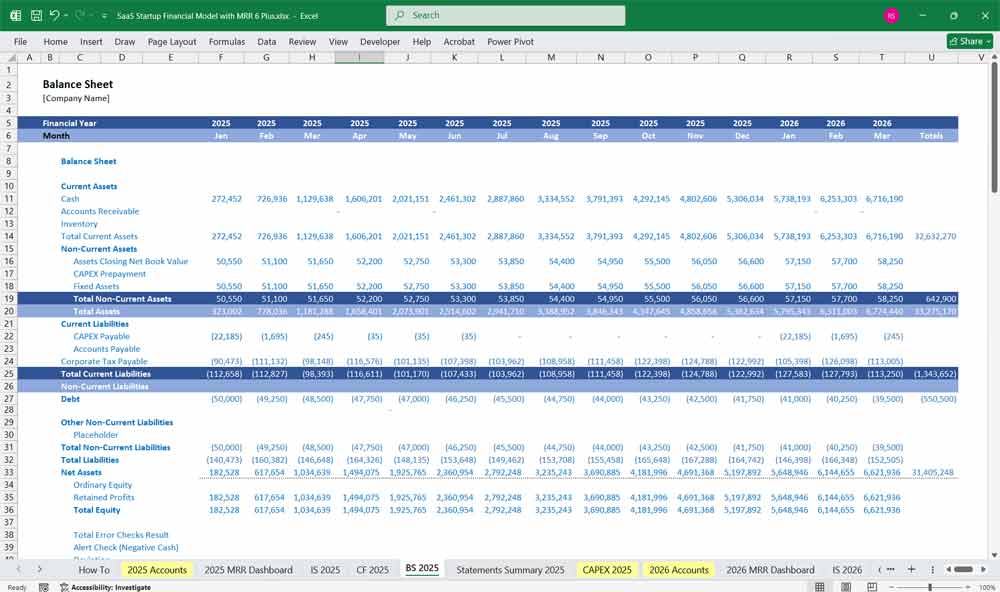
SaaS Startup Financial Model Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of the startup’s financial position at a given time.
Assets (What the Company Owns)
- Current Assets (Short-term assets convertible to cash within a year)
- Cash & Cash Equivalents
- Accounts Receivable (Pending payments from customers)
- Prepaid Expenses (Software subscriptions, office rent)
- Non-Current Assets (Long-term investments)
- Property, Equipment, and Servers
- Software Development Costs (Capitalized R&D)
Liabilities (What the Company Owes)
- Current Liabilities (Obligations due within a year)
- Accounts Payable (Bills due to vendors, hosting costs)
- Deferred Revenue (Prepaid customer subscriptions)
- Short-term Loans
- Long-term Liabilities
- Convertible Notes
- Long-term Loans or Debt
Equity (Shareholder Value)
- Founder’s Equity
- Retained Earnings (Profits reinvested in the business)
- Investor Capital (Funds raised from VCs or Angels)
Key Balance Sheet Formula
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
- Ensures financial stability and solvency.
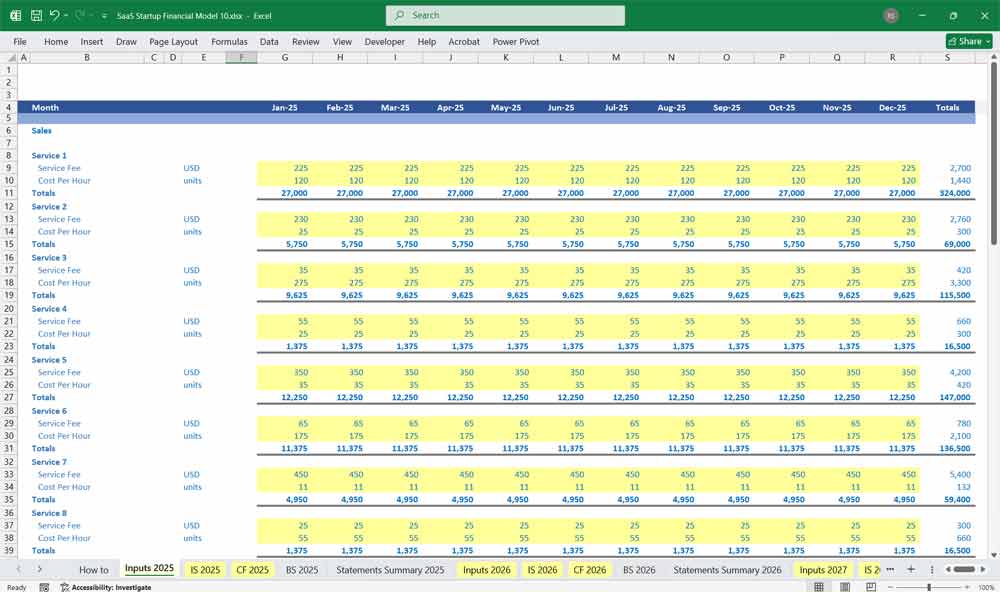
6-Tier Subscription Model For A SaaS Startup
A well-structured SaaS subscription model provides options for different customer segments, from individuals to large enterprises.
1. Free / Freemium SaaS Startup Tier
- Target Audience: Individual users, startups, and small businesses testing the product.
- Features:
- Limited access (e.g., 10 free tasks, 1 user seat, basic reporting).
- Watermark branding (for design or video tools).
- Community support only.
- Monetization:
- Upsells (storage, premium features, removing limits).
- Data collection for improving AI-based recommendations.
2. Basic / SaaS Startup Plan (Entry-Level Paid Tier)
- Price: $10 – $25/month per user.
- Target Audience: Solopreneurs, small businesses, and freelancers.
- Features:
- Full access to core product features.
- Basic customer support.
- Limited integrations (e.g., only Google Drive, not Slack or Zapier).
- Up to 3-5 team members.
3. Pro / SaaS Startup Growth Plan (For Scaling Businesses)
- Price: $50 – $100/month per user.
- Target Audience: Growing startups, mid-sized teams.
- Features:
- Advanced reporting & analytics.
- Priority support (email + chat).
- Custom branding.
- 10+ team members, role-based access control.
- API access & custom integrations.
4. Business / Premium SaaS Startup Plan
- Price: $200 – $500/month (flat or per user).
- Target Audience: Mid-sized companies with complex needs.
- Features:
- Workflow automation, AI-based recommendations.
- Dedicated account manager.
- Advanced security (2FA, SSO, SOC 2 compliance).
- White-label options for customization.
5. Enterprise Plan (For Large SaaS Startup Organizations)
- Price: Custom pricing ($1,000+ per month).
- Target Audience: Large enterprises, corporations, government entities.
- Features:
- Unlimited users, advanced role management.
- On-premise deployment or private cloud.
- SLA-backed 24/7 support.
- Custom development & integrations.
- Dedicated training & onboarding.
6. Custom / White-Label SaaS Startup Plan
- Price: Custom Quote (varies by company size & customization).
- Target Audience: Large enterprises, agencies, software resellers.
- Features:
- Fully white-labeled version of the product.
- Custom feature development based on client needs.
- API-first model for complete integration.
- Enterprise-level SLAs & dedicated engineers.
5 Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) SaaS Revenue Streams
For customers who prefer flexible, usage-based pricing instead of a fixed subscription.
1. SaaS API Usage-Based Billing
- Revenue Model: Charge per API request or data usage.
- Example: $0.01 per API call after the free 1,000 requests.
- Ideal For: AI tools, analytics platforms, fintech services.
2. Storage & SaaS Bandwidth Fees
- Revenue Model: Charge based on GB stored or transferred.
- Example: $0.10 per extra GB after the free 5GB limit.
- Ideal For: Cloud storage services, video hosting, file-sharing platforms.
3. Pay-Per-Feature SaaS Model
- Revenue Model: Charge for accessing premium features on demand.
- Example: $5 per advanced report, $10 for a one-time security scan.
- Ideal For: Business intelligence tools, cybersecurity platforms.
4. Transaction-SaaS-Based Fees
- Revenue Model: Charge a percentage or flat fee on transactions.
- Example: 2.5% fee per payment processed, $0.50 per invoice generated.
- Ideal For: Payment processing, e-commerce SaaS, invoicing platforms.
5. SaaS AI/ML Processing Fees
- Revenue Model: Charge per computation or AI model run.
- Example: $0.02 per AI-generated image, $0.05 per document scanned.
- Ideal For: AI-powered SaaS, automation tools, NLP services.
Conclusion
- The 6-Tier Subscription Model provides a structured upgrade path for users, from free to enterprise levels.
- The 5 PAYG Revenue Streams offer additional revenue flexibility, especially for data-heavy or AI-driven SaaS.
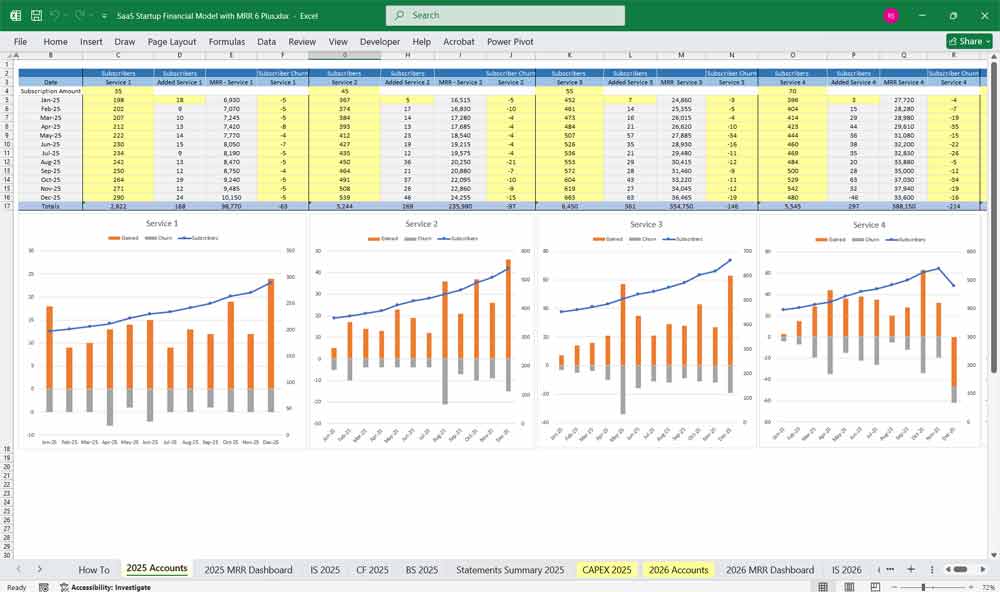
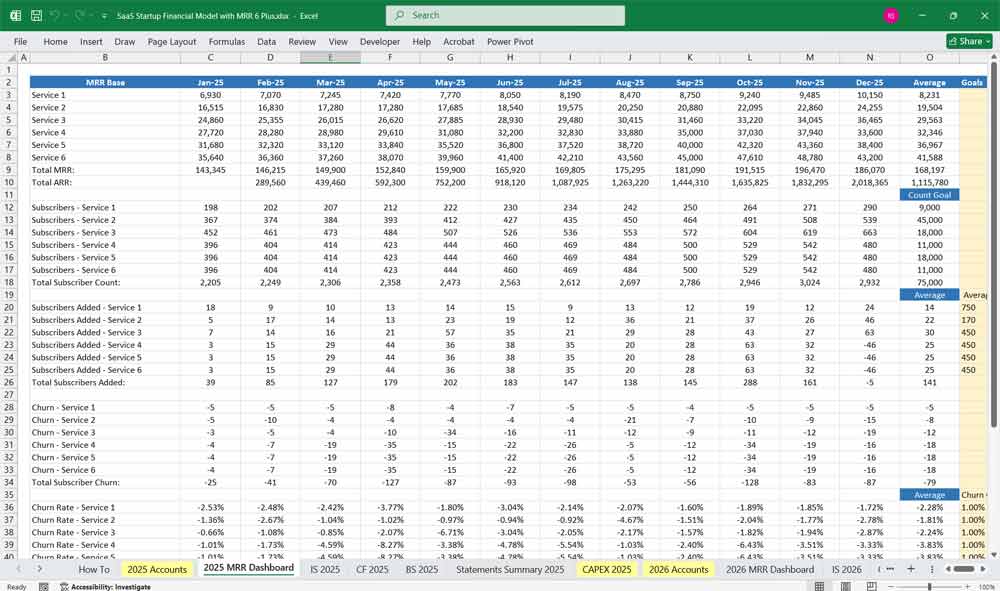

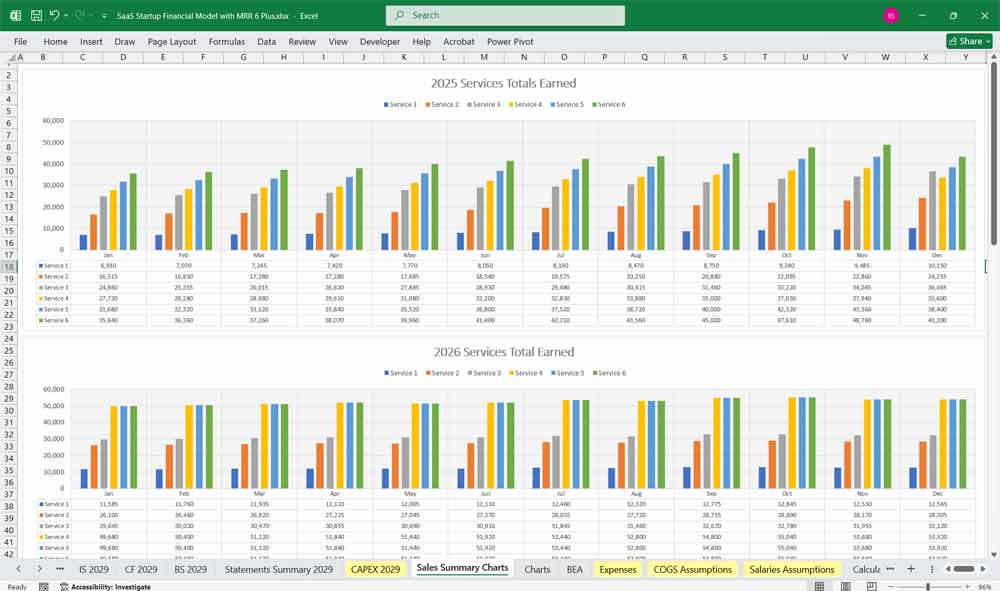
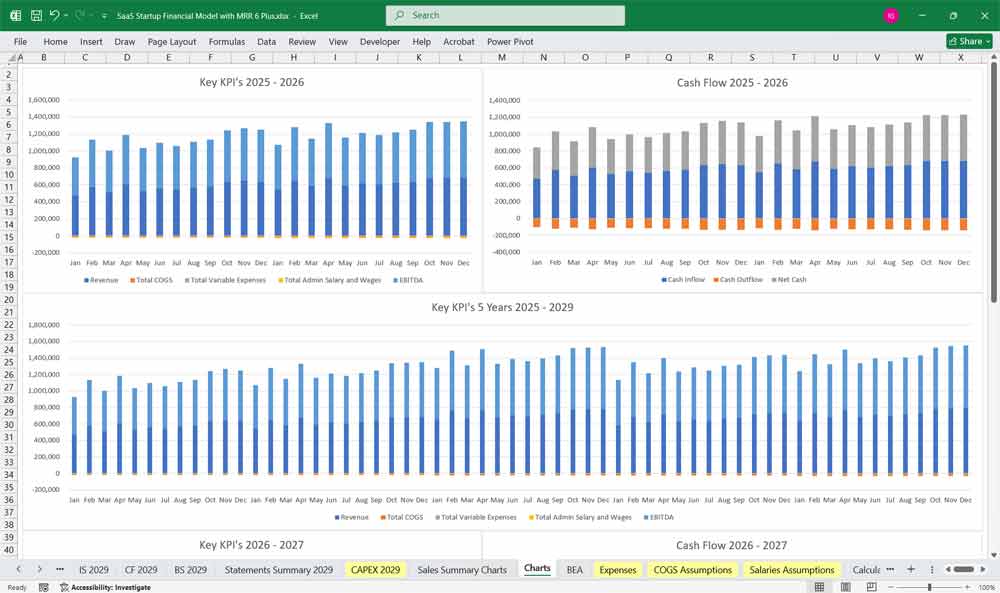
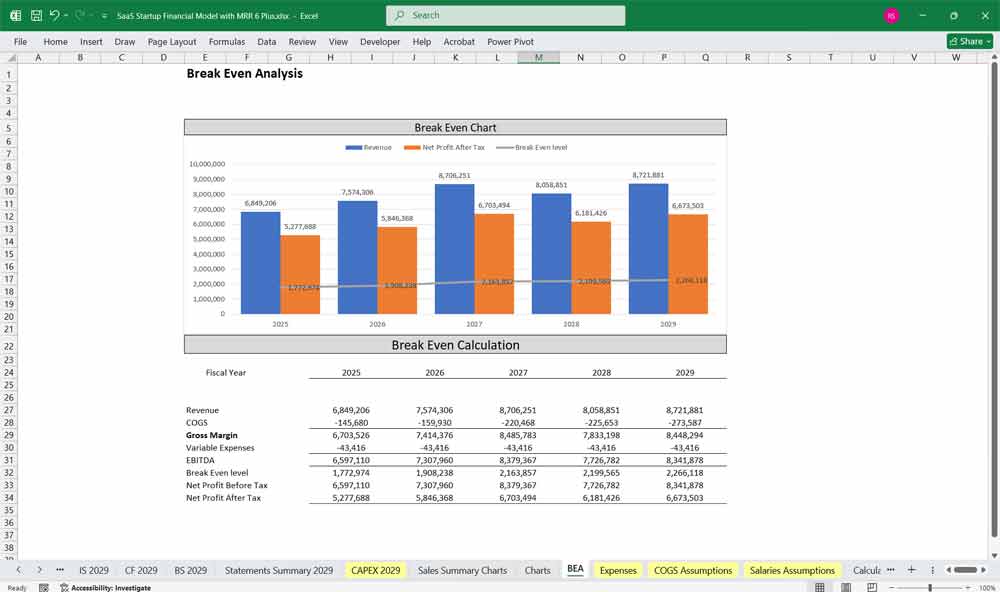
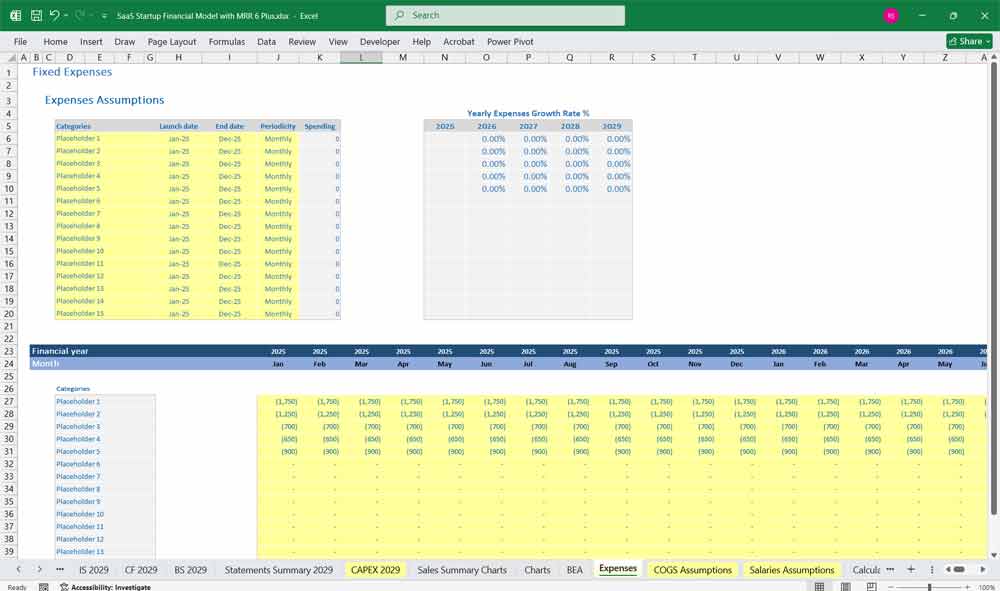
Key Metrics for The Financial Model
To assess financial performance, SaaS startups track key performance indicators (KPIs):
- MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue) & ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue)
- Predictable revenue from subscriptions.
- CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost)
- Total Sales & Marketing spend / New customers acquired.
- LTV (Customer Lifetime Value)
- Average Revenue per Customer × Customer Lifetime.
- Churn Rate
- Percentage of customers canceling subscriptions.
- Burn Rate
- Monthly net cash outflow (Operating Cash Flow – Expenses).
- Runway
- Available cash / Monthly burn rate (Months before funding is needed).
These SaaS startup financial models focus on recurring revenue growth, efficient customer acquisition, and sustainable cash flow management. Balancing customer retention, cost control, and investor funding ensures long-term viability.
Download Link On Next Page
