SaaS Software Financial Model
This 5-Year, 3-Statement SaaS Software Financial Model in Excel is a great tool for viewing all your revenues and projections from your SaaS Software development projects.
Financial Model for SaaS Software
Robust financial model for a SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) company to forecast revenue, expenses, cash flow, and key metrics over a 5 year period. Below is a detailed breakdown of the Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet, along with key SaaS-specific metrics.
Version 1: 5-year 3 statement with 5 PAYG project-based revenue inputs.
Version 2: The same as above, plus a 6-tier subscription for ongoing subscription-based software sales.
Income Statement (Profit & Loss – P&L)
The Income Statement shows revenue, costs, and profitability over time.
Revenue
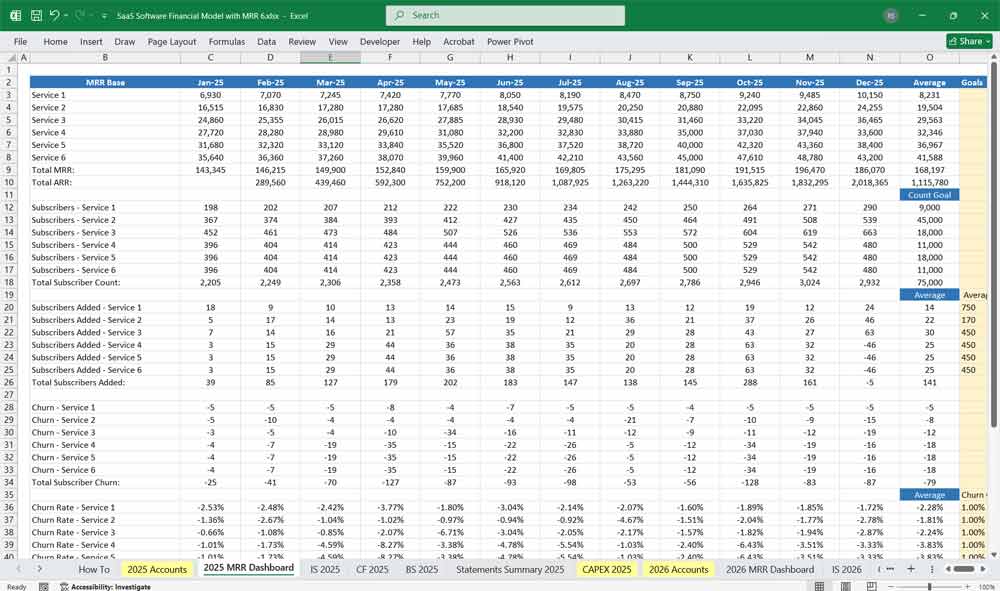
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
New MRR (from new customers)
Expansion MRR (upsells/cross-sells)
Churned MRR (lost revenue from cancellations/downgrades)
Net MRR Growth = (New MRR + Expansion MRR) – Churned MRR
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) = MRR × 12
One-Time Revenue (e.g., setup fees, professional services)
Cost of Revenue (COGS)
Hosting & Infrastructure (AWS, Azure, etc.)
Third-party software licenses
Payment processing fees (~2-3% of revenue)
Customer support & success teams
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
Gross Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Revenue) × 100 (Target: 70-85%)
Operating Expenses (OPEX)
Sales & Marketing (S&M)
Salaries & commissions
Digital ads (Google, LinkedIn, etc.)
Content marketing & SEO
Events & partnerships
Research & Development (R&D)
Engineering salaries
Cloud & DevOps costs
Software tools (GitHub, Jira, etc.)
General & Administrative (G&A)
Executive salaries
Legal & accounting
Office rent & utilities
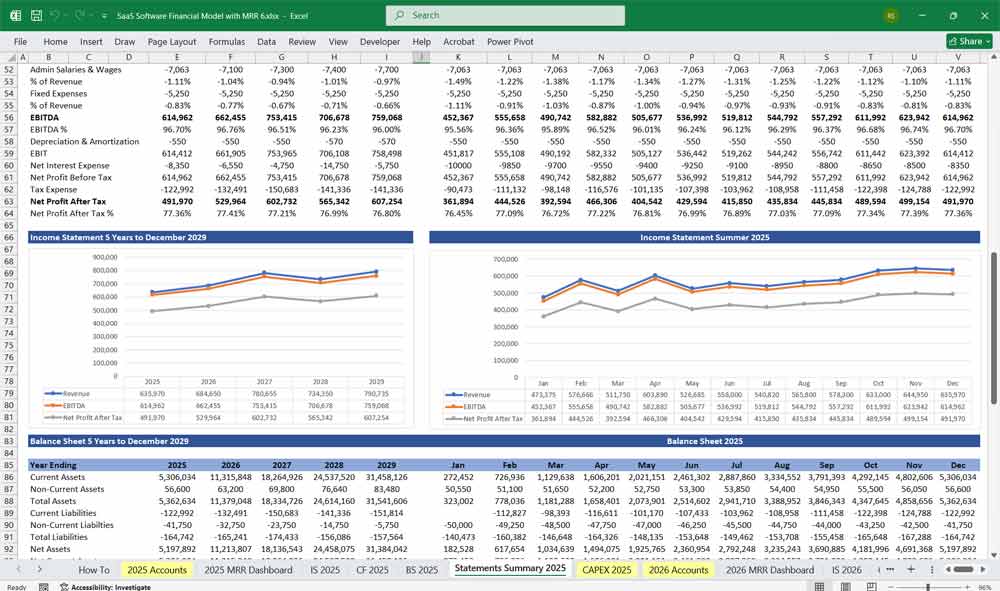
EBITDA & Net Profit
EBITDA = Gross Profit – OPEX (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, Amortization)
Net Profit = EBITDA – Depreciation – Amortization – Taxes – Interest
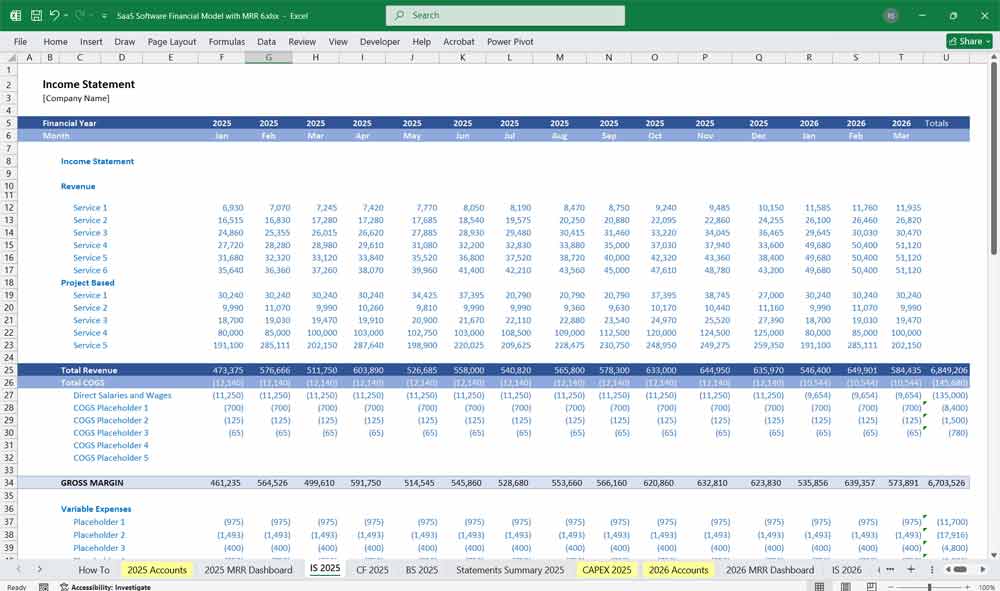
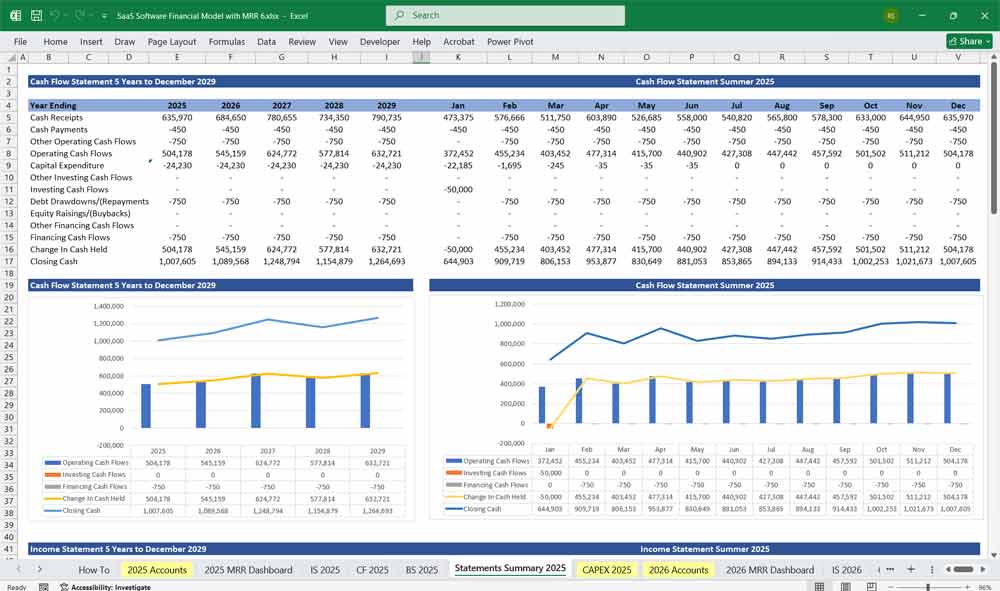
SaaS Software Cash Flow Statement
Tracks cash inflows and outflows to ensure liquidity.
Cash Flow from Operations (CFO)
Net Income (from P&L)
Adjustments:
(+) Depreciation & Amortization (non-cash expenses)
(-) Changes in Working Capital (accounts receivable, prepaid expenses)
Cash Flow from Investing (CFI)
Capital Expenditures (CapEx) – servers, office equipment
SaaS development costs (if capitalized)
Cash Flow from Financing (CFF)
Equity raised (venture capital, angel investors)
Debt (loans, convertible notes)
Dividends or share buybacks (rare in early-stage SaaS)
Net Cash Flow = CFO + CFI + CFF
Ending Cash Balance = Beginning Cash + Net Cash Flow
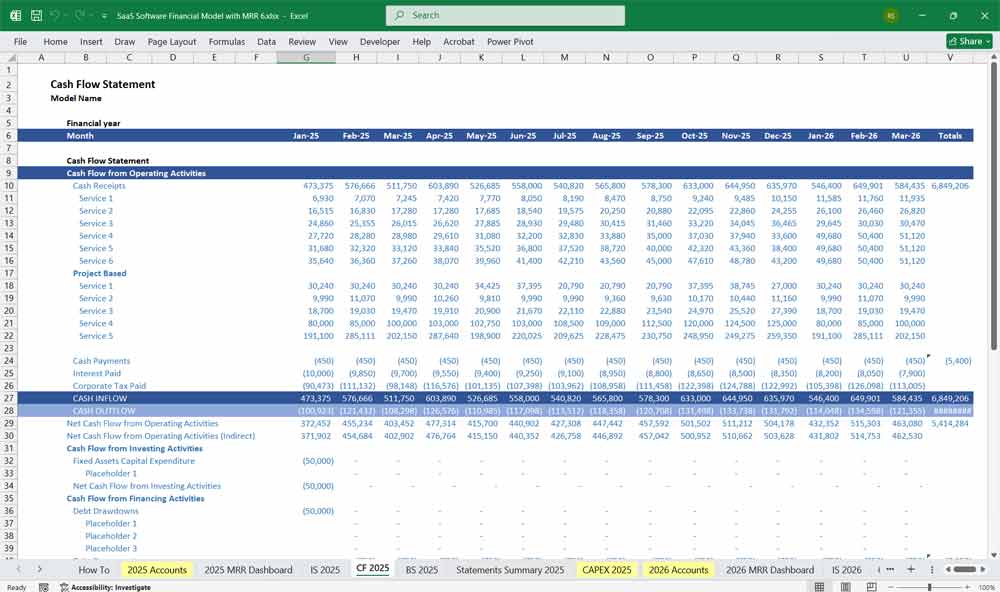
SaaS Software Balance Sheet
Shows assets, liabilities, and equity at a point in time.
Assets
Current Assets
Cash & cash equivalents
Accounts receivable (unpaid invoices)
Prepaid expenses
Long-Term Assets
Property & equipment (if any)
Capitalized software development costs
Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts payable (unpaid bills)
Deferred revenue (unearned revenue from annual subscriptions)
Short-term debt
Long-Term Liabilities
Long-term debt
Lease obligations
Equity
Common stock
Retained earnings (accumulated profits)
Additional paid-in capital (investor funds)
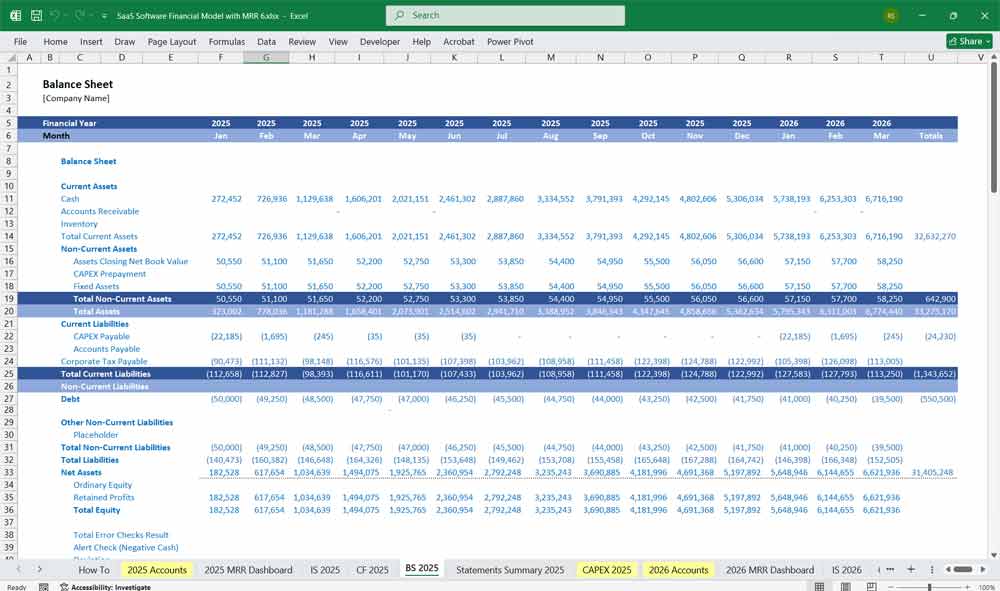
Key SaaS Metrics to Track
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) = Sales & Marketing Spend / New Customers Acquired
Lifetime Value (LTV) = (Avg. Revenue per User × Gross Margin %) / Churn Rate
LTV:CAC Ratio (Target: 3x or higher)
Churn Rate = (Churned Customers / Total Customers) × 100
Quick Ratio = (New MRR + Expansion MRR) / Churned MRR (Target: >4x)
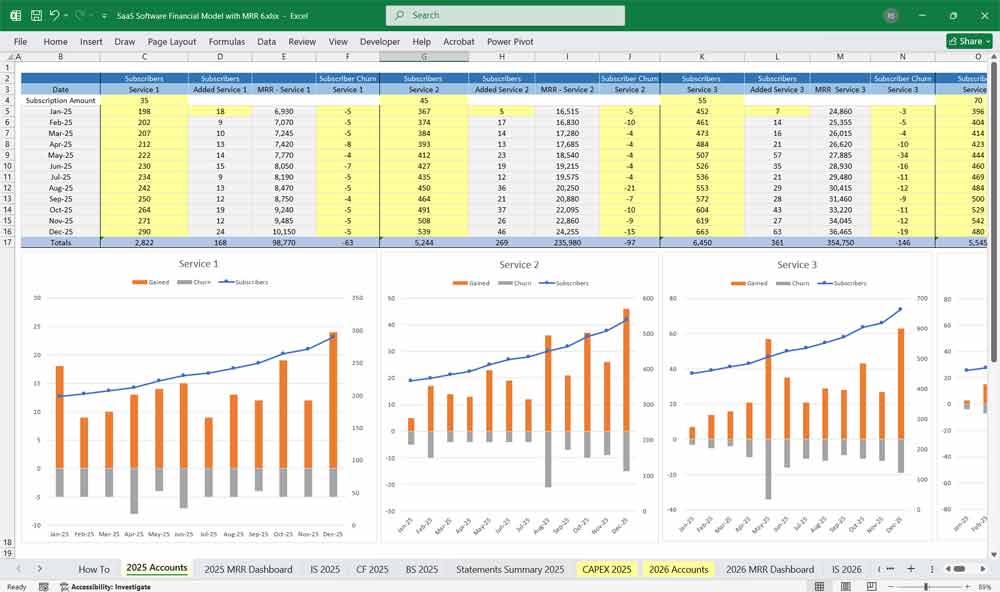
6-Tier Subscription Model for a SaaS Company
A well-structured 6-tier subscription model allows a SaaS company to cater to different customer segments, from small businesses to large enterprises, while maximizing revenue through upsells and cross-sells. Below is a detailed breakdown of six subscription tiers, including pricing, features, target audience, and key differentiators.
1. Free SaaS Tier (Freemium)
Target Audience: Startups, solopreneurs, small businesses testing the software.
Pricing: $0
Key Features:
Basic functionality with limited usage (e.g., 1 user, 10 GB storage).
Entry-level support (community forums, knowledge base).
Branded watermark on exports.
No API access.
Upsell Path: Conversion to “Starter” or “Pro” tiers via in-app prompts.
Monetization Strategy: Lead generation for paid tiers.
2. Starter SaaS Tier
Target Audience: Small businesses, freelancers needing essential features.
Pricing: 19–19–49/month (billed annually for discount).
Key Features:
All Free Tier features + ad-free experience.
1–5 users, 50 GB storage.
Basic analytics & reporting.
Email support (24–48 hour response).
Limited integrations (e.g., Zapier, Google Workspace).
Upsell Path: Highlight limitations (e.g., “Need more users? Upgrade to Pro!”).
Monetization Strategy: Low-cost entry point for SMBs.
3. Professional SaaS Tier (Most Popular)
Target Audience: Growing businesses, mid-sized teams.
Pricing: 99–99–199/month (annual billing preferred).
Key Features:
Everything in Starter + advanced features.
10–20 users, unlimited storage.
Custom reporting & dashboards.
Priority support (12–24 hour response).
API access (limited calls/month).
Single Sign-On (SSO) via Google/Microsoft.
Upsell Path: Push for “Business” tier with advanced security & compliance.
Monetization Strategy: Balances affordability with high perceived value.
4. Business SaaS Tier
Target Audience: Established companies needing scalability & security.
Pricing: 499–499–999/month (custom annual contracts).
Key Features:
All Professional features + enterprise-grade tools.
25–100 users, role-based permissions.
Advanced security (SAML, audit logs).
Dedicated account manager.
SLA guarantees (99.9% uptime).
White-labeling options.
Upsell Path: Custom “Enterprise” solutions for large deployments.
Monetization Strategy: High-margin tier with strong retention.
5. Enterprise SaaS Tier (Custom Pricing)
Target Audience: Large corporations, government agencies.
Pricing: $2,500+/month (negotiated contracts).
Key Features:
Everything in Business + fully customizable.
Unlimited users, on-premise/hybrid deployment.
24/7 VIP support with SLAs.
Custom integrations & workflows.
Compliance certifications (SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA).
Training & onboarding services.
Upsell Path: Multi-year contracts, add-on professional services.
Monetization Strategy: High-touch sales, long-term revenue.
6. SaaS Partner/Reseller Tier
Target Audience: Agencies, consultants, white-label partners.
Pricing: Volume-based discounts (30–50% off retail).
Key Features:
All Enterprise features + reseller rights.
Co-branding & private labeling.
Revenue-sharing/affiliate programs.
API access for embedding into their products.
Dedicated partner support.
Upsell Path: Expand partnership with training & co-marketing.
Monetization Strategy: Expands market reach via third-party sales.
Key Considerations for a 6-Tier SaaS Model:
Clear Differentiation: Each tier should justify its price jump with tangible value.
Upsell Pathways: Use feature gating to encourage upgrades (e.g., “This report requires Pro”).
Churn Reduction: Offer annual discounts & tiered support to retain customers.
Pricing Testing: Continuously A/B test pricing pages for optimal conversion.
SaaS (Software as a Service) Development
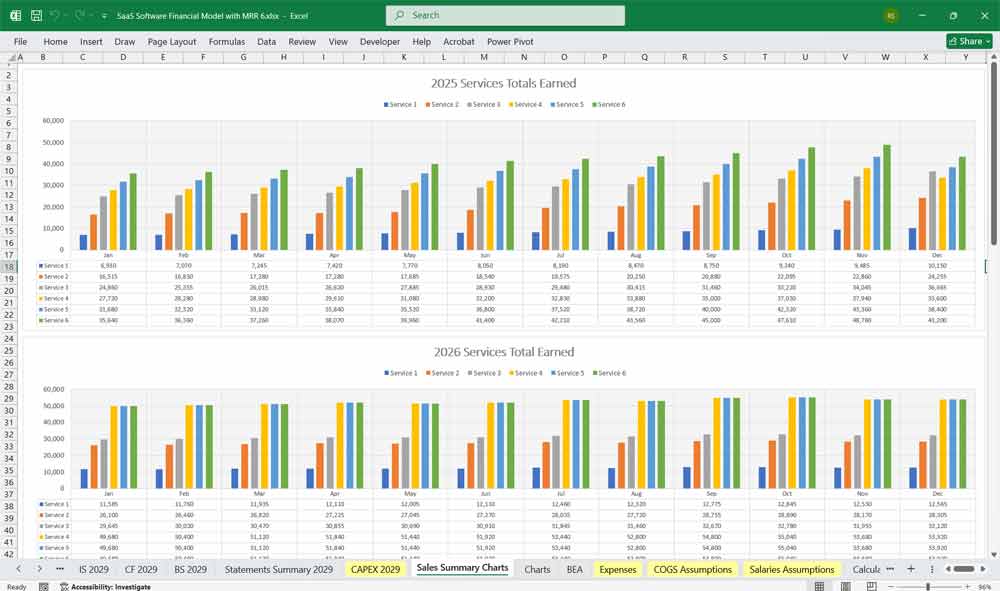
Professional project management significantly impacts a financial model by shifting traditional capital expenditures (CapEx) to operational expenditures (OpEx). Unlike on-premise solutions, SaaS software development requires ongoing cloud infrastructure costs, subscription-based revenue recognition, and continuous updates, affecting cash flow projections and profitability timelines. Efficient project management ensures timely releases, scalability, and customer retention—key drivers of recurring revenue. Metrics like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV), and churn rate become critical in forecasting growth and sustainability. The pay-as-you-go SaaS model also demands flexible budgeting for R&D, customer support, and scaling infrastructure, altering long-term financial planning compared to traditional software sales.
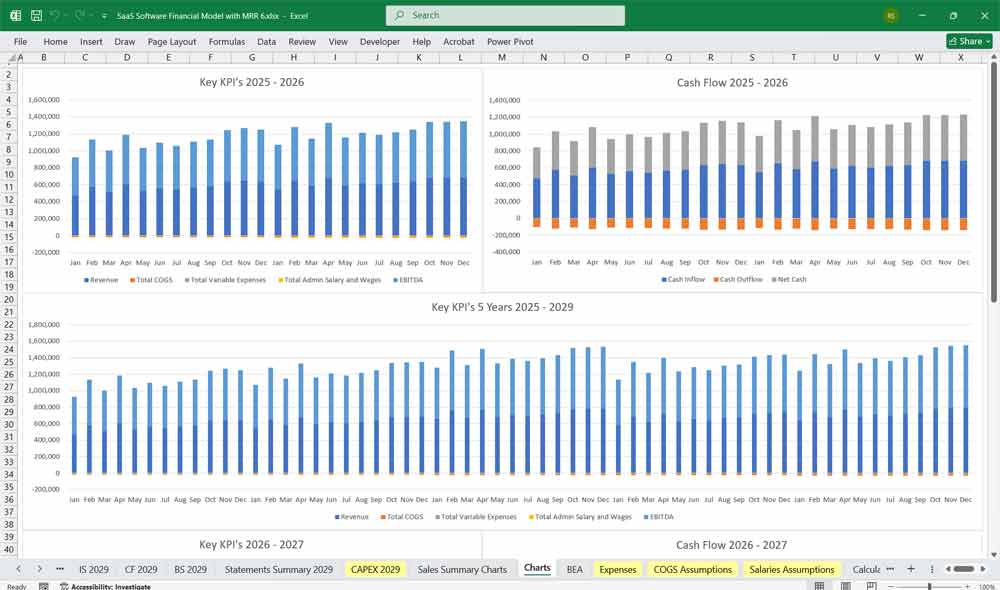
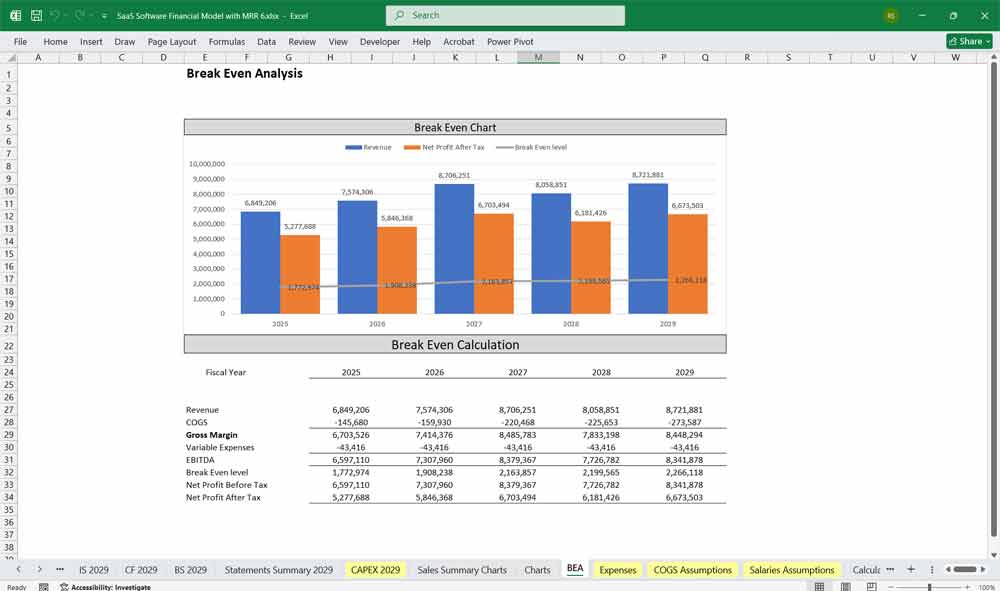
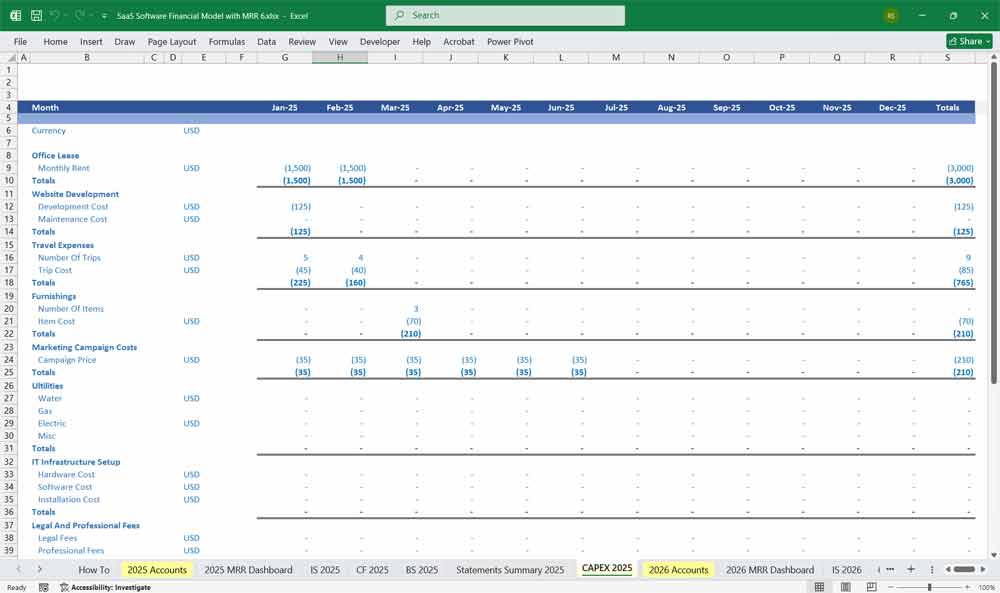

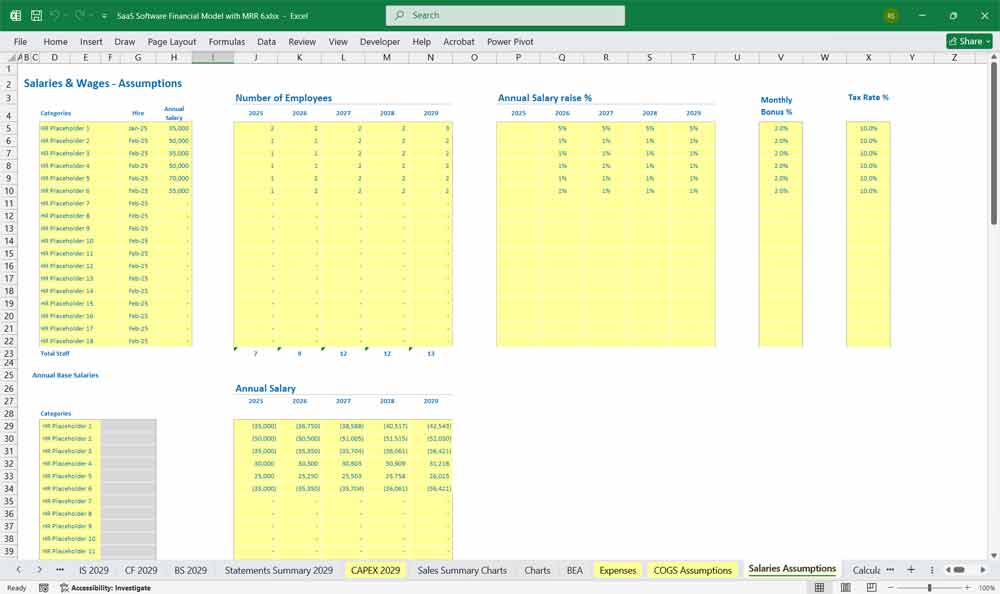
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This 5-Year SaaS Software Financial Model must focus on balancing capital expenditures with steady revenue growth from diversified subscription-based services. By optimizing operational and service costs, and maximizing high-margin services like Project Management, HR, and CMS, the model aids profitability and cash flow stability.
Download Link on Next Page
Download Link On Next Page
