SaaS CRM Financial Model
Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the Excel SaaS CRM Financial Model covering the Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet. With revenues from project-based work and subscriptions. Cost structures and financial model statements to forecast the financial health of your SaaS business.
Financial Model for a SaaS CRM Company
Covering key components such as the Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet.
What Do You Get? 2 Versions In 1 Zip File
Version 1: 5-Year, 3 Statement Financial model with 5 PAYG project-based revenue streams and reporting of your SaaS CRM financials.
Version 2: 5-Year, 3 Statement with a 6 Tier Subscription revenue ‘Managed Service Agreements’. Build your MSA book as quickly as possible.
You would typically sell your services at tiered 12-month agreements that increase in price as SLAs (Service Level Agreement) and monthly consulting hours scale upwards.
Plus 5 PAYG Revenues.
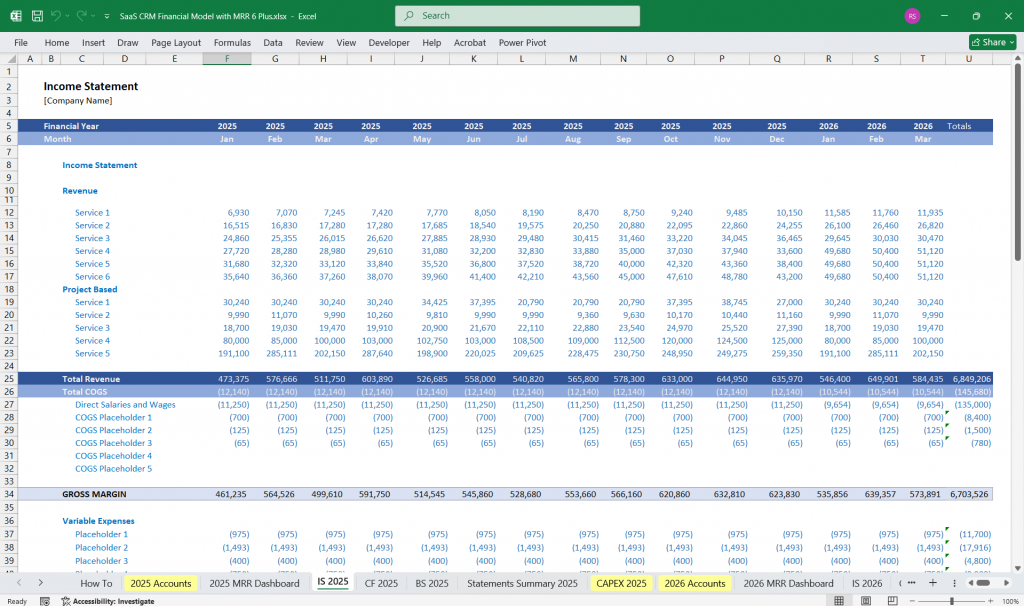
Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
The income statement tracks revenue, expenses, and profitability over a specific period.
Revenue
- Subscription Revenue (MRR & ARR)
- Monthly and Annual Plan revenues
- Tiered pricing (e.g., Basic, Professional, Enterprise)
- Professional Services Revenue
- Onboarding, consulting, training fees
- Add-on Revenue
- API access, integrations, analytics upgrades
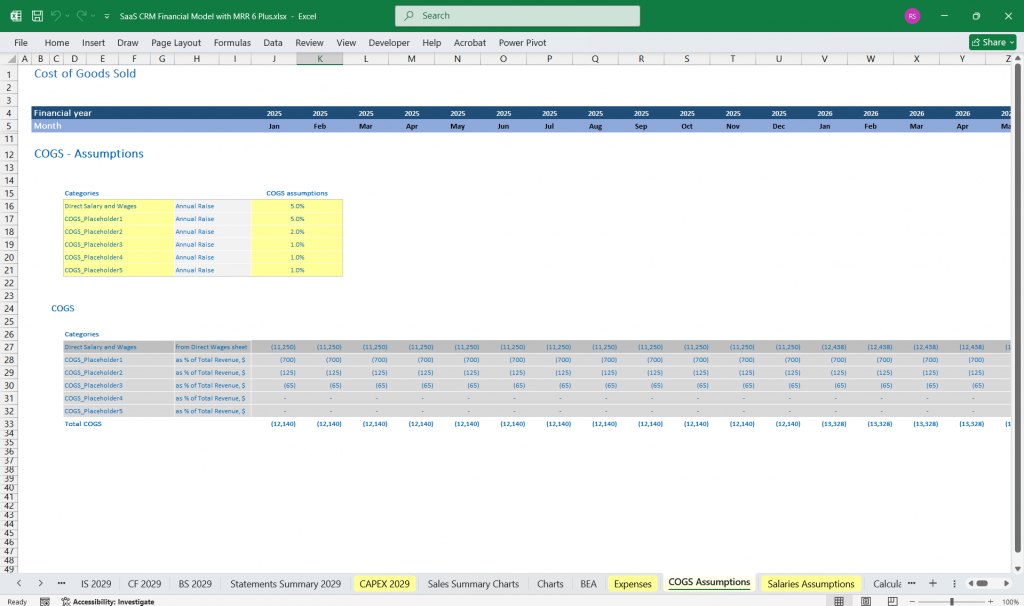
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Hosting Costs (Cloud server costs)
- Customer Support Costs (Salaries, ticketing tools)
- Third-party Software Fees (APIs, payment processing)
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
Gross Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Revenue) * 100
Operating Expenses
- Sales & Marketing (S&M)
- Paid ads (Google, Facebook, LinkedIn)
- Sales team salaries & commissions
- Webinars, trade shows, content marketing
- Research & Development (R&D)
- Developer salaries
- Product design and testing
- Software tools for development
- General & Administrative (G&A)
- Office rent, utilities
- HR, legal, accounting expenses
EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization)
= Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Other Expenses
- Depreciation & Amortization (Software development, capitalized expenses)
- Interest Expense (Loan repayments, credit lines)
- Taxes (Corporate income tax)
Net Income = EBITDA – Other Expenses – Taxes
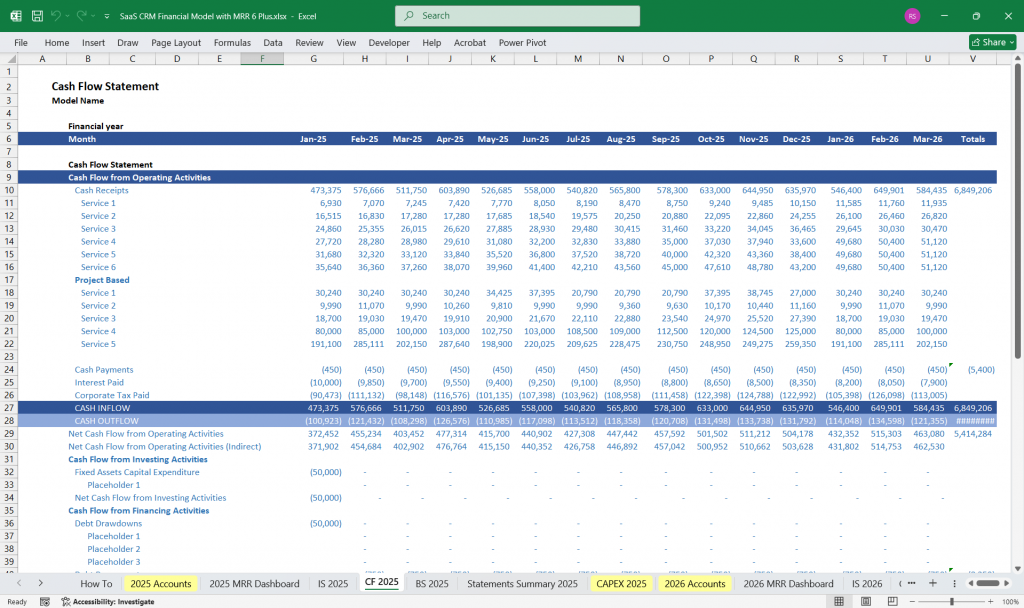
SaaS CRM Financial Model Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement shows how cash moves in and out of the business.
Operating Cash Flow
- Net Income (From Income Statement)
- Adjustments for Non-Cash Items
- Depreciation & Amortization
- Stock-based compensation
- Changes in Working Capital
- Increase/decrease in Accounts Receivable
- Increase/decrease in Accounts Payable
- Deferred Revenue (Prepaid subscriptions)
Investing Cash Flow
- Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
- Investments in software development
- Office equipment, new servers
- Acquisitions of Other Companies
- Mergers, acquisitions, or partnerships
Financing Cash Flow
- Equity Financing
- Venture capital funding rounds (Seed, Series A, B, C)
- Debt Financing
- Loans, credit lines, interest payments
- Stock Buybacks & Dividends
- Rare in growth-stage SaaS companies
Net Cash Flow = Operating Cash Flow + Investing Cash Flow + Financing Cash Flow
Ending Cash Balance = Beginning Cash + Net Cash Flow
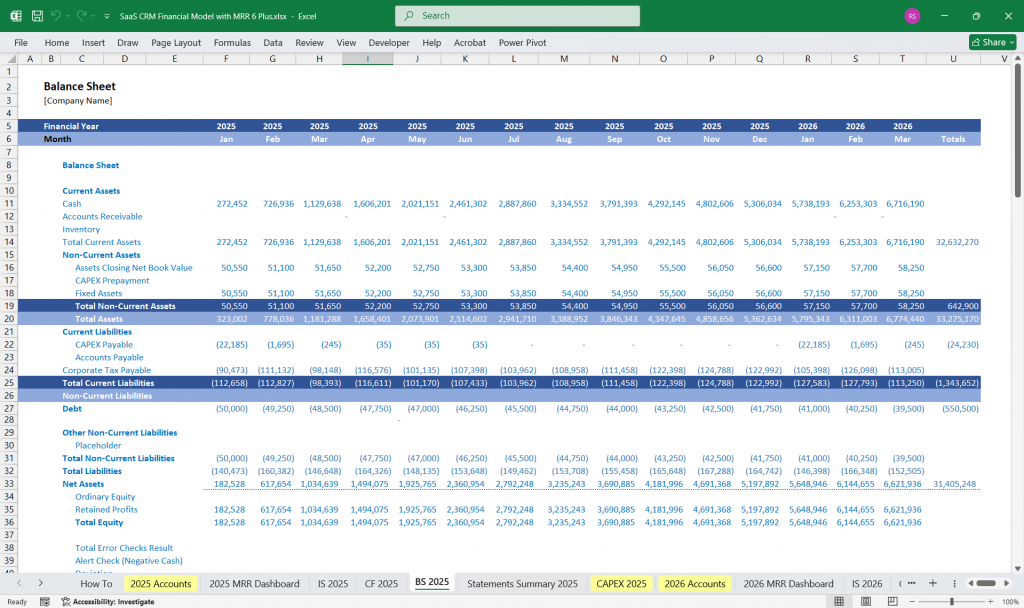
SaaS CRM Financial Model Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a specific time.
Assets
Current Assets
- Cash & Cash Equivalents (Bank balances)
- Accounts Receivable (Unpaid customer invoices)
- Deferred Revenue (Short-Term) (Prepaid annual subscriptions)
- Prepaid Expenses (Software licenses, cloud services)
Non-Current Assets
- Intangible Assets (Capitalized software development costs)
- Property, Plant & Equipment (PP&E) (Office space, IT equipment)
- Long-Term Investments (Acquisitions, equity investments)
Liabilities
Current Liabilities
- Accounts Payable (Unpaid bills for vendors, services)
- Deferred Revenue (Short-Term) (Revenue collected but not yet earned)
- Short-Term Debt (Loans maturing within a year)
Non-Current Liabilities
- Long-Term Debt (Convertible notes, venture debt)
- Deferred Revenue (Long-Term) (Multi-year contracts)
- Lease Obligations (Office space rent)
Equity
- Common Stock & Additional Paid-In Capital (Investor funding)
- Retained Earnings (Cumulative net income over time)
- Stock-Based Compensation Reserves (Employee Stock Options)
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
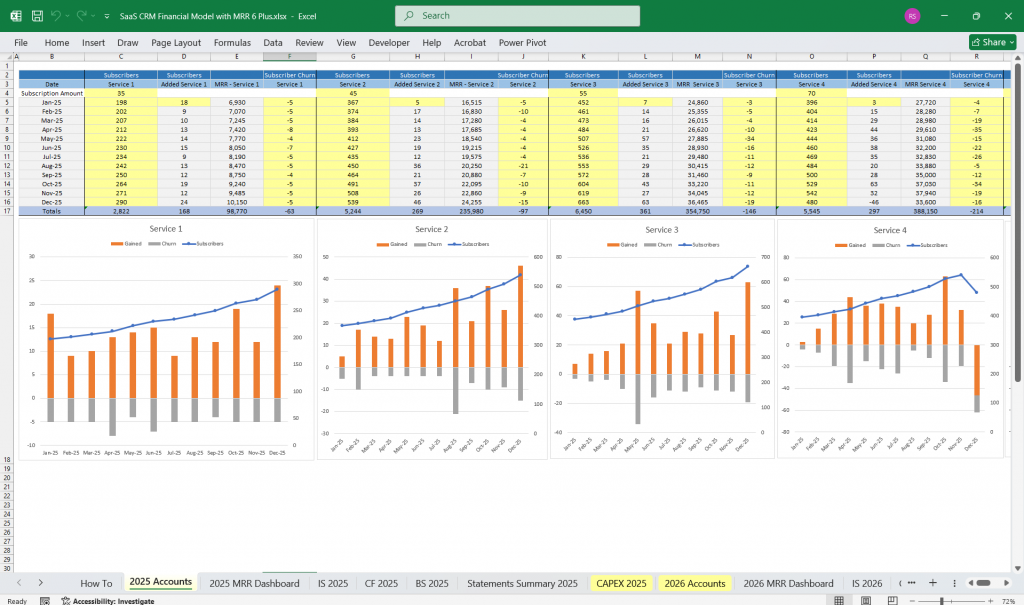
Key Assumptions and Drivers for a SaaS CRM Company
Before diving into financial statements, a financial model for a SaaS CRM company must include key assumptions:
SaaS CRM – Revenue Streams
- SaaS Subscription tiers (monthly/annual plans)
- One-time setup or onboarding fees
- Add-ons and premium features
- SaaS CRM API access fees for integrations
- SaaS Professional services (consulting, training)
SaaS CRM – Customer Acquisition
- SaaS Marketing budget allocation
- SaaS Cost per lead (CPL) analysis
- SaaS Conversion rate optimization
- Sales team commissions and incentives
- SaaS Partner or affiliate program costs
SaaS CRM – Churn and Retention Analysis
- SaaS Monthly churn rate tracking
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) calculation
- Win-back campaign costs
- SaaS Onboarding process effectiveness
- SaaS Support team impact on retention
SaaS CRM – Pricing Strategy
- SaaS Tiered pricing model development
- Freemium vs. premium analysis
- Competitor pricing benchmarks
- Value-based pricing alignment
- SaaS Discount strategies and their impact
SaaS CRM – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- SaaS Cloud hosting and infrastructure costs
- SaaS Data storage and processing fees
- Support team expenses
- SaaS Third-party integrations
- SaaS Software licenses and maintenance
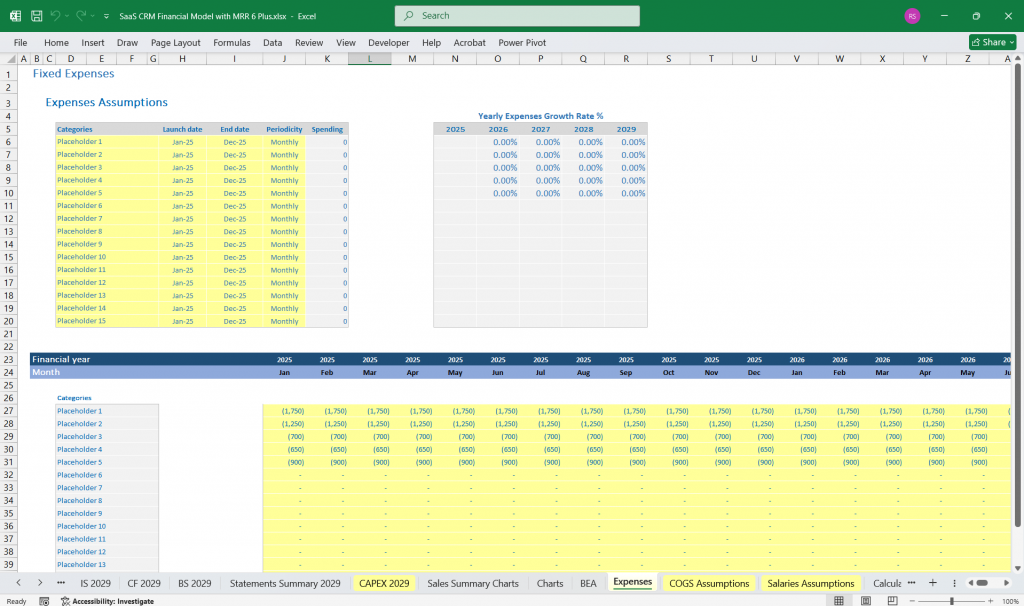
SaaS CRM – Operational Expenses
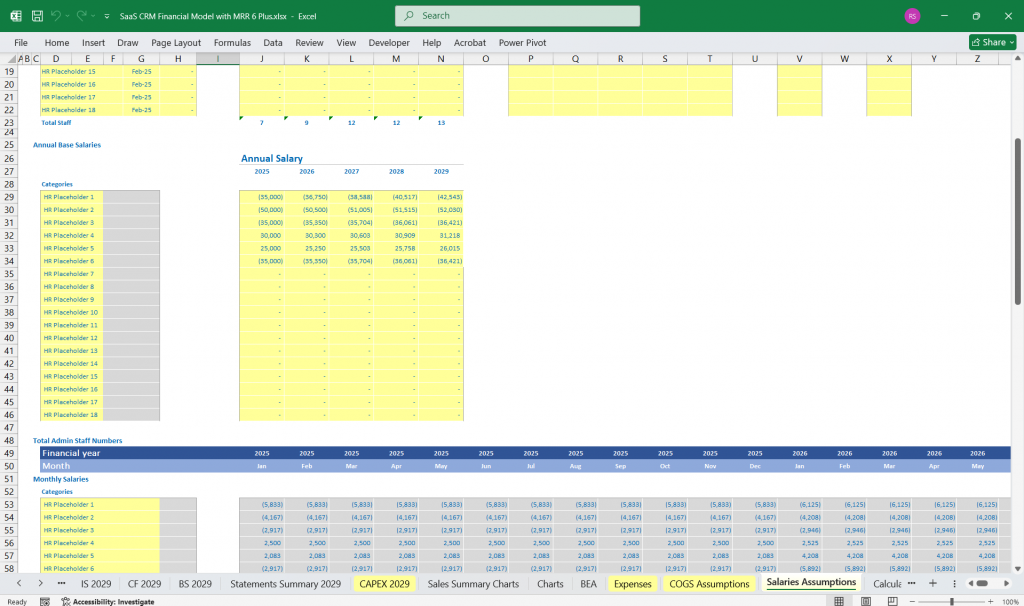
- Salaries and headcount planning
- SaaS Office and remote work infrastructure
- SaaS Sales and marketing spend
- SaaS Research and development (R&D)
- General and administrative (G&A) expenses
SaaS CRM – Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- SaaS and Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- SaaS CRM Churn rate and Net Revenue Retention (NRR)
- SaaS Average Revenue Per User (ARPU)
- Payback period on CAC
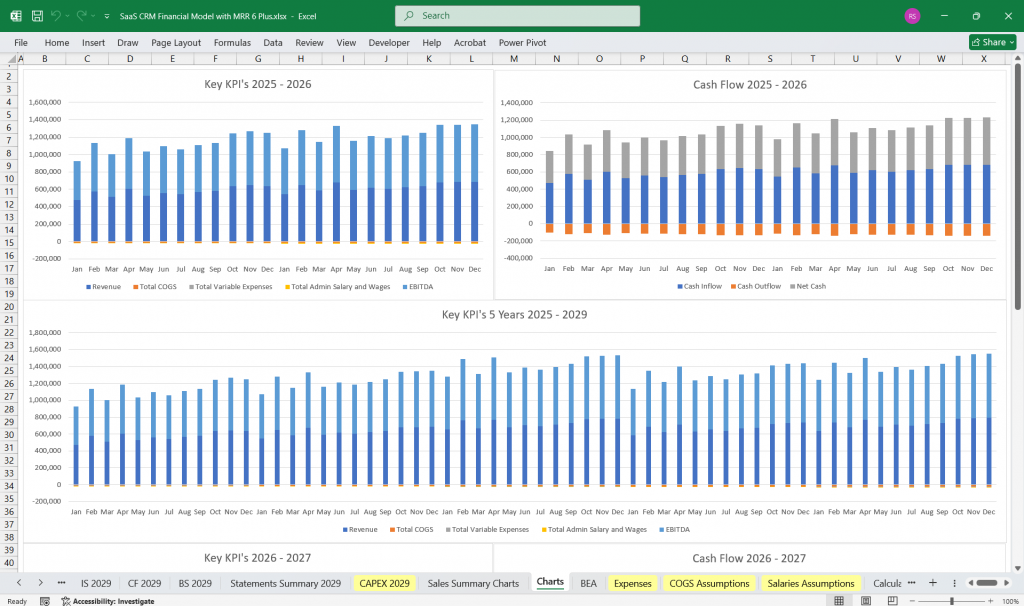
SaaS CRM – Cash Flow Management
- SaaS Forecasting cash inflows and outflows
- Managing deferred revenue
- Planning for capital expenditures
- SaaS Scenario modeling for growth vs. churn
- Building cash reserves for stability
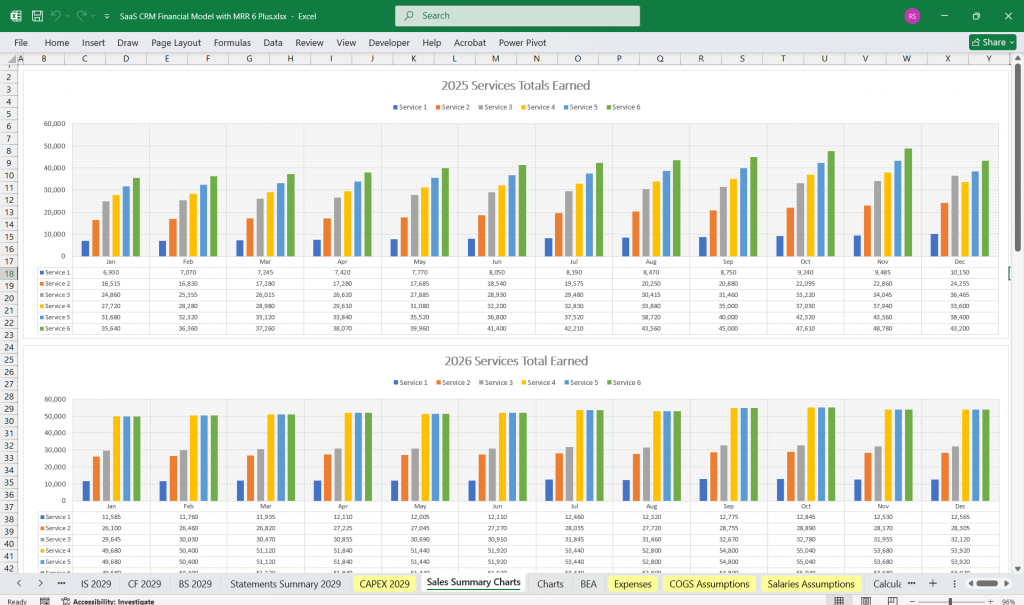
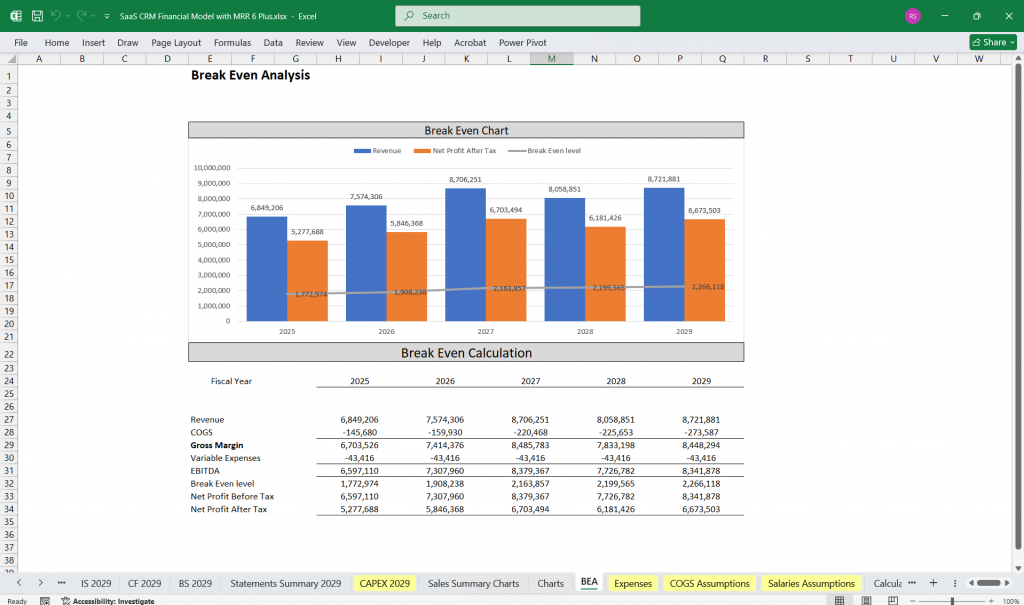
SaaS CRM – Break-Even Analysis
- Fixed vs. variable costs assessment
- SaaS Sales volume required to break even
- Time to profitability estimation
- Impact of pricing changes on break-even
- Sensitivity analysis for SaaS growth scenarios
SaaS CRM – Growth Projections
- Monthly SaaS user acquisition forecasts
- SaaS Revenue growth rate assumptions
- SaaS Expansion into new markets or segments
- SaaS Upsell and cross-sell potential
- SaaS Product development and feature rollouts
Financial Metrics
- Gross Margin (%) (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue
- Net Profit Margin (%) (Net Income / Revenue)
- Burn Rate (Monthly operating expenses)
- Runway (Cash balance / Burn rate)
- ARR & MRR (Annual and Monthly Recurring Revenue)
- Rule of 40 (Growth rate + Profitability > 40%)
6-Tier Subscription Model for a SaaS CRM Company
1. Free SaaS CRM Tier (Freemium Plan)
Target Audience: Solo entrepreneurs, freelancers, and startups testing the CRM before committing.
Features:
✅ Basic contact management (up to 500 contacts)
✅ Limited SaaS CRM pipeline management (1 sales pipeline)
✅ Task and activity tracking
✅ Email integration (basic syncing)
✅ Basic reports & SaaS CRM dashboards
✅ Community support
Pricing Strategy:
- Free forever but heavily encourages upsells to paid tiers through usage limits.
- Monetize via add-ons, integrations, or premium customer support.
Value Proposition:
- Low-friction onboarding for potential long-term customers.
- Users experience core CRM functionality before upgrading.
2. Starter SaaS CRM Tier ($15 – $25/user/month)
Target Audience: Small businesses & startups needing more than the free plan but with a limited budget.
Features:
✅ Everything in Free Tier +
✅ Unlimited SaaS CRM contacts & sales pipelines
✅ Email tracking & templates
✅ Calendar & meeting scheduling
✅ Mobile SaaS CRM app access
✅ 5GB cloud storage per user
✅ Standard customer support
Pricing Strategy:
- Priced competitively for small teams (2-10 users).
- Keeps features simple yet effective to prevent churn.
Value Proposition:
- Affordable automation & sales tracking for growing teams.
- Helps small businesses improve productivity without high costs.
3. Growth SaaS CRM Tier ($40 – $60/user/month)
Target Audience: Mid-sized businesses scaling their sales and customer success efforts.
Features:
✅ Everything in Starter Tier +
✅ Advanced sales automation (e.g., auto-follow-ups)
✅ AI-powered lead scoring
✅ Custom SaaS CRM workflow automation
✅ Social media integrations
✅ 50GB cloud storage per user
✅ Standard API access
✅ 24/7 SaaS CRM chat & email support
Pricing Strategy:
- Positioned as the best value-for-money tier.
- Encourages annual subscriptions with 10-20% discount.
Value Proposition:
- Boosts efficiency through automation and AI insights.
- Designed for companies expanding their sales & marketing efforts.
4. Professional SaaS CRM Tier ($80 – $120/user/month)
Target Audience: Established companies with complex sales processes and larger teams.
Features:
✅ Everything in Growth Tier +
✅ Advanced CRM customization (custom fields, dashboards)
✅ Territory & team-based sales management
✅ AI-driven SaaS CRM predictive analytics
✅ Multi-currency & multi-language SaaS CRM support
✅ 100GB cloud storage per user
✅ Premium API access & integrations
✅ Dedicated SaaS CRM account manager
Pricing Strategy:
- Ideal for businesses requiring scalability & customization.
- Encourages long-term contracts (discounts for 2-3 year deals).
Value Proposition:
- Enables highly customized CRM workflows.
- Ideal for organizations with regional/global teams.
5. Enterprise SaaS CRM Tier ($150 – $250/user/month, custom pricing for large teams)
Target Audience: Large corporations & enterprises needing high security, compliance, and integrations.
Features:
✅ Everything in Professional Tier +
✅ Enterprise-grade SaaS CRM security (SSO, HIPAA, SOC 2 compliance)
✅ Custom AI-driven analytics dashboards
✅ Advanced role-based SaaS CRM access controls
✅ Unlimited cloud storage
✅ Priority 24/7 phone & chat support
✅ Custom API limits & SLA-backed SaaS CRMuptime guarantee
✅ Onboarding & SaaS CRM training services
Pricing Strategy:
- Custom quotes based on seats, storage, and integrations.
- Focus on multi-year contracts (3-5 years) with enterprise discounts.
Value Proposition:
- Ultimate security, scalability, and integrations for enterprises.
- Dedicated customer success team for onboarding & support.
6. Elite/White-Label SaaS CRM Tier ($500+/user/month, fully custom pricing)
Target Audience: Large corporations, franchises, and companies needing a white-labeled CRM solution.
Features:
✅ Everything in Enterprise Tier +
✅ Fully white-labeled CRM (custom branding & UI)
✅ Dedicated private cloud hosting
✅ AI-powered SaaS CRM business intelligence tools
✅ On-premise deployment (if needed)
✅ 99.99% uptime SLA with dedicated server clusters
✅ Full-scale API customization & SaaS CRM developer support
✅ Personalized team training & consulting services
Pricing Strategy:
- Completely custom pricing, tailored for big-ticket clients.
- Heavy focus on multi-year contracts (5+ years).
Value Proposition:
- Designed for organizations wanting full control & branding over their CRM.
- Best for franchises, SaaS resellers, and large enterprises with unique needs.
Key Takeaways for the 6-Tier SaaS CRM Model
The freemium strategy captures leads and drives upgrades.
Tiered pricing ensures that businesses of all sizes find a suitable plan.
Customization & API access become key differentiators at higher tiers.
Annual & multi-year discounts increase customer lifetime value (LTV).
Enterprise & Elite tiers offer white-labeling and security for high-value clients.
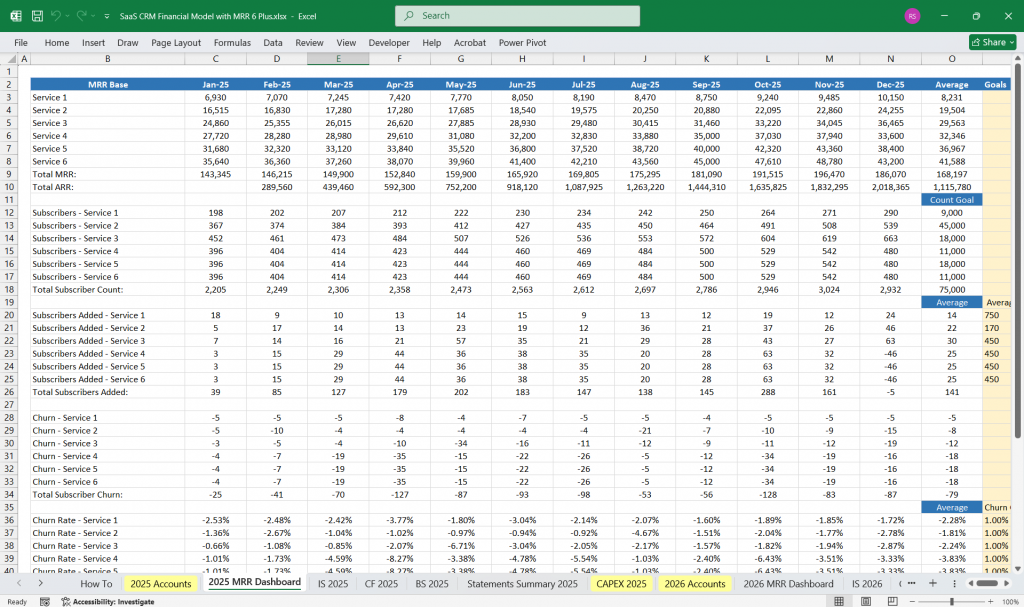
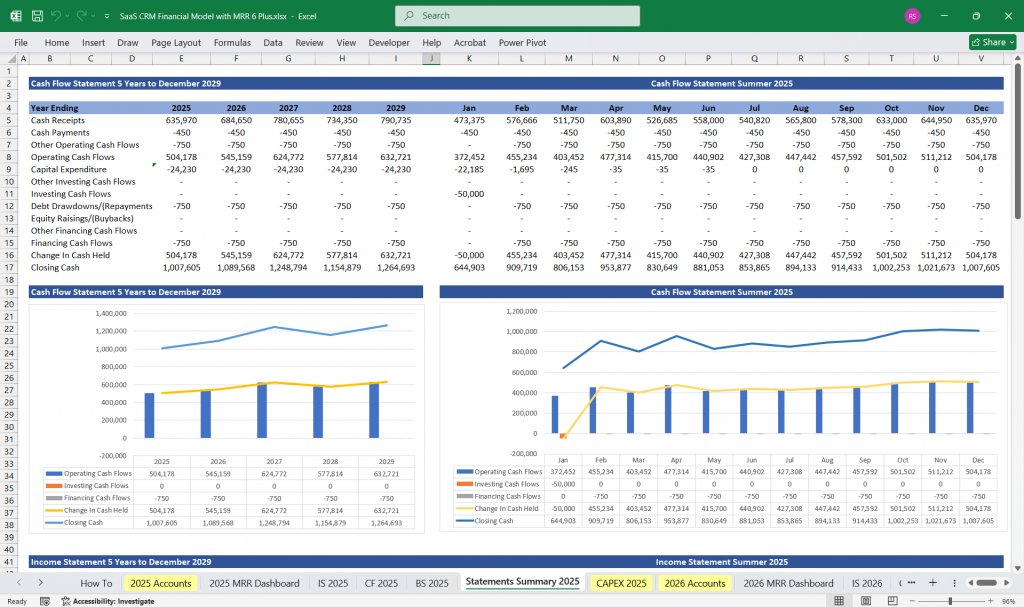
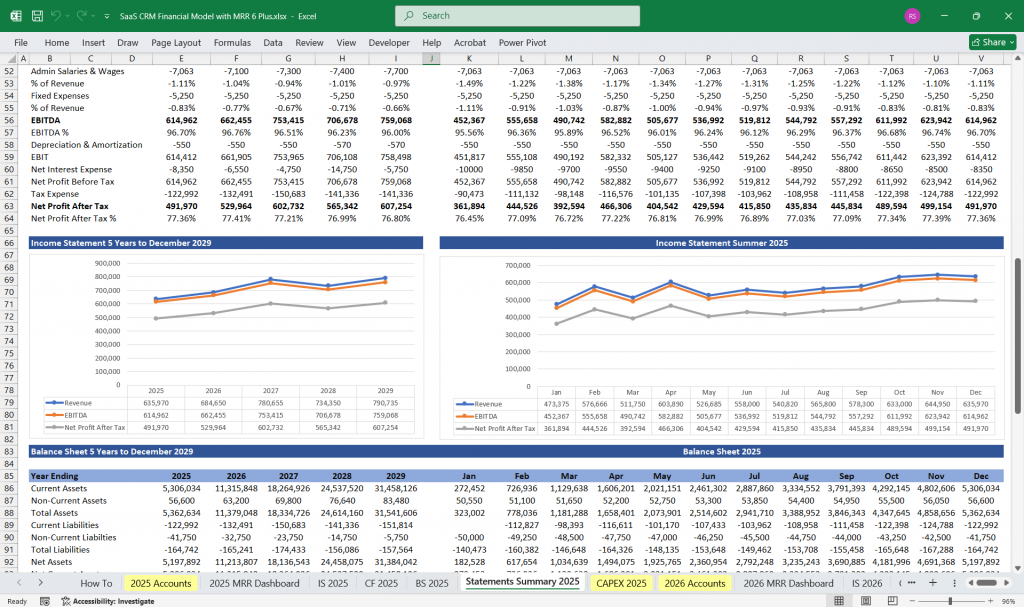
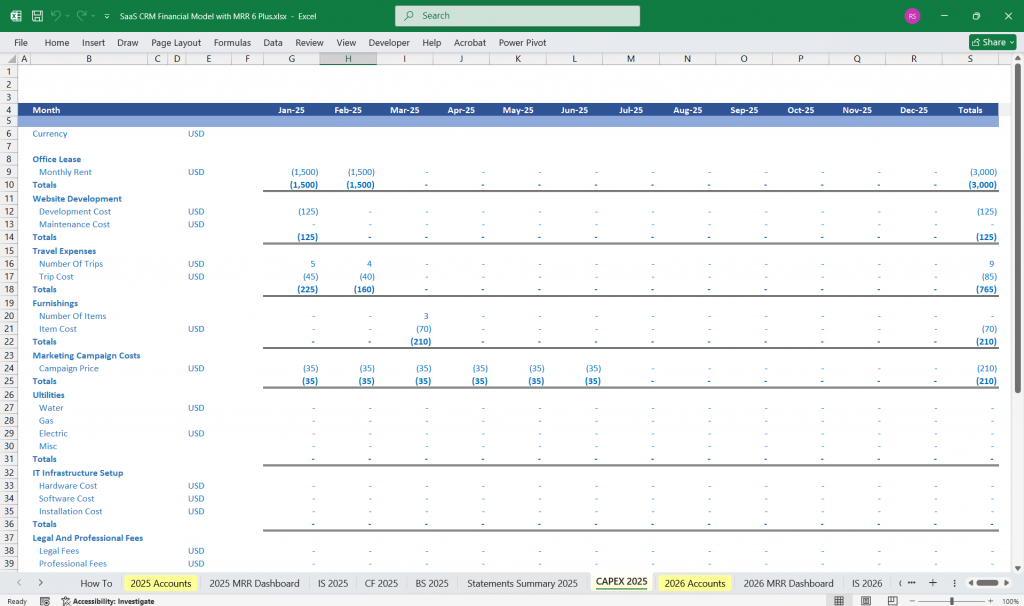
Final Notes on the Financial Model
Financial model for a SaaS CRM Company
- Scenario Analysis: Create best-case, base-case, and worst-case projections.
- Break-even Analysis: Determine sales volume required to cover fixed & variable costs.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Assess how changes in raw material costs, pricing, or demand impact profitability.
This structured model helps a SaaS CRM business address a broad market spectrum, offering the right balance between cost, production capacity, support, and customization at each subscription and project based level.
Download Link On Next Page
