Rubber and Plastics Manufacturer Financial Model
This 20 Year 80 product line Rubber and Plastics Manufacturer Financial Model in Excel is a comprehensive financial planning tool designed to help your manufacturing company, investors, and financial analysts evaluate the financial feasibility and profitability of your company.
Financial Model for a Rubber & Plastics Manufacturer
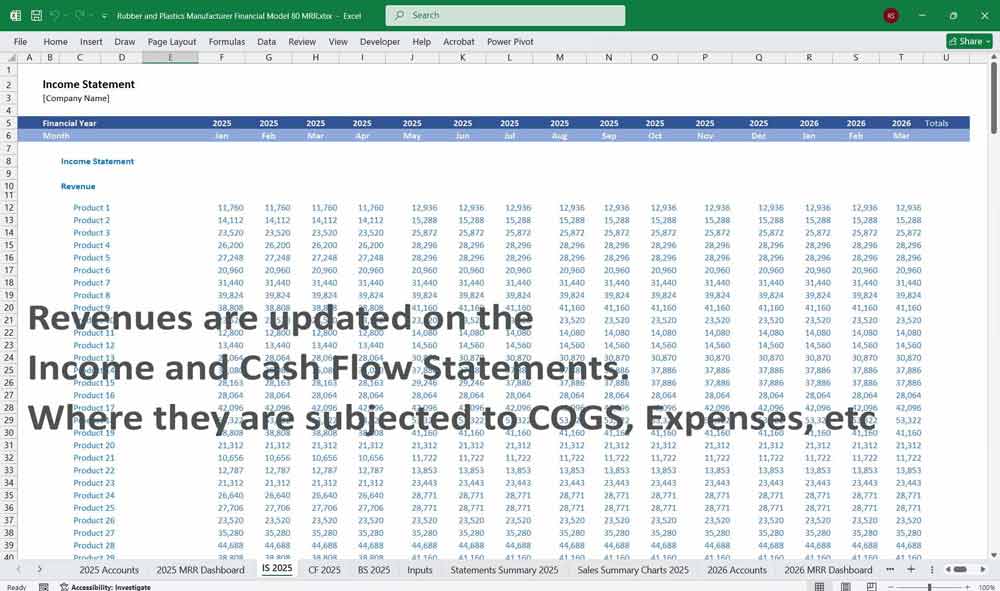
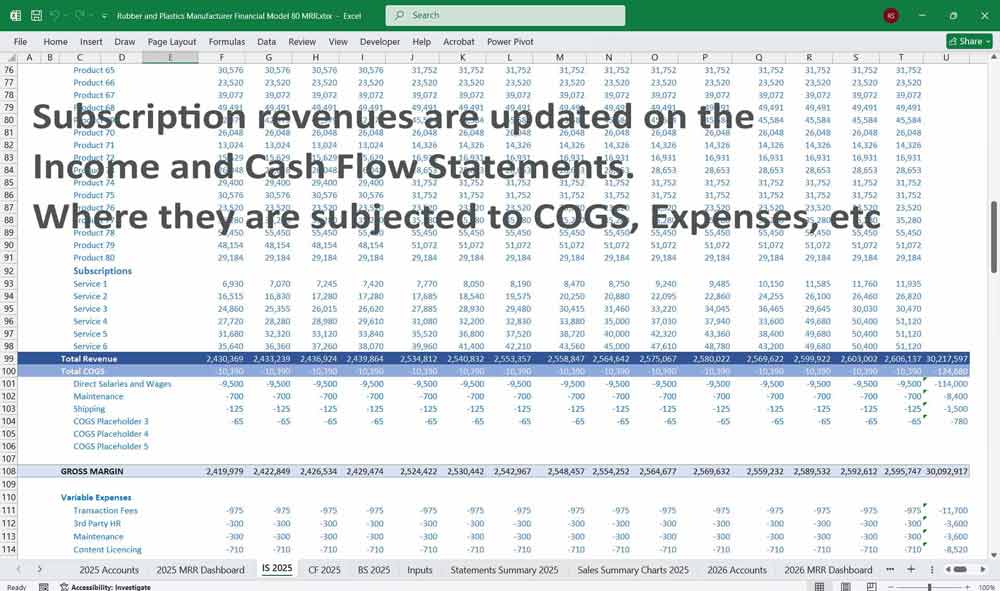
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
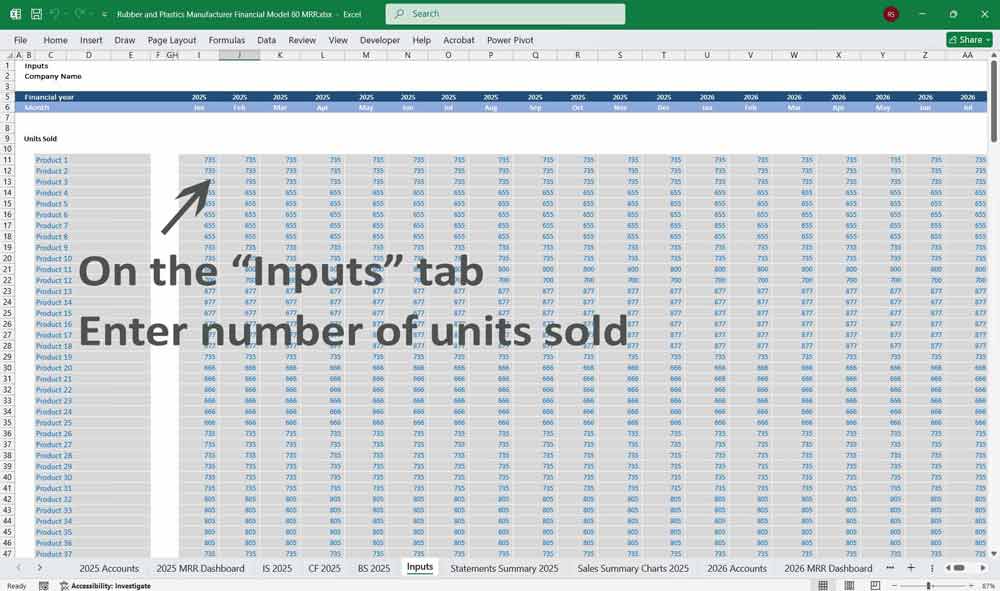
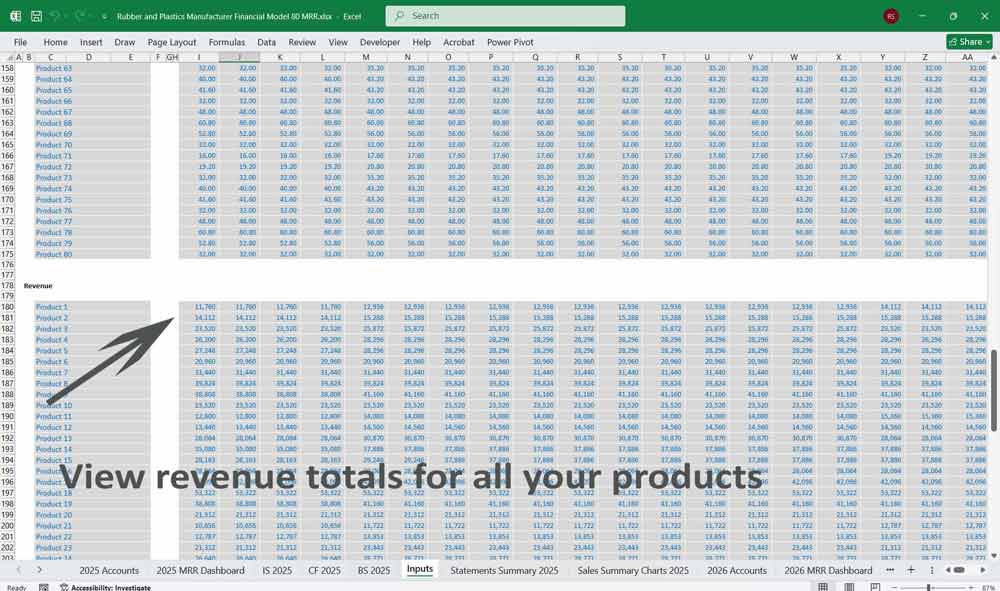
- Revenue:
- Sales of Rubber Products
- Sales of Plastic Products
- Custom Manufacturing Revenue
- Other Operating Revenue (e.g., scrap sales, recycling)
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):
- Raw Materials (Rubber, Plastic Resins, Additives)
- Direct Labor
- Manufacturing Overheads (utilities, factory rent, maintenance)
- Depreciation on Manufacturing Equipment
- Gross Profit:
- Calculated as Revenue – COGS
- Operating Expenses:
- Selling, General, and Administrative (SG&A) Expenses
- Marketing and Sales Expenses
- Research and Development (R&D)
- Depreciation and Amortization (non-production assets)
- Operating Income (EBIT):
- Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
- Other Income and Expenses:
- Interest Income
- Interest Expense
- Foreign Exchange Gains/Losses (if applicable)
- Net Income Before Tax:
- Operating Income + Other Income – Other Expenses
- Taxes:
- Income Tax Expense
- Net Income:
- Net Income Before Tax – Taxes
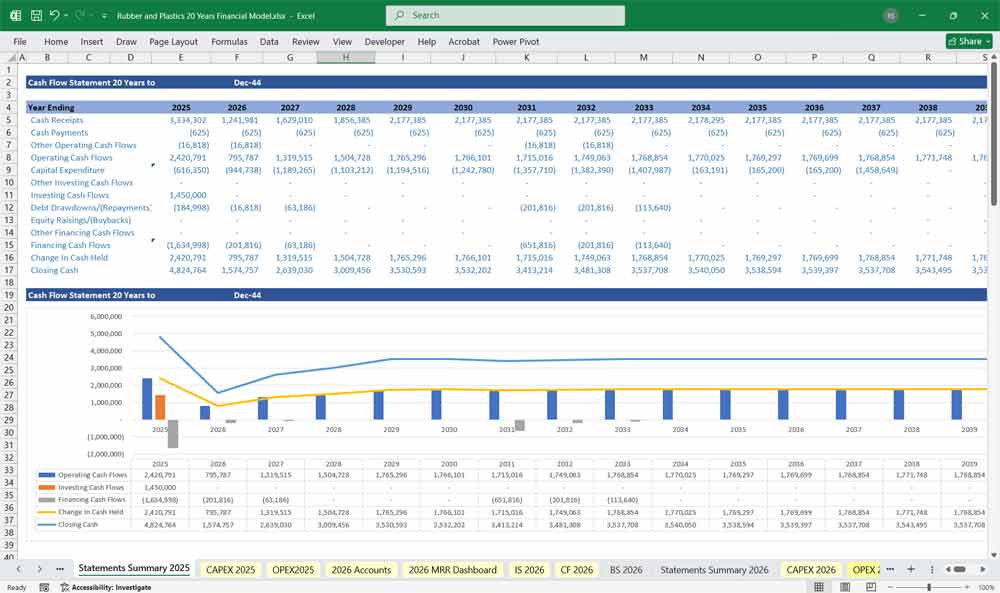
Rubber and Plastics Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow from Operating Activities:
- Net Income
- Adjustments for Non-Cash Items:
- Depreciation and Amortization
- Changes in Working Capital:
- Accounts Receivable
- Inventory
- Accounts Payable
- Other Current Assets and Liabilities
- Cash Flow from Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures (purchase of new equipment or facility upgrades)
- Proceeds from Sale of Fixed Assets
- Investments in Subsidiaries or Joint Ventures
- Cash Flow from Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Issuing Debt or Equity
- Repayment of Loans
- Dividend Payments
- Lease Payments
- Net Change in Cash:
- Sum of Cash Flow from Operating, Investing, and Financing Activities
- Opening Cash Balance:
- Closing Cash Balance:

Rubber and Plastics Balance Sheet
- Assets:
- Current Assets:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Accounts Receivable
- Inventory (Raw Materials, Work in Progress, Finished Goods)
- Prepaid Expenses
- Non-Current Assets:
- Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE)
- Intangible Assets (patents, trademarks)
- Investments
- Deferred Tax Assets
- Current Assets:
- Liabilities:
- Current Liabilities:
- Accounts Payable
- Short-term Debt
- Accrued Expenses
- Taxes Payable
- Non-Current Liabilities:
- Long-term Debt
- Deferred Tax Liabilities
- Lease Obligations
- Current Liabilities:
- Equity:
- Common Stock
- Additional Paid-in Capital
- Retained Earnings
- Other Comprehensive Income

Key Assumptions For A Rubber And Pladtics Manufacturer:
These assumptions drive the financial model. They’re based on industry norms, historical performance, and market conditions.
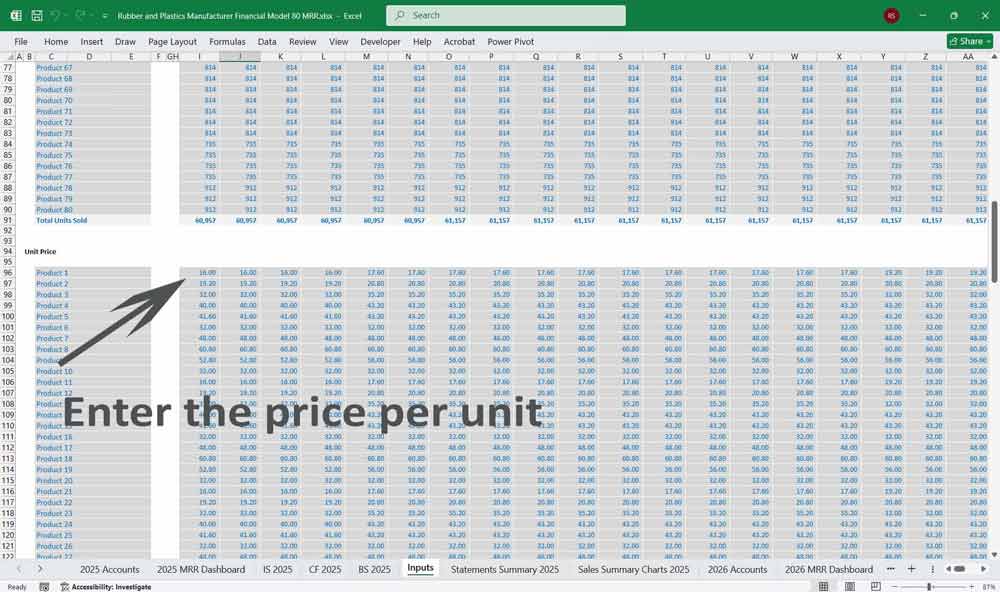
Revenue Assumptions:
- Annual Sales Growth: 5%–10% (based on market demand and capacity)
- Product Mix: % of Rubber vs. Plastic product sales
- Pricing Strategy: Annual price increase due to inflation or value addition
Cost Assumptions:
- Raw Material Costs: 40%–60% of revenue, depending on product complexity
- Direct Labor Costs: 15%–20% of revenue
- Manufacturing Overheads: 10%–15% of revenue
- Depreciation Rate: 5%–10% annually on PPE
Operating Expense Assumptions:
- SG&A Expenses: 10%–15% of revenue
- Marketing Expenses: 2%–5% of revenue
- R&D Expenses: 1%–3% of revenue
Working Capital Assumptions:
- Accounts Receivable Days: 45–60 days
- Inventory Turnover: 4–6 times per year
- Accounts Payable Days: 30–45 days
Financing Assumptions:
- Interest Rate on Debt: 5%–8% annually
- Dividend Payout Ratio: 20%–40% of net income
Tax Assumptions:
- Corporate Tax Rate: 20%–30%
When structuring product lines for a rubber and plastics manufacturer, it’s important to organize them in a way that aligns with customer needs, market demand, and operational efficiency. Below are detailed sections for up to 80 product lines, including categorization, examples, and strategic considerations.
Smaller Product Line Scenario
This structure focuses on a concise range of product lines, suitable for a mid-sized manufacturer.
1. Automotive Plastics Components
Rubber Seals and Gaskets
Plastic Bumpers
Rubber Hoses (Fuel, Air, Coolant)
Plastic Interior Trim Parts
Rubber Anti-Vibration Mounts
2. Industrial Plastic Products
Rubber Conveyor Belts
Plastic Rollers
Rubber Grommets
Plastic Bushings
Rubber Mats (Anti-Fatigue, Safety)
3. Plastic Consumer Goods
Plastic Kitchenware (Containers, Utensils)
Rubber Grips (Tools, Handles)
Plastic Toys
Rubber Footwear Soles
Plastic Storage Bins
4. Healthcare Rubber and Plastics
Rubber Stoppers (for Vials)
Plastic Syringes
Rubber Tubing (Medical Grade)
Plastic Disposable Cups and Trays
Rubber Gloves
5. Construction and Infrastructure Plastics
Rubber Expansion Joints
Plastic Pipes (PVC, HDPE)
Rubber Roofing Membranes
Plastic Insulation Panels
Rubber Flooring Tiles
6. Electrical Rubber & Plastics
Plastic Cable Ties
Rubber Cable Insulation
Plastic Enclosures (for Electronics)
Rubber Keypads
Plastic Connectors
7. Plastic Packaging
Plastic Bottles and Jars
Rubber Stoppers (for Bottles)
Plastic Film and Sheets
Rubber Bands
Plastic Caps and Closures
8. Specialty Plastic Products
Rubber Molding (Custom Shapes)
Plastic Prototyping (3D Printing Filaments)
Rubber Gaskets (High-Temperature)
Plastic Composites (Reinforced)
Rubber Adhesives and Coatings
80 Product Line Breakdown
This expanded structure includes more specialized and niche product lines, catering to a broader market.
1. Automotive Plastic Components
Rubber Seals and Gaskets
Plastic Bumpers
Rubber Hoses (Fuel, Air, Coolant)
Plastic Interior Trim Parts
Rubber Anti-Vibration Mounts
Plastic Dashboard Components
Rubber Wiper Blades
Plastic Light Covers
Rubber Tire Components
Plastic Fuel Tanks
2. Industrial Platic Products
Rubber Conveyor Belts
Plastic Rollers
Rubber Grommets
Plastic Bushings
Rubber Mats (Anti-Fatigue, Safety)
Plastic Chains (Conveyor)
Rubber Couplings
Plastic Bearings
Rubber Linings (for Tanks)
Plastic Sheets (Cut-to-Size)
3. Consumer Rubber Goods
Plastic Kitchenware (Containers, Utensils)
Rubber Grips (Tools, Handles)
Plastic Toys
Rubber Footwear Soles
Plastic Storage Bins
Rubber Erasers
Plastic Furniture Components
Rubber Yoga Mats
Plastic Cosmetic Packaging
Rubber Sports Equipment
4. Medical and Healthcare Plastics
Rubber Stoppers (for Vials)
Plastic Syringes
Rubber Tubing (Medical Grade)
Plastic Disposable Cups and Trays
Rubber Gloves
Plastic IV Bags
Rubber Catheters
Plastic Surgical Instruments
Rubber Prosthetics
Plastic Labware (Petri Dishes, Pipettes)
5. Construction and Infrastructure Plastic
Rubber Expansion Joints
Plastic Pipes (PVC, HDPE)
Rubber Roofing Membranes
Plastic Insulation Panels
Rubber Flooring Tiles
Plastic Wall Cladding
Rubber Bridge Bearings
Plastic Drainage Systems
Rubber Soundproofing Materials
Plastic Window Frames
6. Electrical and Electronics Plastic
Plastic Cable Ties
Rubber Cable Insulation
Plastic Enclosures (for Electronics)
Rubber Keypads
Plastic Connectors
Rubber Gaskets (for Electronics)
Plastic Circuit Board Components
Rubber Heat Shields
Plastic Switch Covers
Rubber Wire Coatings
7. Plastic Packaging
Plastic Bottles and Jars
Rubber Stoppers (for Bottles)
Plastic Film and Sheets
Rubber Bands
Plastic Caps and Closures
Plastic Blister Packs
Rubber Liners (for Packaging)
Plastic Pouches
Rubber Seals (for Containers)
Plastic Trays (for Food Packaging)
8. Specialty Plastic Products
Rubber Molding (Custom Shapes)
Plastic Prototyping (3D Printing Filaments)
Rubber Gaskets (High-Temperature)
Plastic Composites (Reinforced)
Rubber Adhesives and Coatings
Plastic Foams (for Insulation)
Rubber Diaphragms
Plastic Films (Barrier Films)
Rubber Extrusions (Custom Profiles)
Plastic Laminates (Decorative)
Conclusion
This 80 product line breakdown provides a detailed view of the rubber and plastics manufacturing industry, categorizing products by construction, automotive, consumer, industrial, and decorative applications
6-Tier Subscription Model for a Rubber and Plastics Manufacturer
This involves structuring offerings that cater to different customer segments, from small businesses to large enterprises. Each tier should provide increasing value, services, and benefits to justify the higher price points.
Tier 1: Basic Rubber and Plastics Plan (Entry-Level)
Target Audience: Small businesses or startups with minimal material needs.
Features:
Access to standard rubber and plastic materials (e.g., basic grades of rubber, general-purpose plastics).
Limited monthly order volume (e.g., 500 kg).
Basic technical support and documentation.
Email support with a 48-hour response time.
Pricing: Low-cost or pay-as-you-go model to attract new customers.
Value Proposition: Affordable entry point for small businesses to access essential materials.
Tier 2: Starter Rubber and Plastics Plan (Growing Businesses)
Target Audience: Medium-sized businesses with moderate material needs.
Features:
Access to a wider range of materials (e.g., specialized rubbers, engineering plastics).
Increased monthly order volume (e.g., 2,000 kg).
Regular technical support and access to material datasheets.
Phone support with a 24-hour response time.
Pricing: Mid-range pricing to reflect added value.
Tier 3: Professional Rubber and Plastics Plan (Established Businesses)
Target Audience: Established businesses with consistent material needs.
Features:
Access to advanced materials (e.g., high-performance rubbers, specialty plastics).
Higher monthly order volume (e.g., 5,000 kg).
Priority technical support and access to material experts.
Dedicated account manager and 24/7 support.
Pricing: Higher pricing to reflect advanced features and support.
Value Proposition: Comprehensive solution for established businesses with regular material usage.
Tier 4: Advanced Rubber and Plastics Plan (High-Growth Operations)
Target Audience: High-growth companies or larger businesses with complex needs.
Features:
Access to premium materials (e.g., custom formulations, high-temperature plastics).
Custom monthly order volume based on business requirements.
On-site technical support and material testing services.
Access to exclusive industry reports and material innovation updates.
Pricing: Premium pricing for high-value features.
Value Proposition: Tailored solutions for businesses scaling rapidly and requiring high-performance materials.
Tier 5: Enterprise Rubber and Plastics Plan (Large Corporations)
Target Audience: Large corporations with high-volume and complex material requirements.
Features:
Access to the full range of materials and custom formulations.
Unlimited monthly order volume.
Custom material development and co-engineering services.
Executive-level consulting and strategic planning.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on volume and needs.
Value Proposition: End-to-end solutions for large-scale operations with extensive material requirements.
Tier 6: Custom Rubber and Plastics Plan (Bespoke Solutions)
Target Audience: Businesses with unique or highly specialized needs.
Features:
Fully customized material solutions tailored to the client’s requirements.
Co-development of specialized materials and formulations.
Exclusive access to beta materials and early releases.
SLA-backed 24/7 premium support with a dedicated team.
Pricing: Negotiated pricing based on scope and complexity.
Value Proposition: A partnership approach to deliver maximum value for specialized operations.
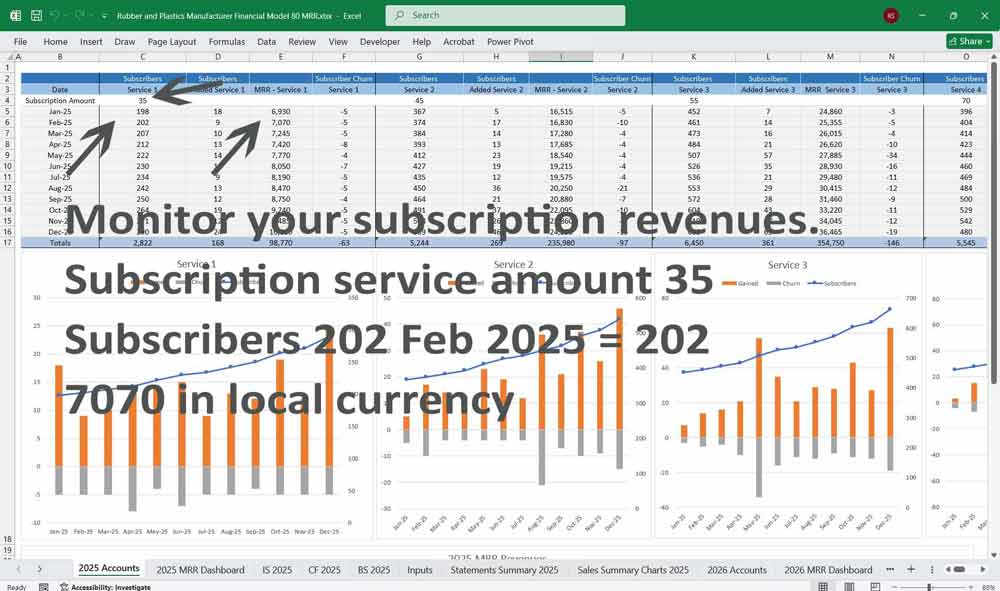
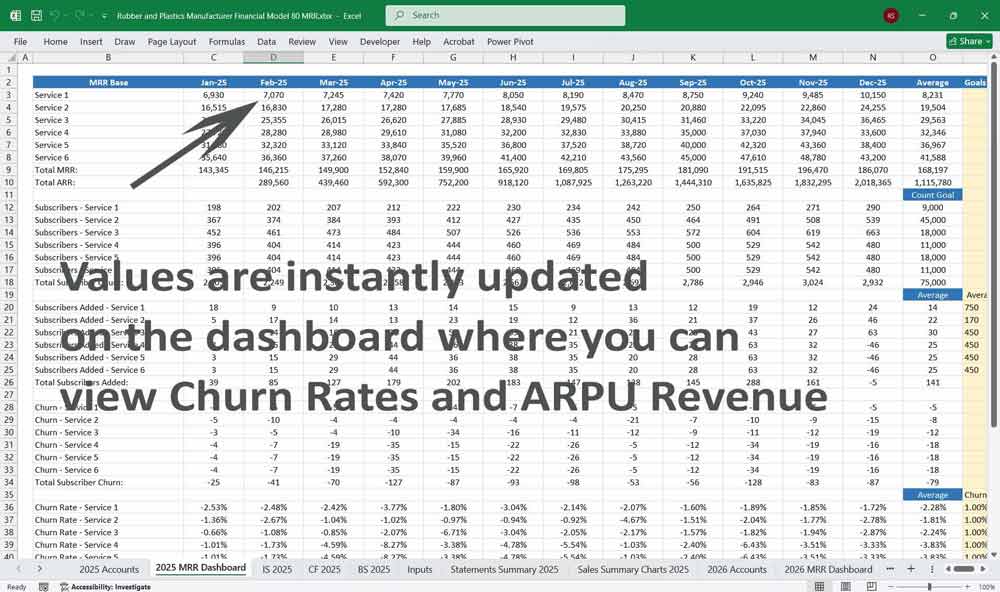
Subscription Metrics
- MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue): Recurring revenue driven by client adoption.
- ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) = MRR × 12.
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) = Average subscription value × lifespan.
- Churn Rate: Evaluates loss of subscribers over time.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Sales/marketing spend per subscription signup.
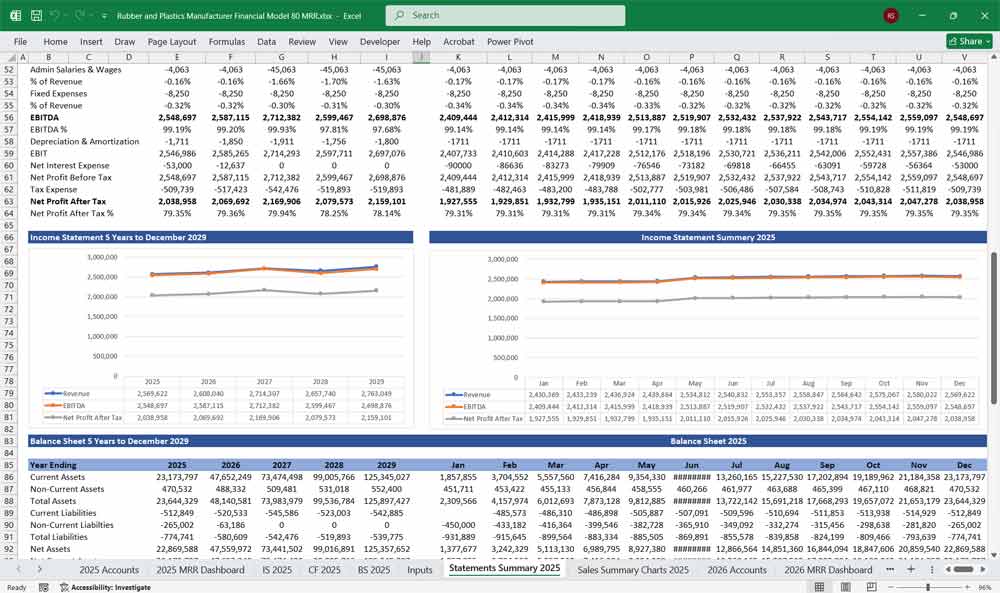
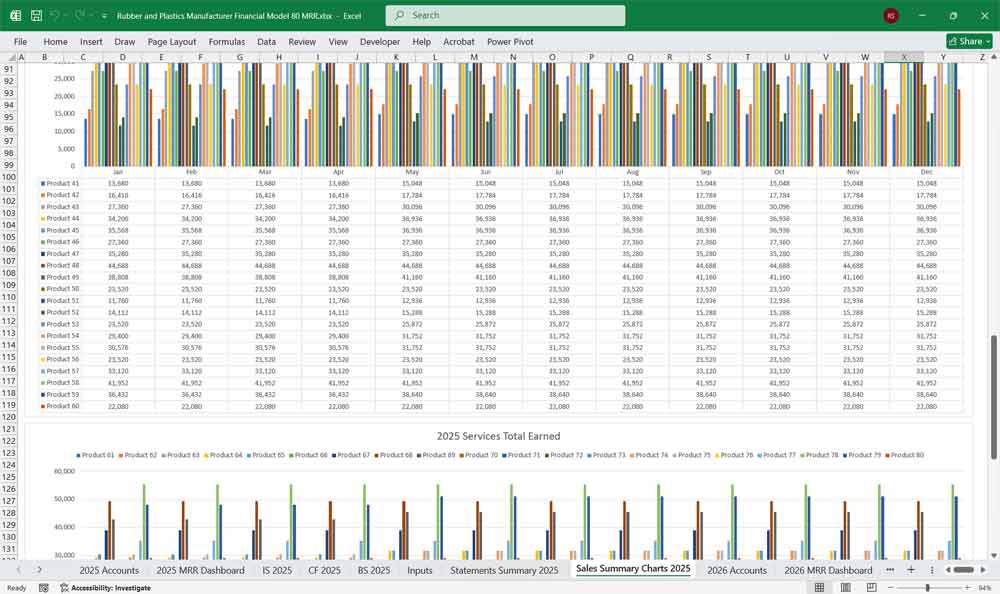

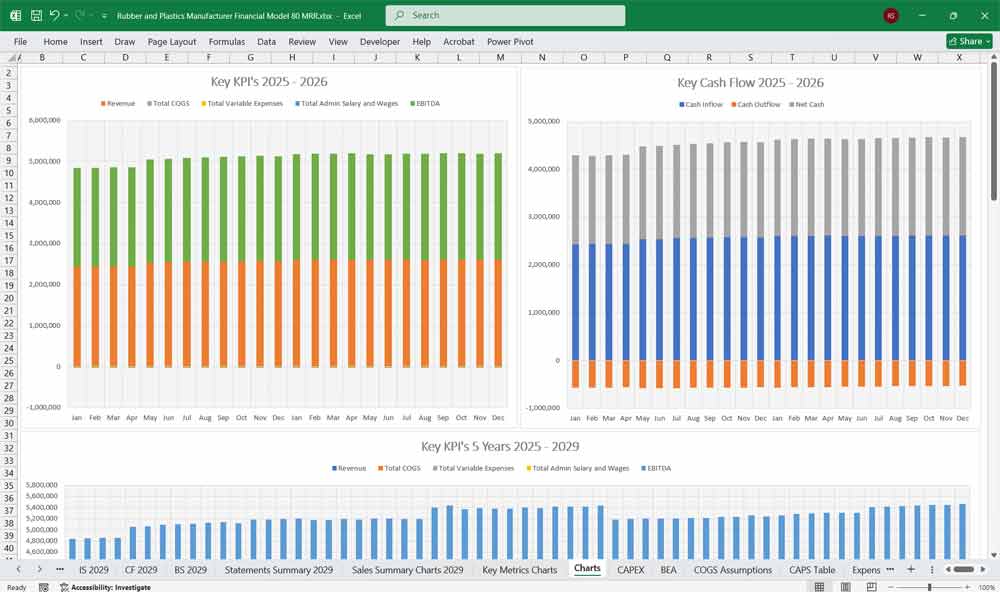
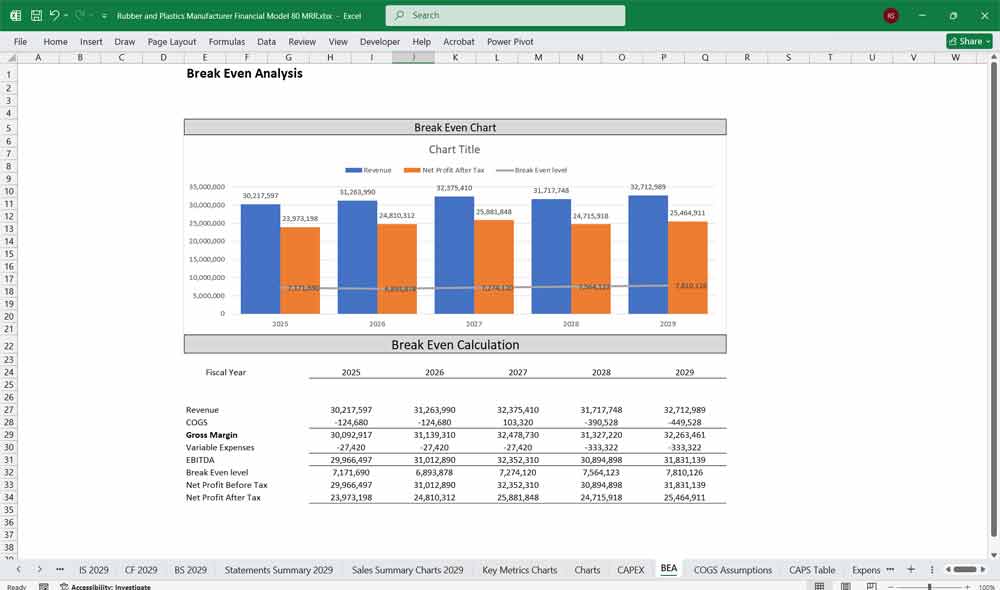
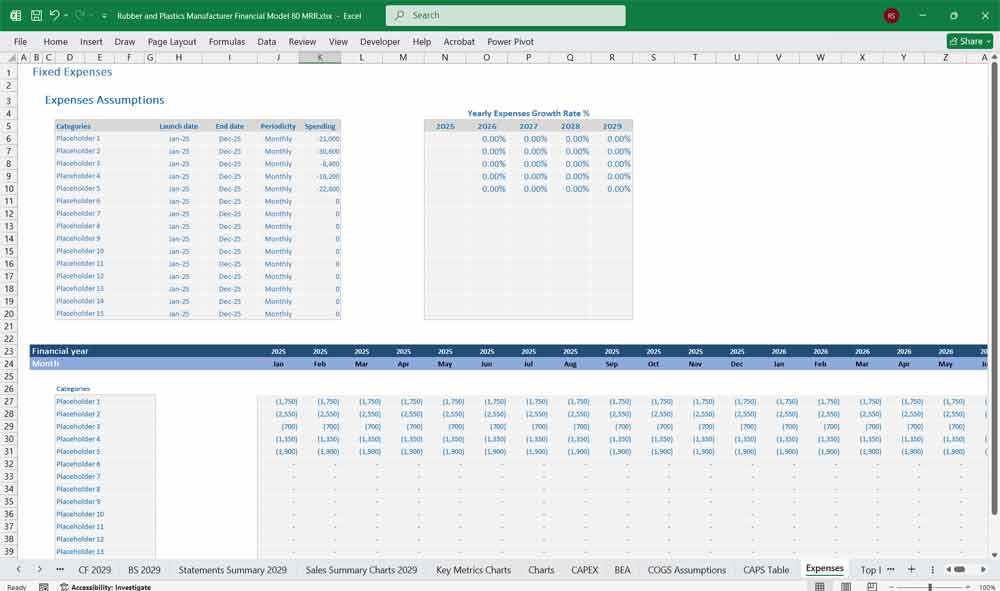
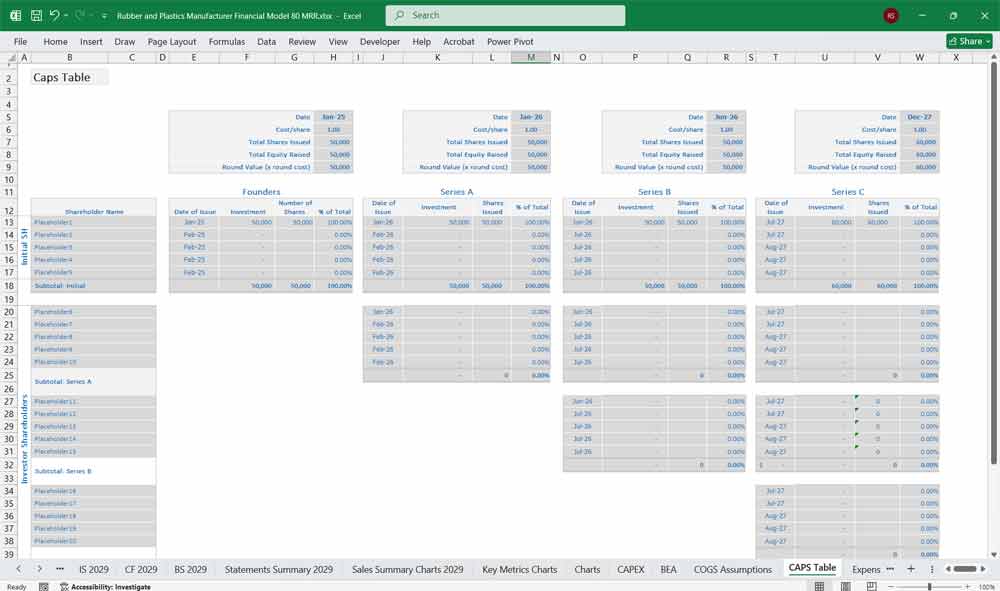
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This Rubber and Plastics Manufacturer Financial Model provides a structured approach to managing revenues, expenses, cash flows, and financial stability for your Rubber and Plastics company. By tracking financial model statements and key metrics, the company can optimize profitability, control costs, and plan for future expansion.
Download Link On Next Page
