Fintech Mobile App Finance Model
Financial Model for a Fintech Mobile App
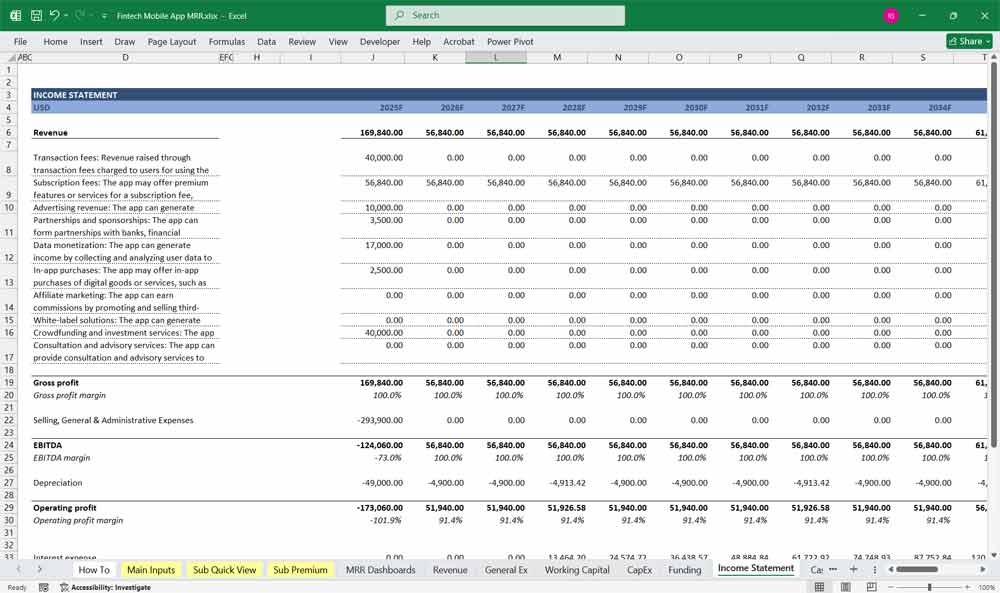
Income Statement
The Income Statement (or Profit and Loss Statement) shows the app’s revenues, costs, and profitability over time.
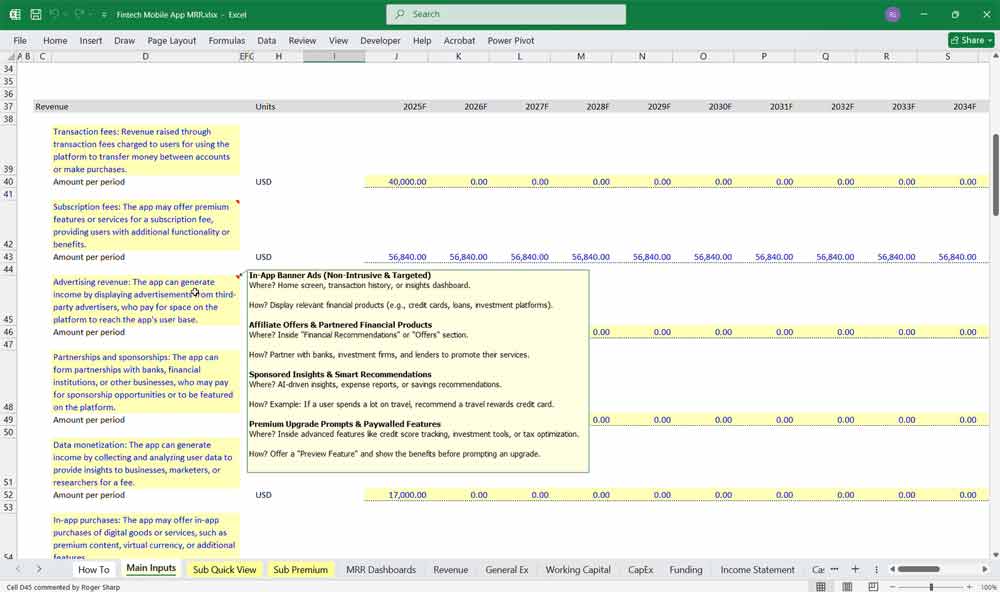
Revenue Streams
-
Transaction Fees: Revenue from fees charged on transactions (e.g., peer-to-peer payments, money transfers).
-
Subscription Fees: Recurring revenue from premium features or subscription plans.
-
Interchange Fees: Revenue from card transactions (if applicable).
-
Interest Income: Earnings from lending activities or holding user balances.
-
Advertising Revenue: Income from in-app ads or partnerships.
-
Other Revenue: Ancillary income (e.g., data analytics services, white-label solutions).
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
-
Payment Processing Fees: Costs paid to payment gateways or card networks.
-
Server and Cloud Costs: Hosting and infrastructure expenses.
-
Third-Party API Costs: Fees for using external APIs (e.g., KYC, fraud detection).
-
Customer Support Costs: Expenses related to user support.
Operating Expenses
-
Research and Development (R&D): Costs for app development, updates, and new features.
-
Marketing and Customer Acquisition: Expenses for digital ads, influencer partnerships, and referral programs.
-
Salaries and Benefits: Compensation for employees (developers, marketers, customer support).
-
Administrative Costs: Office rent, utilities, software subscriptions, etc.
-
Legal and Compliance: Costs for regulatory compliance, licenses, and legal fees.
Profitability Metrics
-
Gross Profit: Revenue – COGS.
-
Operating Profit: Gross Profit – Operating Expenses.
-
Net Profit: Operating Profit – Taxes and Interest.
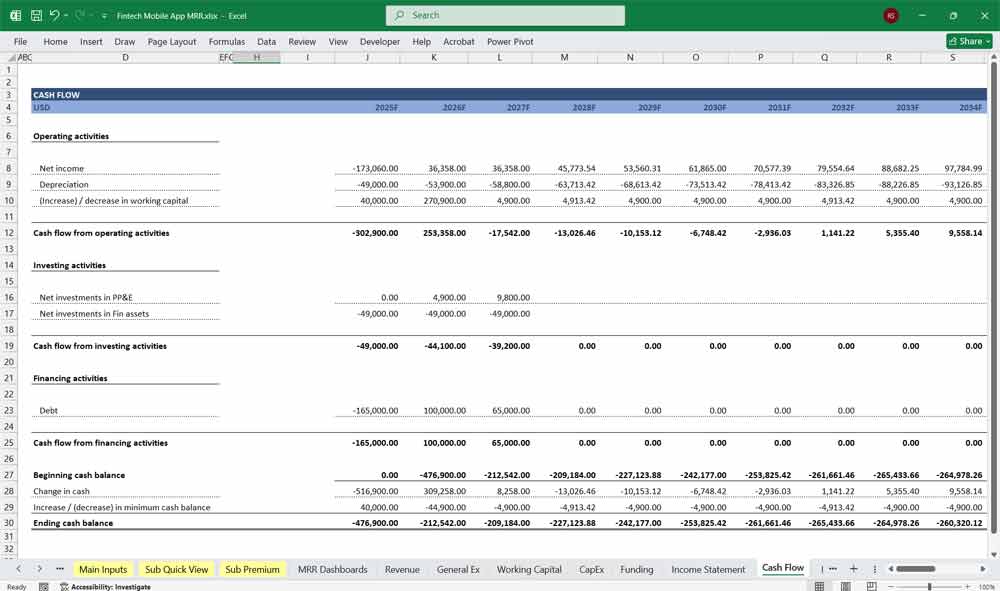
Fitech App Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of the business, divided into three sections: Operating Activities, Investing Activities, and Financing Activities.
Operating Activities
Cash Inflows:
Revenue from transactions, subscriptions, and other income streams.
Interest or dividends received.
Cash Outflows:
Payments for COGS (e.g., payment processing fees, server costs).
Operating expenses (e.g., salaries, marketing, administrative costs).
Taxes paid.
Investing Activities
Cash Outflows:
Capital expenditures (e.g., development of new features, infrastructure upgrades).
Investments in technology or partnerships.
Cash Inflows:
Returns from investments (if applicable).
Financing Activities
Cash Inflows:
Equity funding from investors.
Debt financing (loans or credit lines).
Cash Outflows:
Repayment of loans or credit lines.
Dividends or distributions to shareholders (if applicable).
Net Cash Flow
Sum of cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities.
Indicates the app’s liquidity and ability to sustain operations.
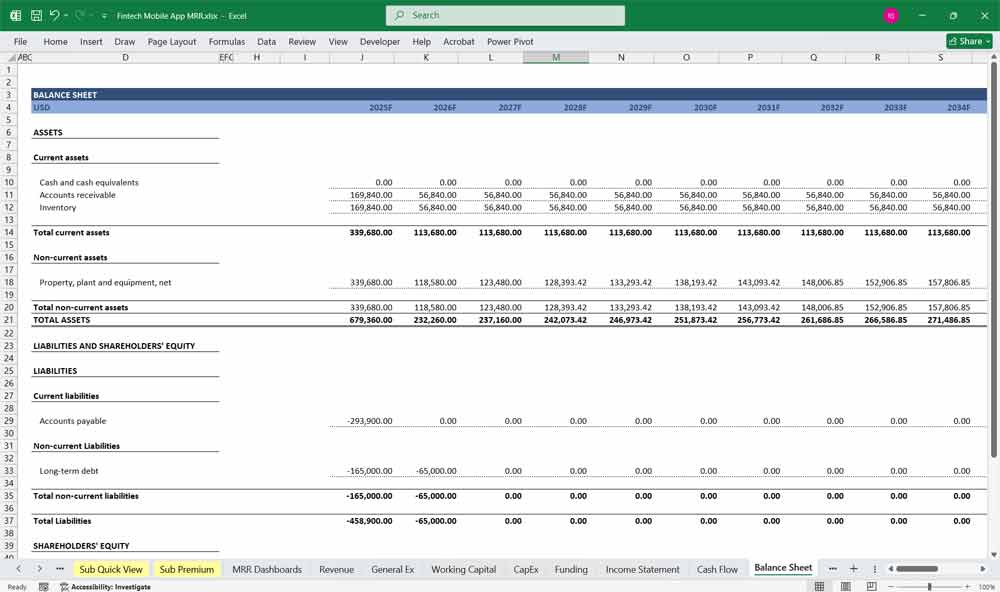
Finech App Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of the app’s financial position at a specific point in time, showing Assets, Liabilities, and Equity.
Assets
Current Assets:
Cash and Cash Equivalents: Liquid funds available for operations.
Accounts Receivable: Payments due from customers or partners.
Prepaid Expenses: Costs paid in advance (e.g., software subscriptions).
Non-Current Assets:
Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E): Hardware or infrastructure investments.
Intangible Assets: Intellectual property, patents, or trademarks.
Liabilities
Current Liabilities:
Accounts Payable: Amounts owed to vendors or service providers.
Accrued Expenses: Unpaid operating expenses (e.g., salaries, utilities).
Short-Term Debt: Loans or credit lines due within a year.
Non-Current Liabilities:
Long-Term Debt: Loans or credit lines due beyond a year.
Deferred Revenue: Subscription fees received in advance.
Equity
Shareholder Equity:
Common Stock: Equity issued to investors.
Retained Earnings: Cumulative net profits reinvested in the business.
Additional Paid-In Capital: Funds raised from investors above the par value of shares.
Balance Sheet Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
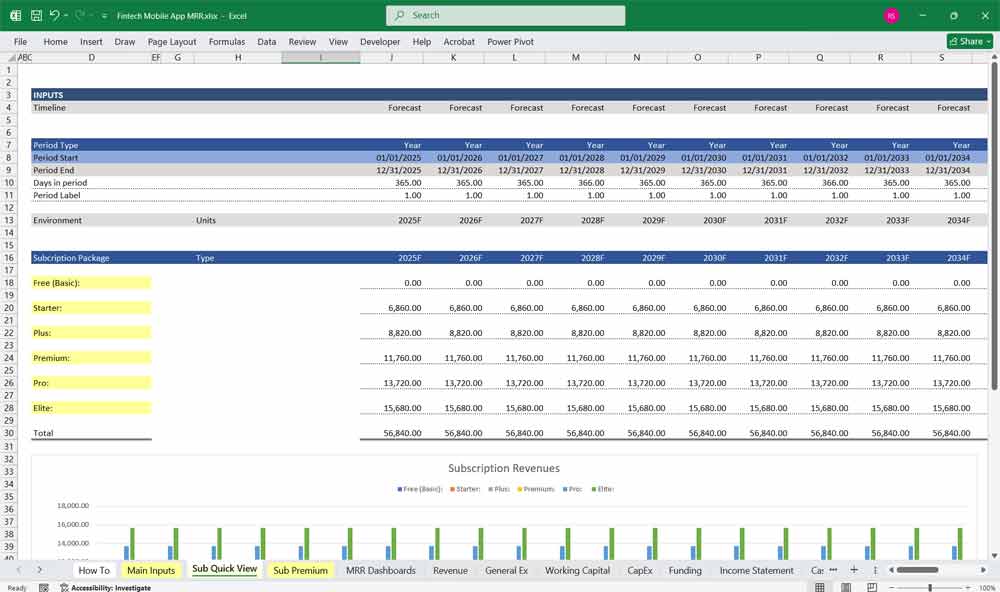
A 6-tier subscription model for a Fintech mobile app allows users to choose from multiple subscription levels, each offering progressively more features, benefits, or services. This model is designed to cater to a wide range of users, from casual users to high-value customers.
Free Tier (Tier 1)
Target Audience:
Casual users, first-time users, or those testing the app.
Features:
Basic Functionality: Access to core features (e.g., peer-to-peer payments, account balance checks).
Limited Transactions: Cap on the number or value of transactions per month.
Ads: Display of non-intrusive ads to generate revenue.
Basic Support: Email or chatbot support with slower response times.
Revenue Model:
Ad-based revenue.
Upsell opportunities to higher tiers.
Purpose:
Acquire users and introduce them to the app’s value proposition.
Starter Tier (Tier 2)
Target Audience:
Users who want to use the app regularly but don’t need advanced features.
Features:
Ad-Free Experience: No ads.
Increased Transaction Limits: Higher caps on transactions compared to the free tier.
Basic Analytics: Access to spending insights or transaction history.
Priority Support: Faster response times via email or chat.
Pricing:
Low monthly fee (e.g., $4.99/month).
Revenue Model:
Recurring subscription revenue.
Purpose:
Encourage users to upgrade from the free tier for a better experience.
Pro Tier (Tier 3)
Target Audience:
Frequent users who need more advanced features.
Features:
Unlimited Transactions: No caps on the number or value of transactions.
Advanced Analytics: Detailed financial insights, budgeting tools, and spending trends.
Cashback Rewards: Small percentage of cashback on transactions.
Multi-Currency Support: Ability to hold and transact in multiple currencies.
24/7 Chat Support: Access to live chat support.
Pricing:
Moderate monthly fee (e.g., $9.99/month).
Revenue Model:
Recurring subscription revenue + interchange fees from transactions.
Purpose:
Attract power users who value convenience and advanced tools.
Business Tier (Tier 4)
Target Audience:
Small business owners or freelancers using the app for business transactions.
Features:
Business Accounts: Separate accounts for personal and business use.
Invoicing Tools: Create and send invoices directly from the app.
Tax Reporting: Automated tax calculations and reports.
Team Access: Add team members with role-based permissions.
Dedicated Account Manager: Personalized support for business needs.
Pricing:
Higher monthly fee (e.g., $19.99/month).
Revenue Model:
Recurring subscription revenue + transaction fees.
Purpose:
Cater to small businesses and increase average revenue per user (ARPU).
Premium Tier (Tier 5)
Target Audience:
High-net-worth individuals or users who want exclusive benefits.
Features:
Exclusive Rewards: Higher cashback percentages, discounts, or exclusive offers.
Premium Support: 24/7 phone support and priority resolution.
Investment Tools: Access to robo-advisory or investment portfolios.
Concierge Services: Personalized financial planning or expense management.
Enhanced Security: Advanced fraud protection and insurance coverage.
Pricing:
High monthly fee (e.g., $49.99/month).
Revenue Model:
Recurring subscription revenue + revenue from investment services.
Purpose:
Target high-value customers and increase lifetime value (LTV).
Enterprise Tier (Tier 6)
Target Audience:
Large businesses or enterprises with complex financial needs.
Features:
Custom Solutions: Tailored features for enterprise needs (e.g., payroll integration, bulk payments).
API Access: Integration with the company’s existing systems.
Unlimited Team Members: Add as many users as needed with advanced permissions.
Dedicated Support Team: 24/7 access to a dedicated support team.
Compliance and Security: Enterprise-grade security and compliance tools (e.g., SOC 2, GDPR).
Pricing:
Custom pricing based on business size and requirements.
Revenue Model:
High recurring subscription revenue + transaction fees + custom service fees.
Purpose:
Serve large businesses and generate significant revenue from high-volume users.
Key Considerations for the Subscription Model
Pricing Strategy:
Ensure pricing aligns with the value provided at each tier.
Offer discounts for annual subscriptions to improve cash flow.
Upsell Opportunities:
Use in-app prompts, email campaigns, and personalized recommendations to encourage upgrades.
Churn Management:
Provide exceptional customer support and continuously improve features to retain users.
Localization:
Adjust pricing and features to suit different markets and currencies.
Trial Periods:
Offer free trials for higher tiers to reduce friction in upgrading.
Feedback Loop:
Collect user feedback to refine features and pricing for each tier.
This 6-tier subscription model ensures that the Fintech app can cater to a diverse user base while maximizing revenue and user satisfaction. Each tier is designed to provide incremental value, encouraging users to upgrade as their needs grow.
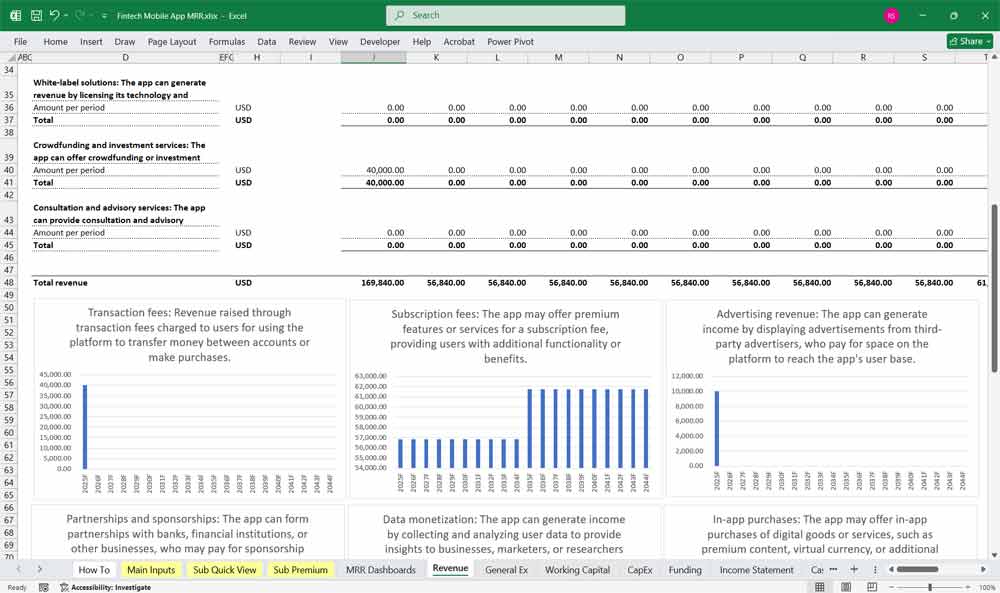
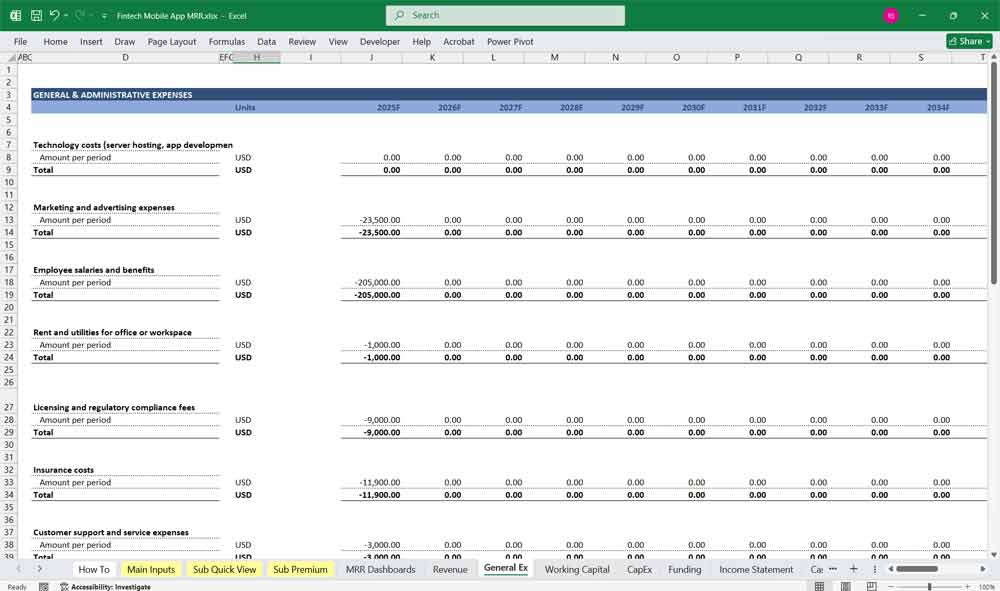
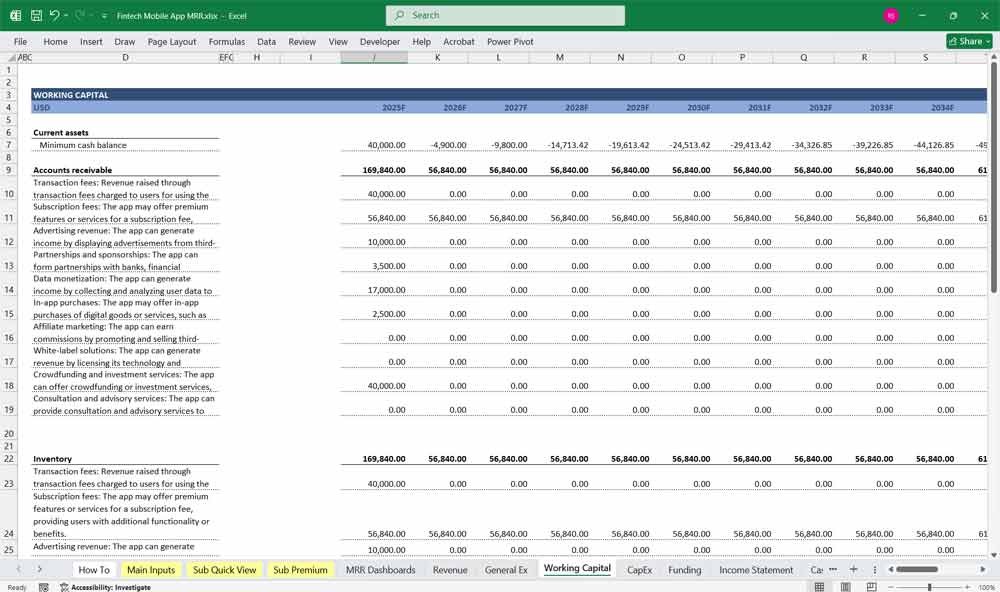
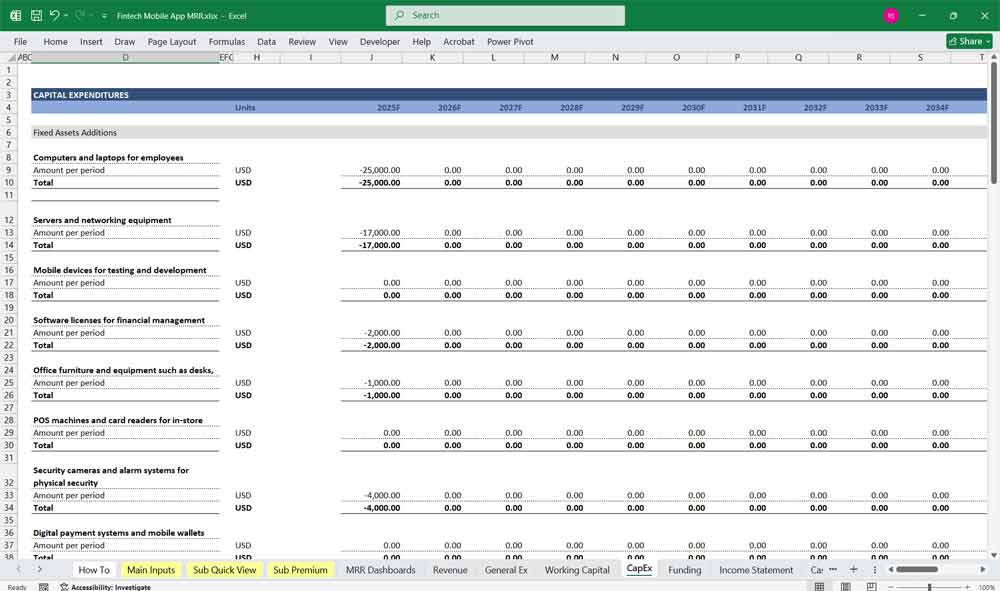
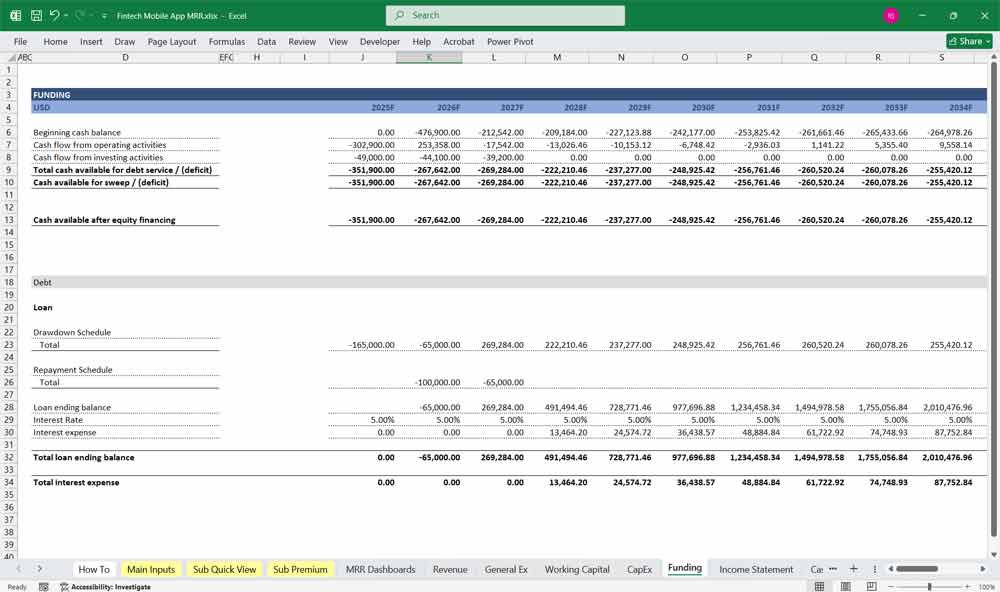
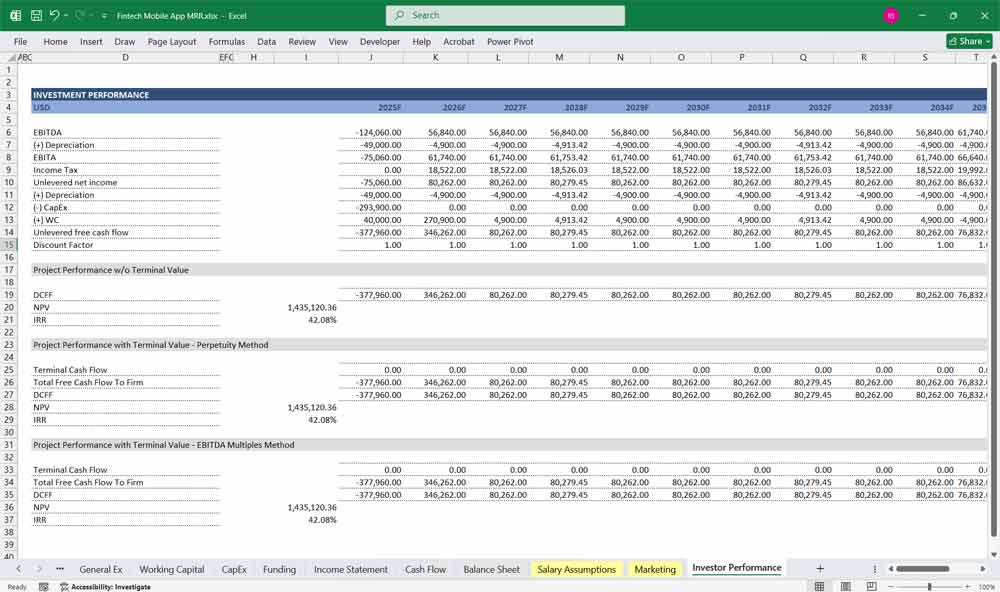
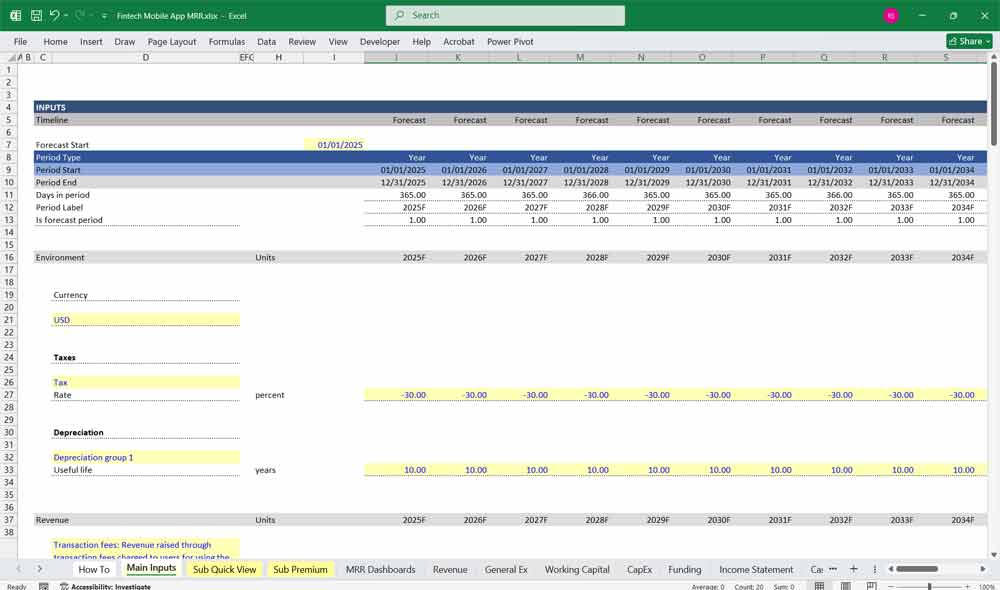
Fintech Key Assumptions and Drivers
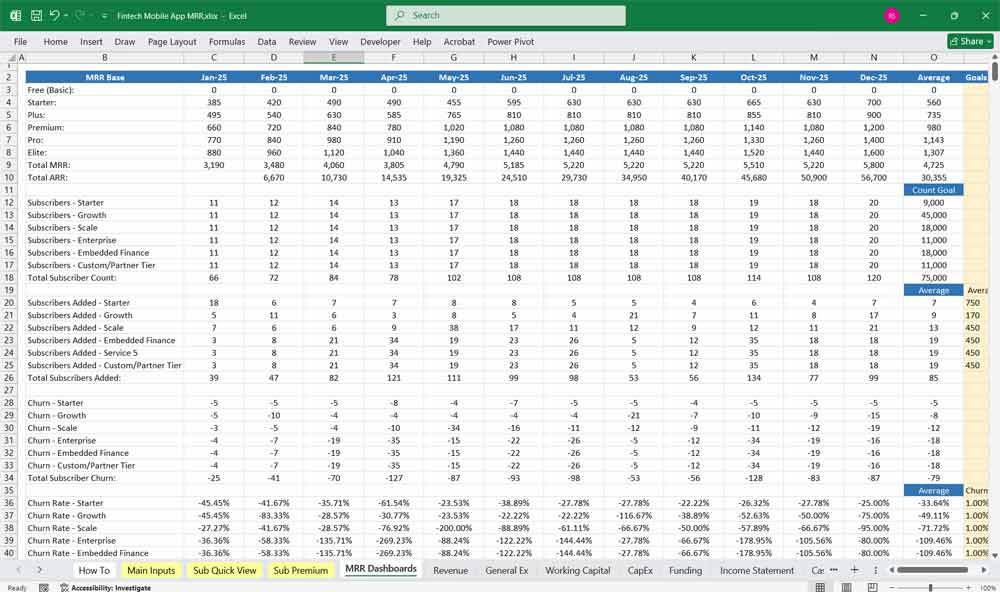
User Growth: Projected number of users and their growth rate.
Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): Revenue generated per user annually.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Cost to acquire a new user.
Churn Rate: Percentage of users who stop using the app.
Operating Leverage: How fixed and variable costs scale with revenue.
Scenario Analysis
Base Case: Realistic assumptions for user growth, revenue, and costs.
Optimistic Case: Higher user growth and revenue, lower costs.
Pessimistic Case: Slower user growth, higher costs, and lower revenue.
Conclusion
This Fintech Mobile App Finance Model must focus on balancing capital expenditures with steady revenue growth from diversified subscription-based services. By optimizing operational costs, and power efficiency, and maximizing high-margin services like higher-tier subscriptions and affiliate offerings, the model ensures sustainable profitability and cash flow stability.
Download Available Immediately After Payment
