Equipment Rental Company Financial Model
This Equipment Rental Company Finance Model in Excel is a comprehensive financial planning tool designed to help business owners, investors, and financial analysts evaluate the financial feasibility and profitability of your Equipment Rental Company over 5 years.
Financial Model for an Equipment Rental Company
1. Revenue Model (Income Streams)
The revenue of an equipment rental company primarily comes from renting out equipment. It may also include additional income sources:
Revenue Components
- Rental Revenue – Fees earned from renting equipment to customers.
- Delivery & Pickup Fees – Charges for transporting equipment to and from customer locations.
- Late Fees & Penalties – Extra charges applied when equipment is not returned on time.
- Maintenance Fees – Charges for wear and tear beyond normal usage.
- Sale of Used Equipment – Revenue from selling old or retired equipment.
- Insurance Charges – Additional fees if the company offers optional rental insurance.
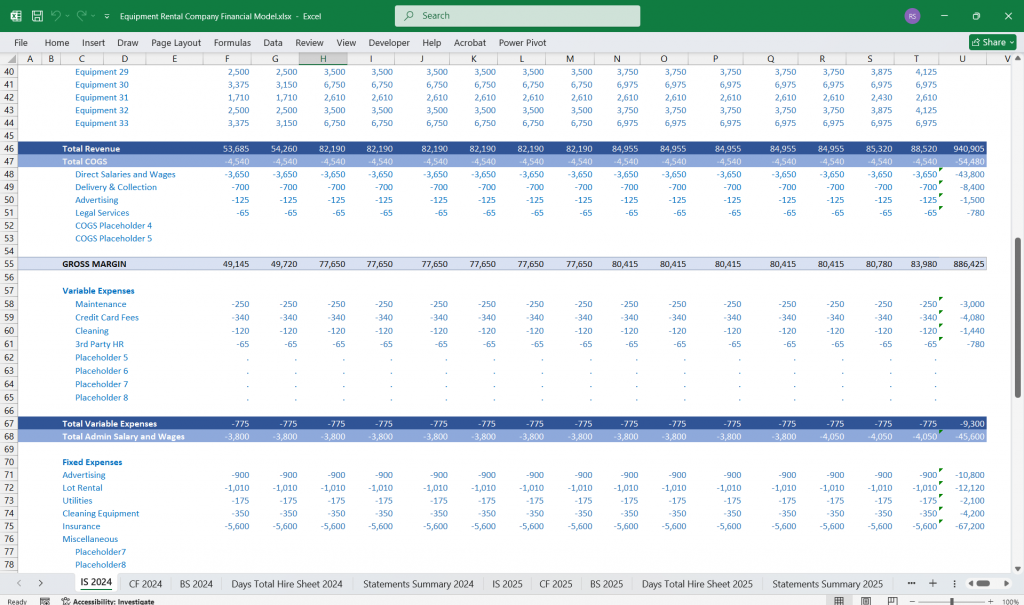
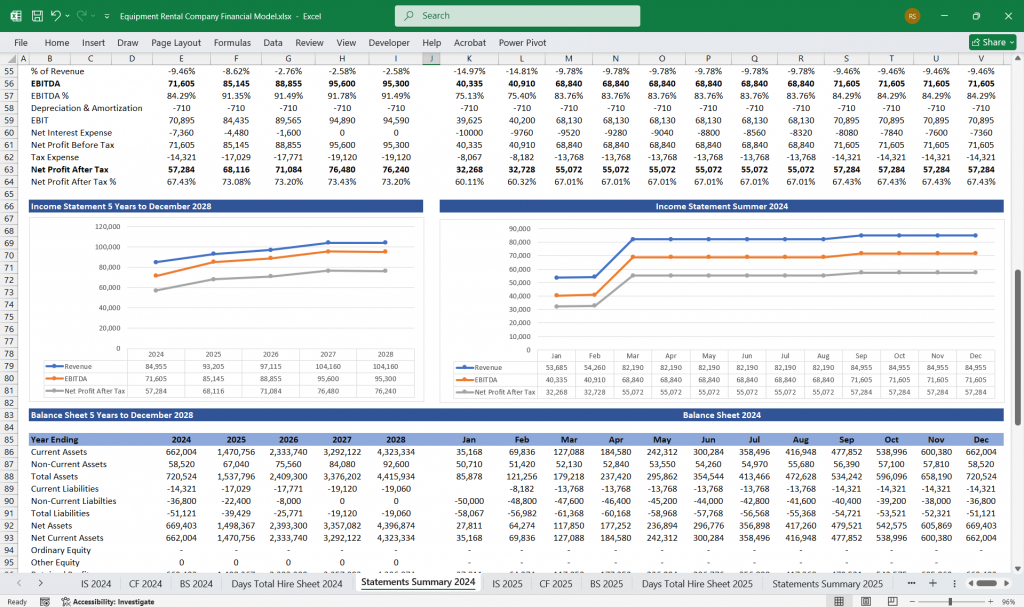
Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
The Income Statement shows profitability over a specific period.
Revenue Section
- Gross Rental Revenue
- Other Income (e.g., delivery, insurance, penalties)
- Total Revenue = Gross Rental Revenue + Other Income
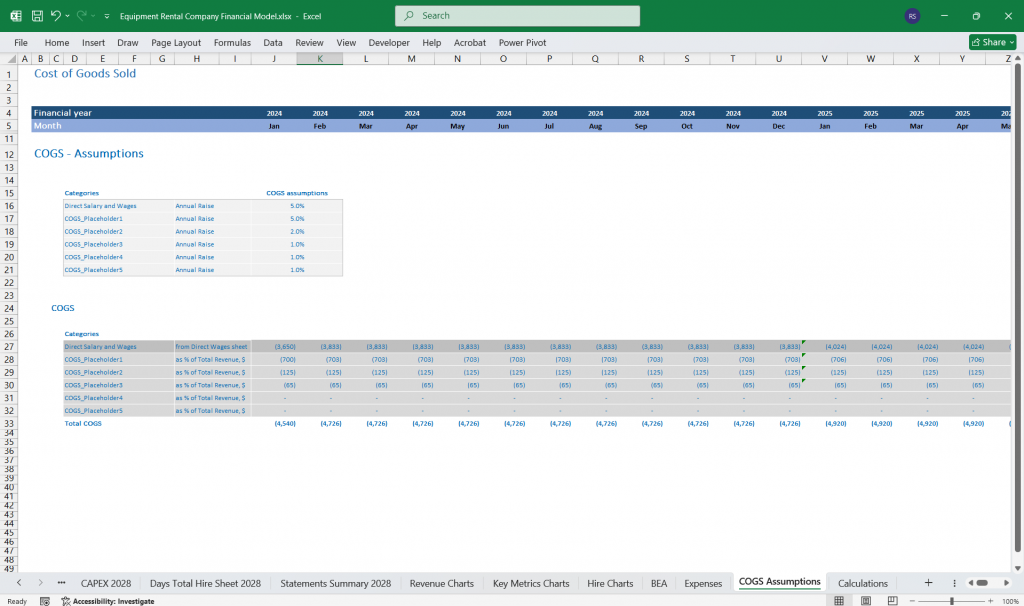
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Depreciation of Rental Equipment (allocated over the useful life)
- Maintenance & Repairs
- Insurance Cost (for owned equipment)
- Total COGS
Gross Profit
- Gross Profit = Total Revenue – Total COGS
Operating Expenses (OPEX)
- Salaries & Wages (staff, mechanics, managers)
- Rent & Utilities (for office, storage yard, warehouse)
- Marketing & Advertising (digital ads, traditional media)
- Administrative Expenses (software, office supplies)
- Transportation Costs (fuel, vehicle maintenance)
- Bad Debt Expense (unpaid rental invoices)
- Licensing & Permits (business compliance costs)
Operating Profit (EBIT)
- EBIT = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Other Expenses
- Interest Expense (if financing equipment with loans)
- Taxes (corporate income tax, property tax)
- Depreciation & Amortization (of office and non-rental assets)
Net Profit
- Net Profit = EBIT – Interest – Taxes
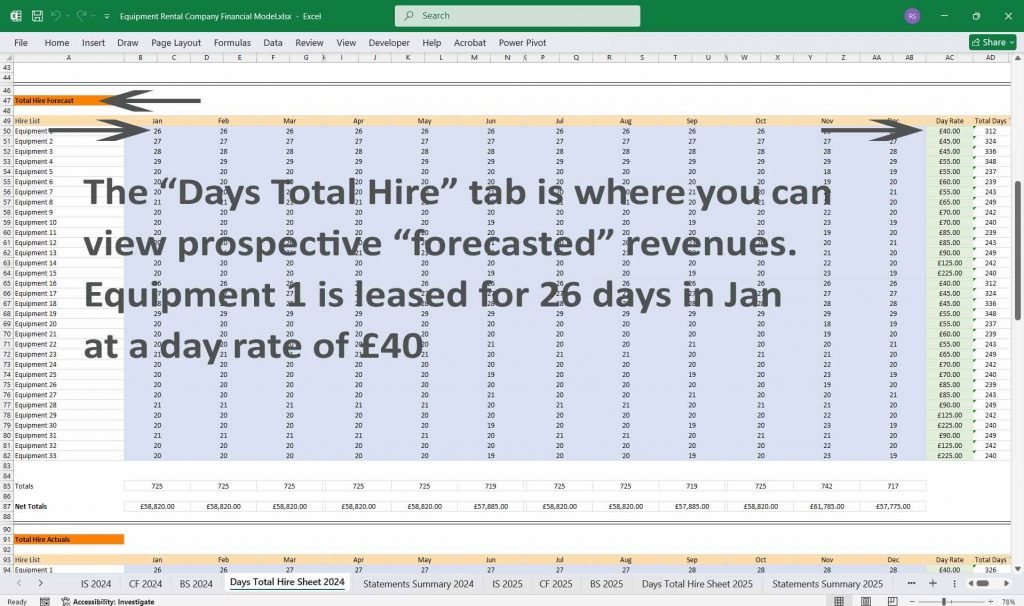
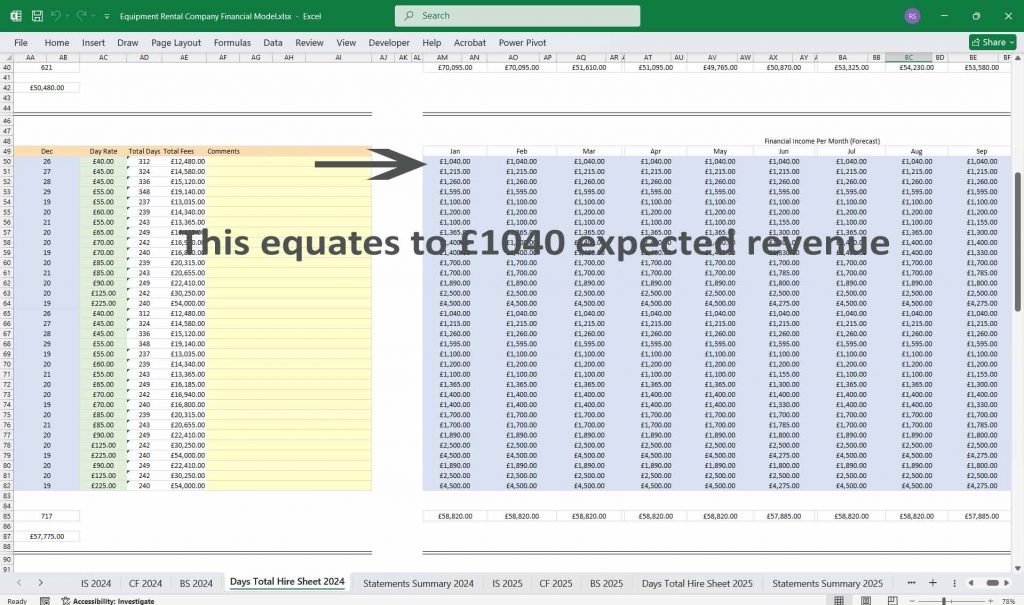
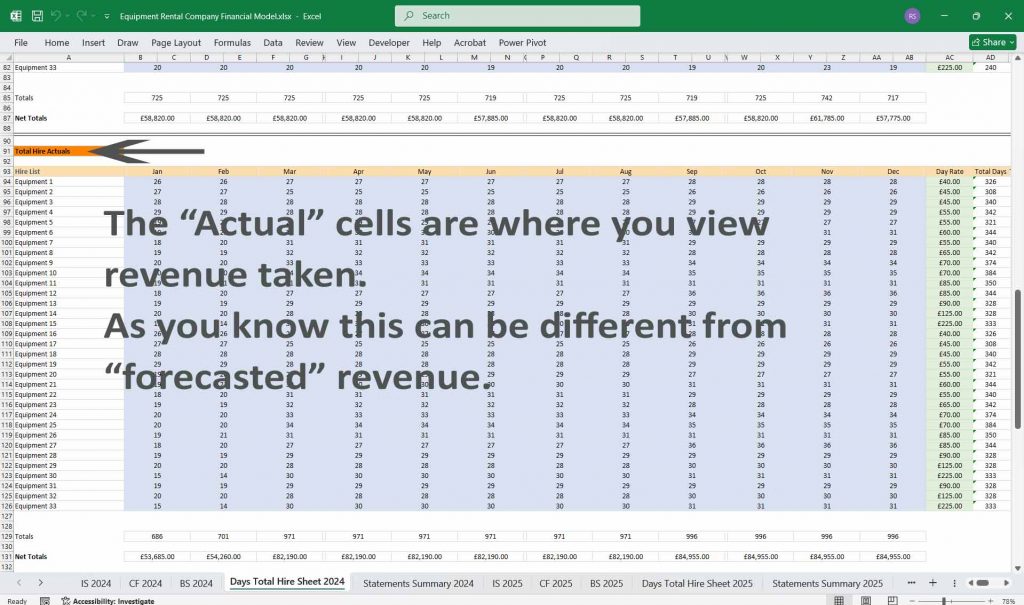

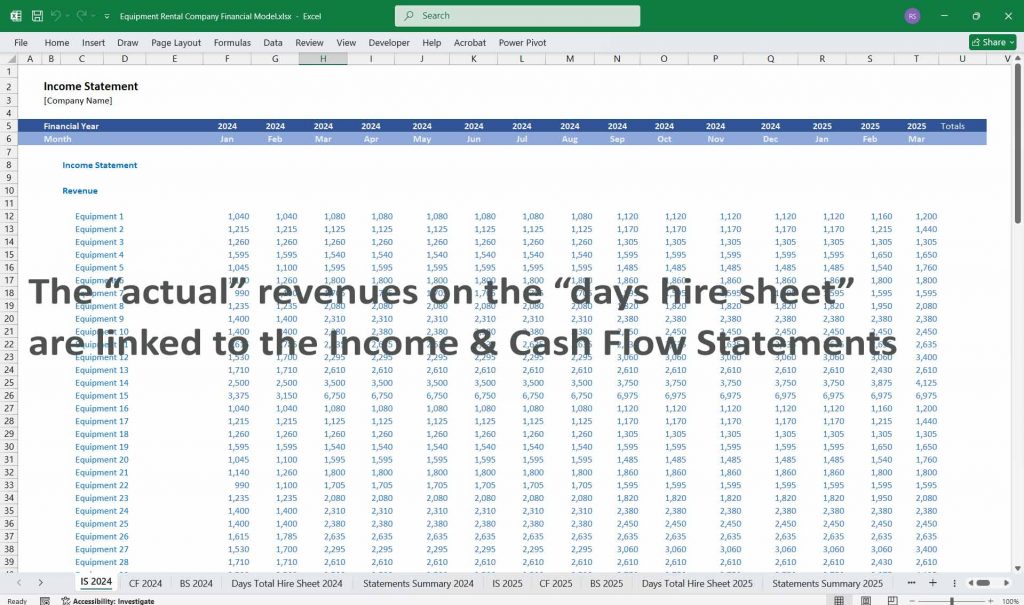
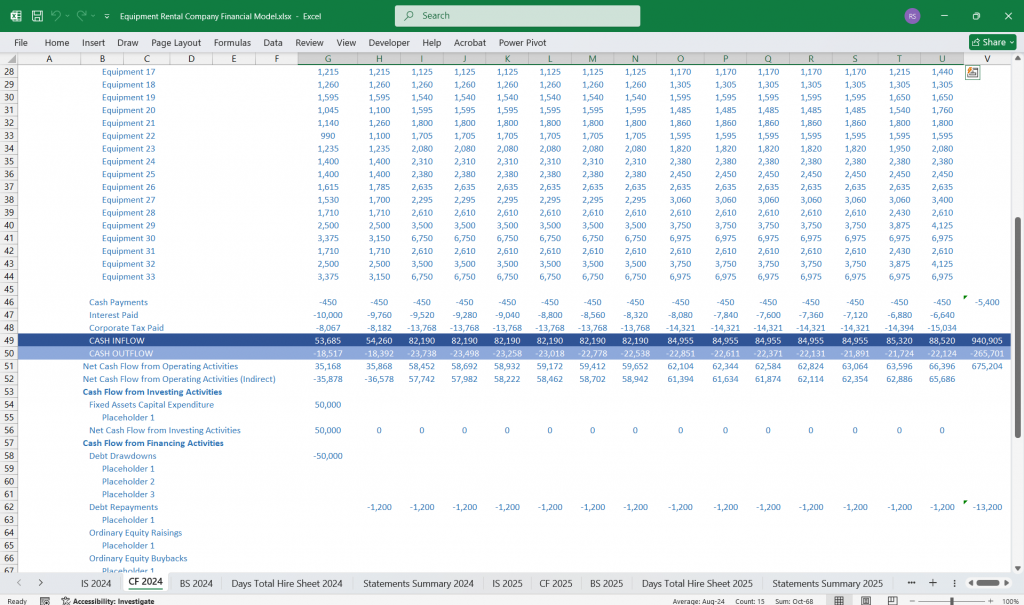
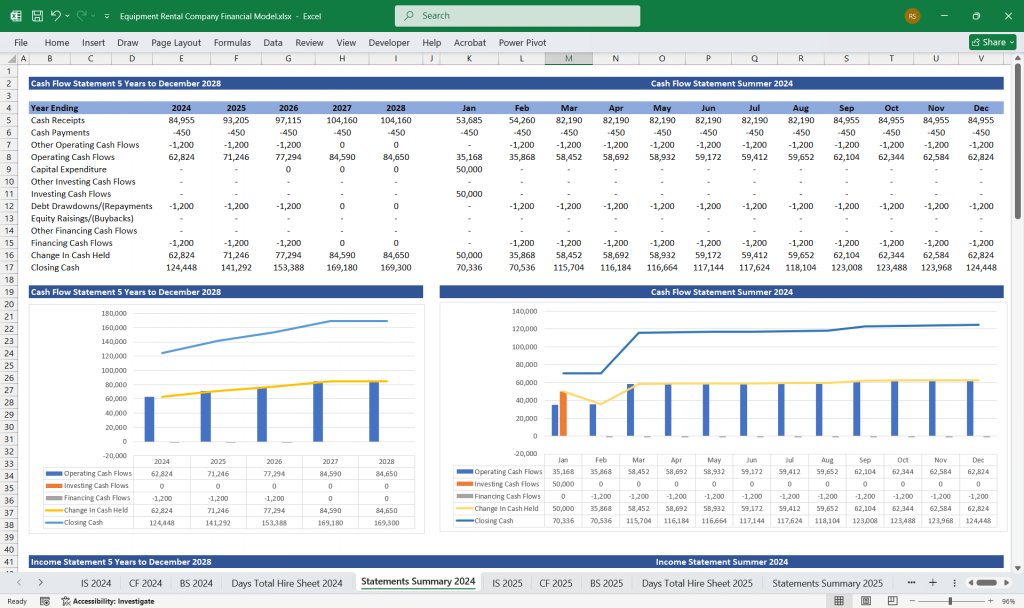
Equipment Rental Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement tracks cash movement and categorizes it into three main activities.
Cash Flow from Equipment Operating Activities
- Inflows:
- Cash Received from Equipment Rentals
- Late Fees and Penalties Collected
- Insurance and Service Fees Collected
- Outflows:
- Employee Salaries & Wages
- Equipment Maintenance & Repairs
- Office Rent, Utilities, and Admin Costs
- Marketing & Advertising Expenses
- Business Taxes Paid
- Net Cash Flow from Operations = Inflows – Outflows
Equipment Cash Flow from Investing Activities
- Inflows:
- Sale of Old Equipment
- Outflows:
- Purchase of New Equipment
- Office & Warehouse Expansion
- Net Cash Flow from Investing = Equipment Sales – Equipment Purchases
Equipment Cash Flow from Financing Activities
- Inflows:
- Loans for Equipment Purchase
- Equity Investment (if raising funds)
- Outflows:
- Loan Repayments (Principal & Interest)
- Dividend Payments
- Net Cash Flow from Financing = Inflows – Outflows
Net Cash Flow
- Net Increase (or Decrease) in Cash = Net Cash from Operations + Investing + Financing
- Ending Cash Balance = Beginning Cash Balance + Net Increase in Cash
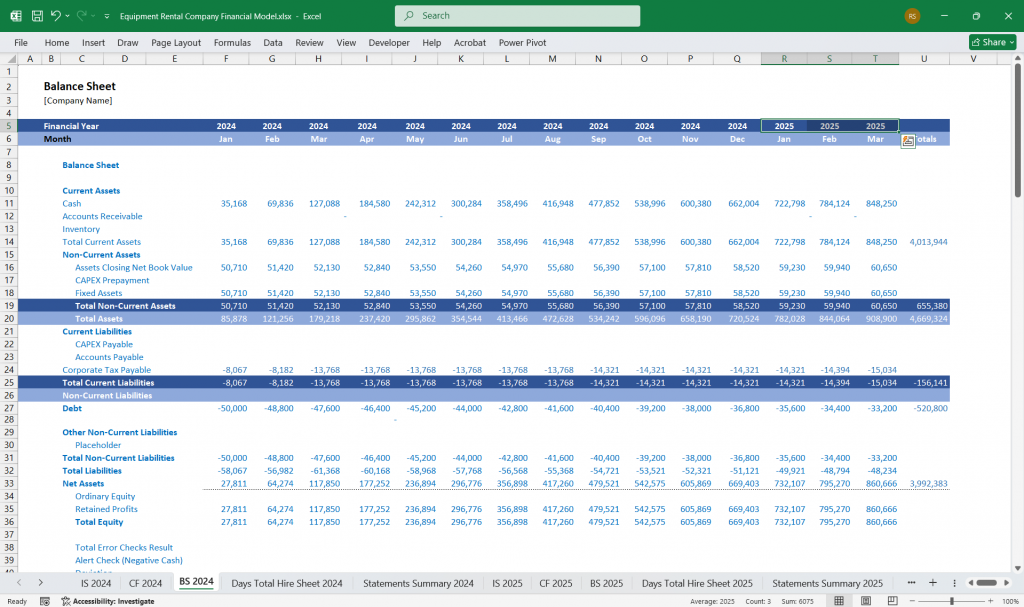
Equipment Rental Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity.
Assets
- Current Assets:
- Cash & Bank Balances
- Accounts Receivable (Outstanding invoices from customers)
- Prepaid Expenses (insurance, rent, utilities)
- Non-Current Assets:
- Rental Equipment (at book value after depreciation)
- Vehicles (for equipment transportation)
- Office & Storage Facilities
- Intangible Assets (brand value, software licenses)
Liabilities
- Current Liabilities:
- Accounts Payable (supplier bills)
- Short-Term Loans or Equipment Financing
- Taxes Payable
- Unearned Revenue (prepaid rentals)
- Long-Term Liabilities:
- Long-Term Loans for Equipment & Property
- Lease Obligations (if renting storage space)
Equity
- Owner’s Equity
- Retained Earnings (accumulated profits)
- Paid-in Capital (if external investors exist)
Balance Sheet Equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
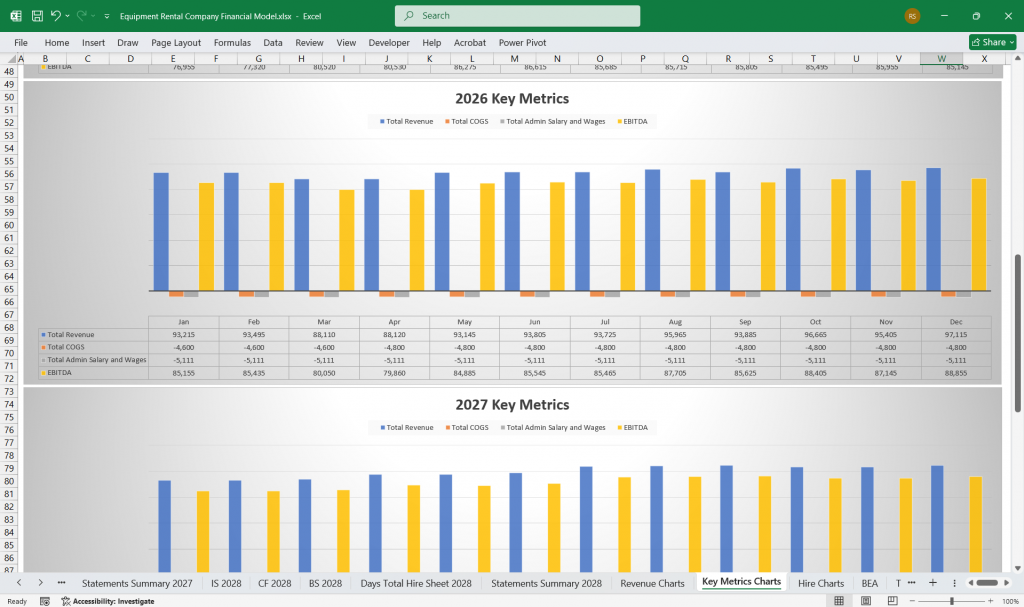
Key Financial Ratios & Metrics for the Financial Model
To assess financial health, the company can track:
- Gross Profit Margin = Gross Profit / Total Revenue
- Net Profit Margin = Net Profit / Total Revenue
- Operating Cash Flow Ratio = Operating Cash Flow / Current Liabilities
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Owner’s Equity
- Return on Assets (ROA) = Net Income / Total Assets


Conclusion
This Equipmnt Rental Company financial model provides a structured approach to managing revenues, expenses, cash flows, and financial stability for an equipment rental company. By tracking financial statements and key metrics, the company can optimize profitability, control costs, and plan for future expansion.
Download Link On Next Page
