CMBS Financial Model Commercial Mortgage Asset-Backed Securities
Excel 20 Year CMBS ABS Securitization Finance Model, Combined Commercial Mortgage and Asset-Backed Securities, covering the Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet. Cost structures, and financial statements to forecast the financial health of your Combined CMBS and ABS funding.
A 20-Year 3-Statement Commercial Mortgage & Asset-Backed Securities (CMBS) Finance Model incorporates interconnected financial statements to evaluate the cash flows, profitability, and investor performance of a commercial mortgage-backed security. Below is a detailed breakdown of the components and sections:
20x Asset Revenue and CMBS Input Tabs, Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, Balance Sheets, CAPEX Sheets, OPEX Sheets, Statement Summary Sheets, and Revenue Forecasting Charts with the specified revenue streams, BEA charts, revenue summary charts, employee salary tabs and expenses sheets.
Real Estate Private Equity Fund Financial Projection Model
CMBS Model Overview
- Purpose: To analyze a 20-year CMBS investment scenario, projecting cash flows, assessing risks, determining profitability, and gauging returns to investors.
- Inputs: Loan structure, property cash flows, market assumptions (interest rates, property values), expenses, and securitization tranche specifications.
- Outputs: Projected income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and investor performance metrics.
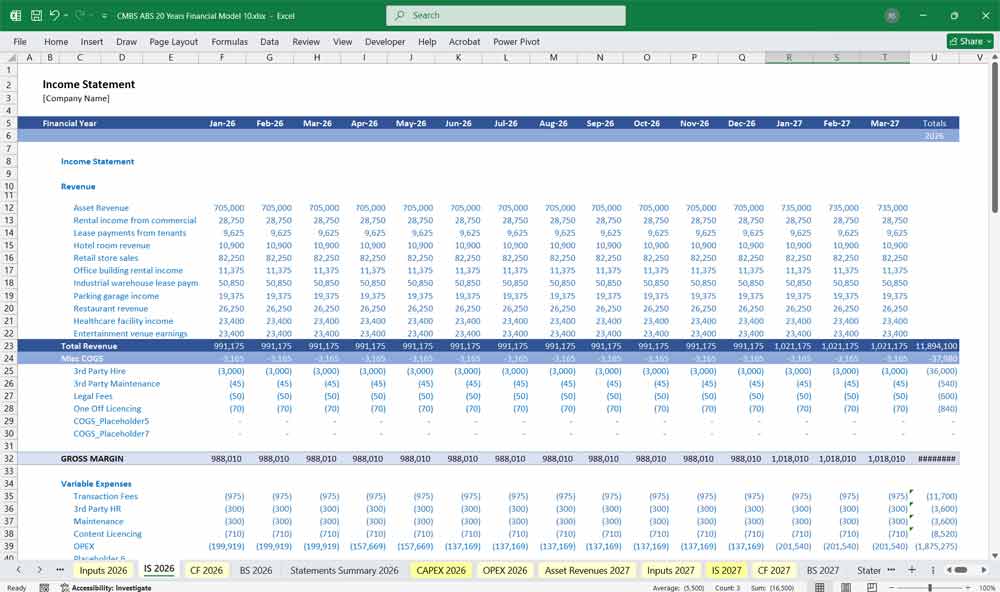
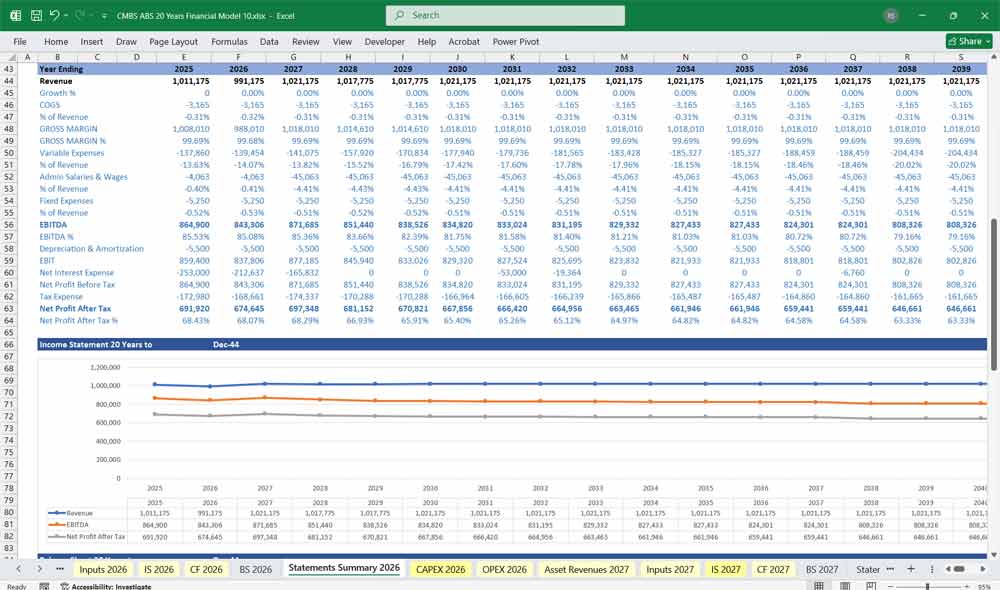
Income Statement
The income statement tracks revenues, costs, and profitability over the 20-year period. Key sections:
Revenue Components:
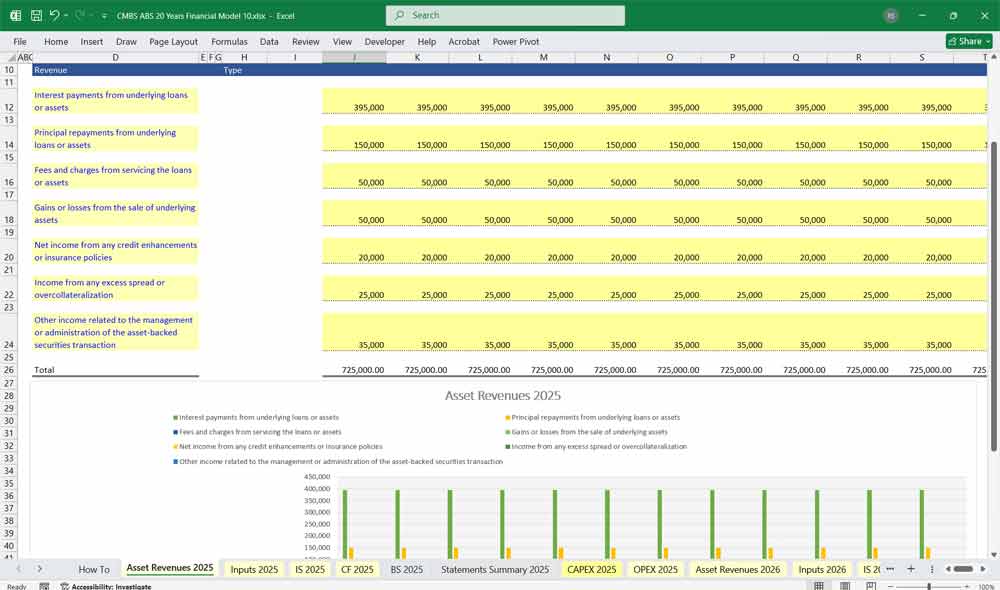
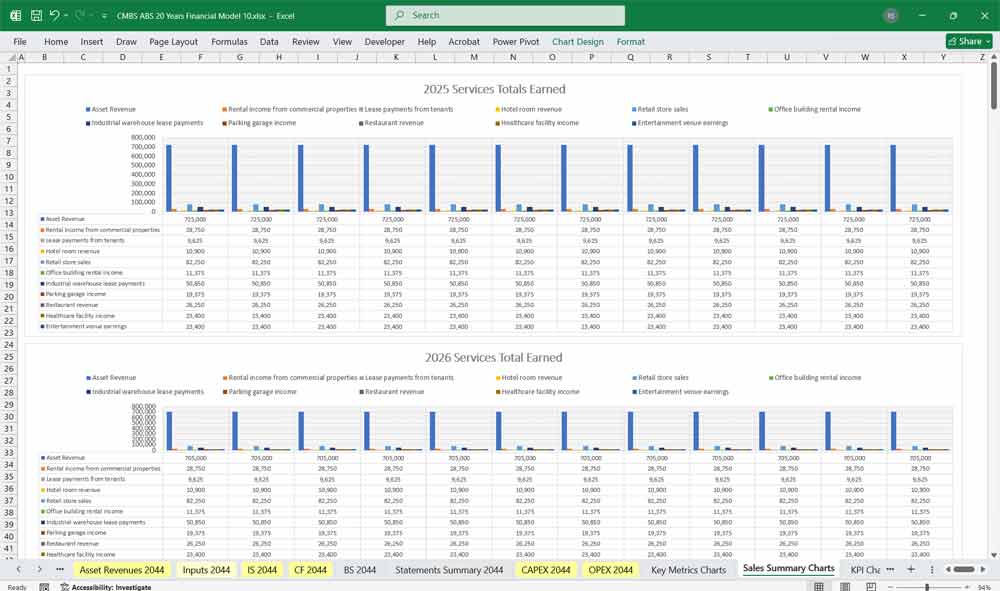
- Asset revenue input examples:
- Interest payments from underlying loans or assets
- Principal repayments from underlying loans or assets
- Fees and charges from servicing the loans or assets
- Gains or losses from the sale of underlying assets
- Net income from any credit enhancements or insurance policies
- Income from any excess spread or overcollateralization
- Other income related to the management or administration of the asset-backed securities transaction
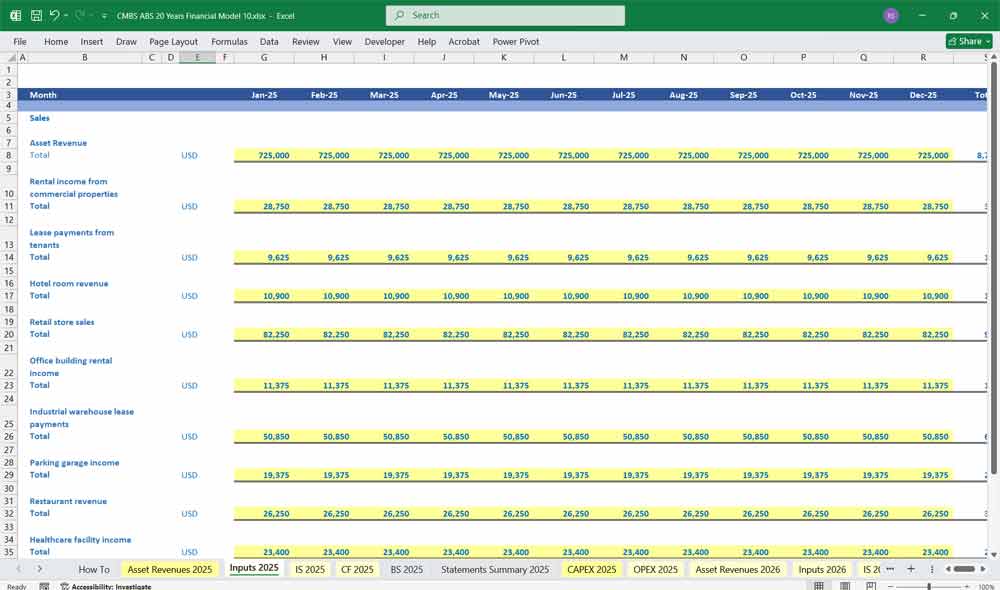
- Commercial Mortgage Input examples:
- Rental income from commercial properties.
- Lease payments from tenants
- Hotel room revenue
- Retail store sales
- Office building rental income
- Industrial warehouse lease payments
- Origination Fee Income: Fees earned from originating mortgages.
- Late Payment/Prepayment Penalties: Assumed based on borrower behaviour and loan covenants.
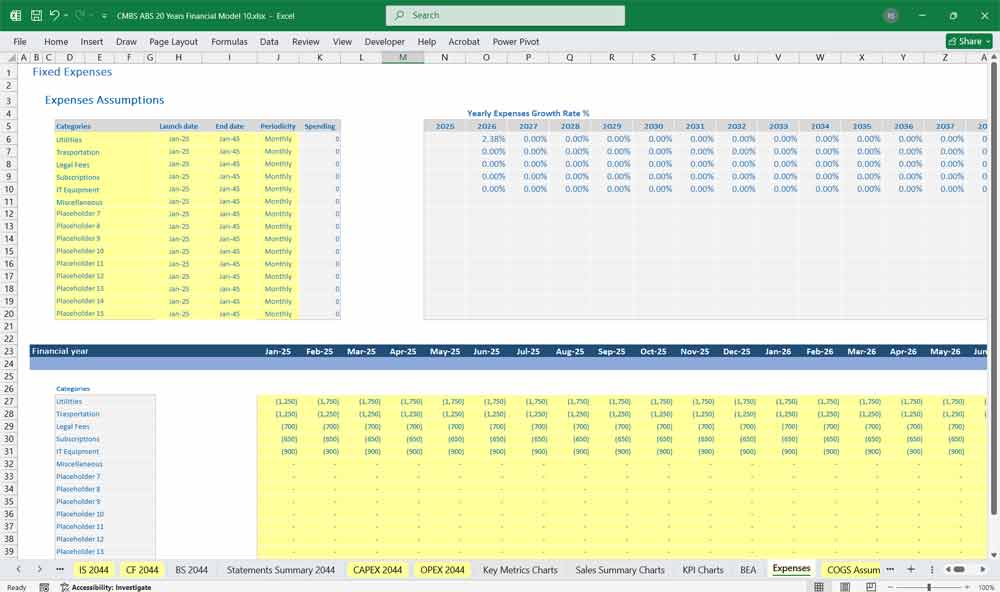
Expenses:
- Loan Servicing Costs: Payment to service mortgage obligations.
- Amortization of Fees and Costs: Spread origination fees and issuance costs over the expected life of the CMBS.
- Credit Loss Provisions: Set aside for expected loan defaults.
- Trust Management Fees: Administrative costs for CMBS trust operations.
Other Income/Expense:
- Hedging Gains/Losses: If interest rate swaps or caps are used.
- Fair Value Adjustments: Revaluation of mortgage pool or securitized assets.
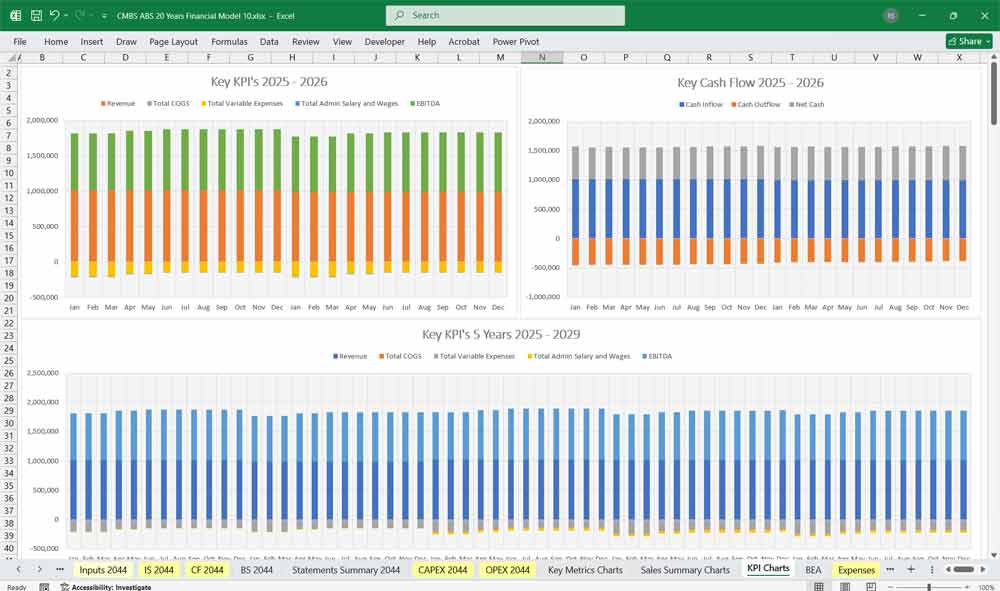
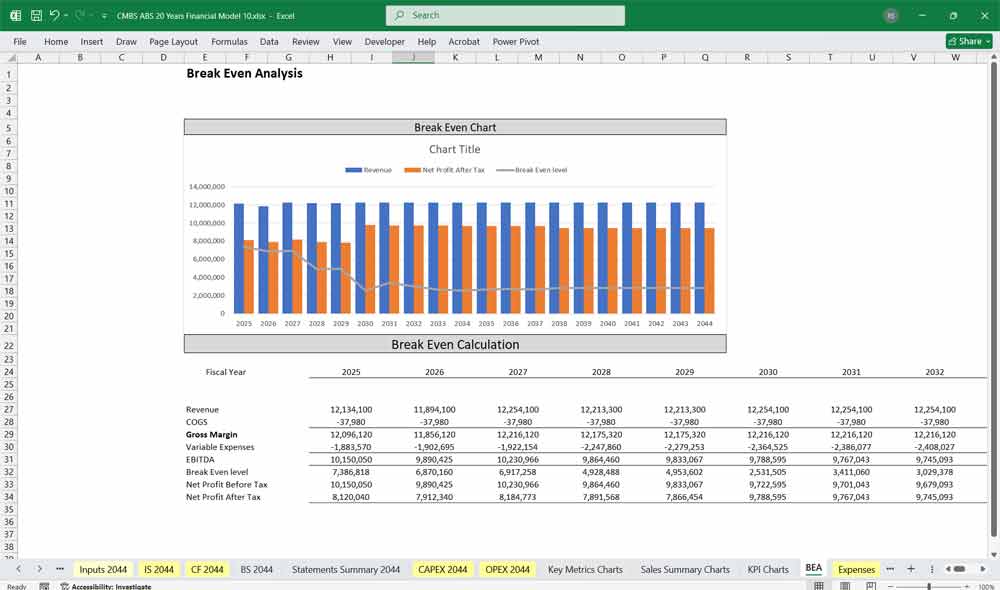
Profitability Metrics:
- Operating Income (EBIT).
- Net Income Before Tax and After Tax.
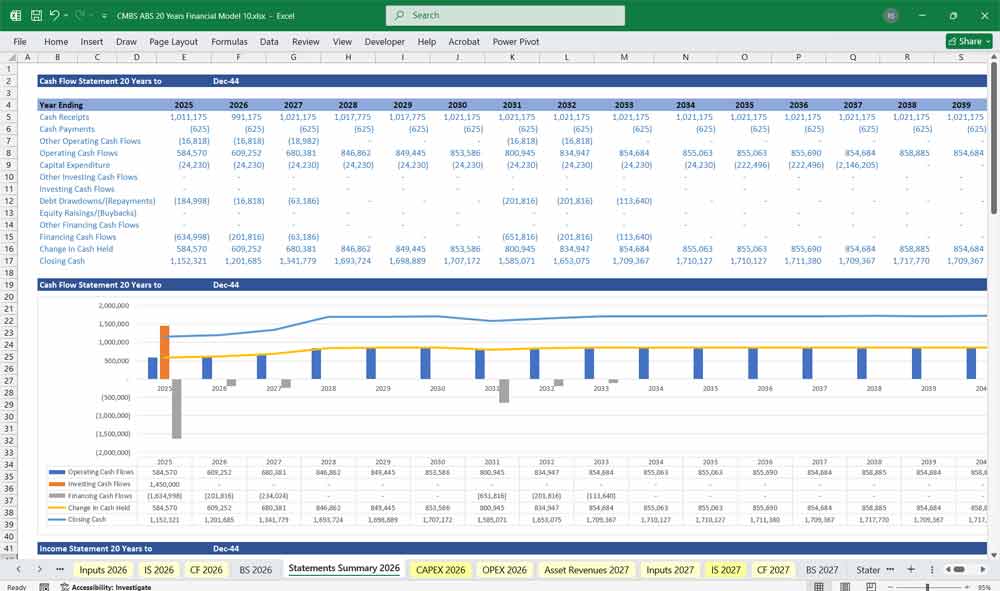
CMBS Cash Flow Statement
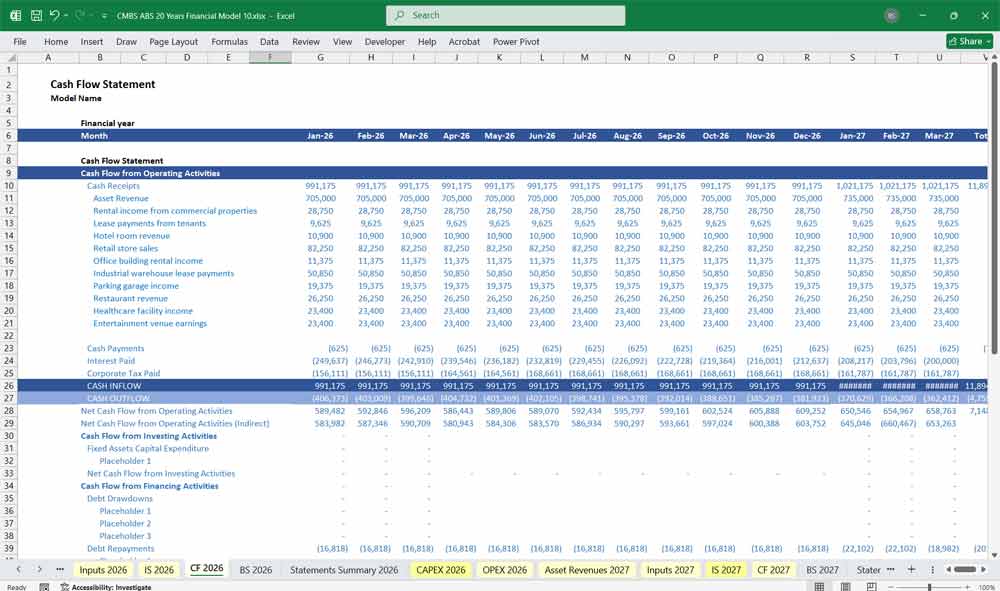
Tracks inflows and outflows to provide insight into liquidity. This model is direct and categorized into three sections:
Operating Cash Flows:
- Cash Inflows: Interest payments, principal repayments, fee income, and penalties.
- Cash Outflows: Operating expenses, servicing costs, credit loss reserves.
- Net Cash Flow: Essential for ensuring cash flow sufficiency to pay bondholders.
Investing Cash Flows:
- Mortgage Origination Costs: Disbursements for mortgage loans.
- Proceeds from Prepayments or Property Sales: Recoveries or gains from early loan repayment or foreclosures.
Financing Cash Flows:
- Securitization Proceeds: Issuance of CMBS tranches.
- Investor Payouts: Interest and principal payments to CMBS holders.
- Debt Service Costs: Repayment of trust debt.
Ending Cash Balances:
- Ensures cash reserve accounts and excess spread reserves are replenished for future coverage.
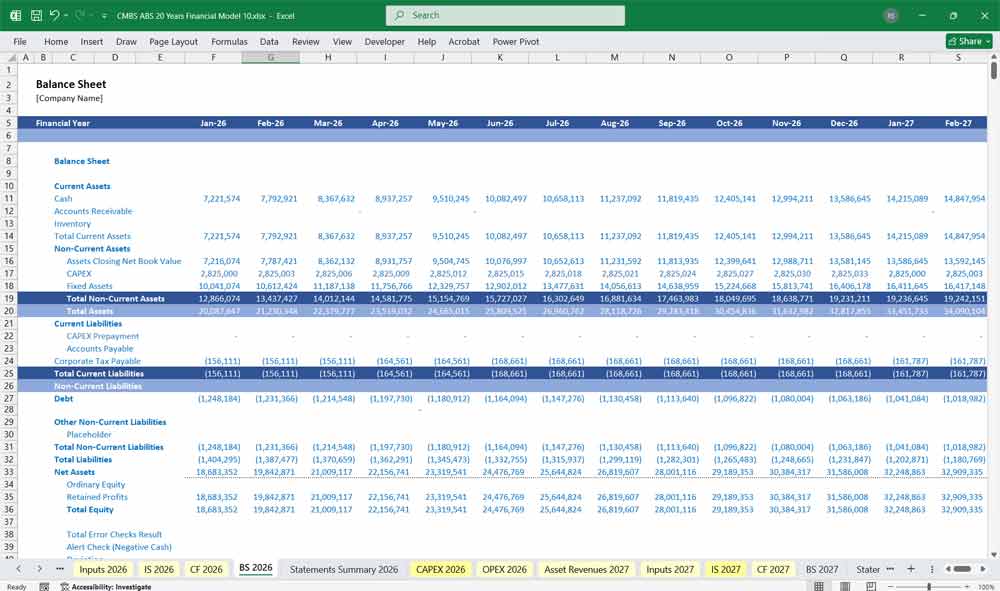
CMBS Balance Sheet
Represents the financial position of the CMBS trust over 20 years.
Assets:
- Mortgage Loan Pool: Value of outstanding principal of loans, adjusted for defaults, repayments, and prepayments.
- Cash Reserves: Trust reserves for contingencies, interest coverage, and credit enhancement.
- Other Assets: Accrued interest receivable, property collateral value (for defaulted loans).
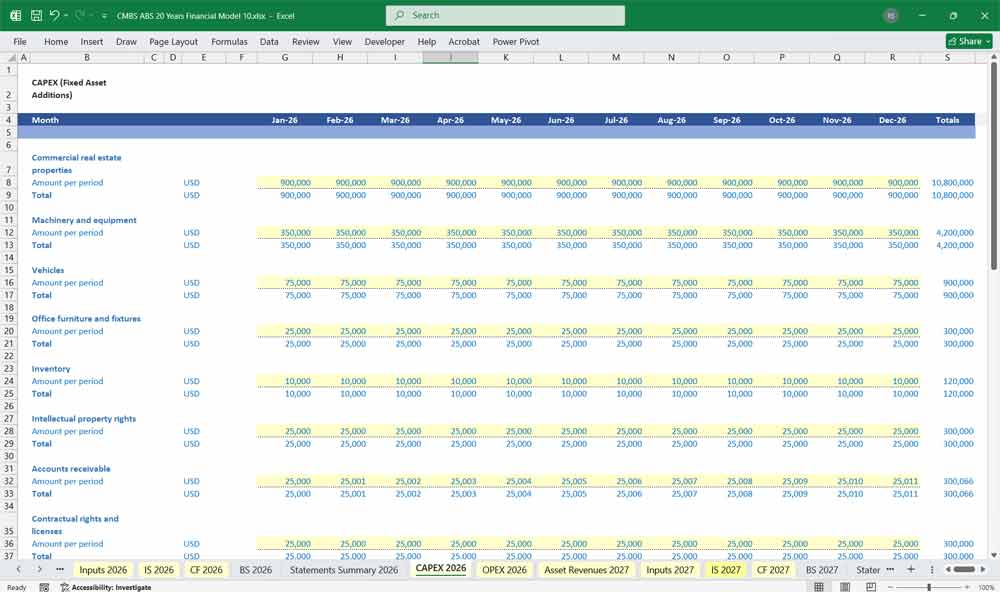
CAPEX examples x20 :
- Commercial real estate properties.
- Machinery and equipment.
- Office furniture and fixtures.
- Intellectual property rights.
- Contractual rights and licenses.
- Aircraft and watercraft.
- Mineral rights and natural resources.
- Retail properties.
- Industrial warehouses.
- Multifamily apartment buildings.
Liabilities:
- Securitized Debt: CMBS tranches, with breakdown by seniority and payment priority (A, B, mezzanine, etc.).
- Accrued Expenses: Outstanding trust costs or management fees.
- Credit Loss Reserves: Accounted separately under liabilities.
Equity:
- Excess Spread/Residual: Accumulated trust income after paying liabilities.
- Unrealized Gains/Losses: Value changes in mortgage pool or hedging instruments.
CMBS Investor Performance
Focuses on return metrics for CMBS investors.
Key Metrics:
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): Determines profitability for different CMBS tranches.
- Net Present Value (NPV): Discounted cash flow analysis for tranche cash flows.
- Weighted Average Life (WAL): Duration analysis for cash flows to tranches.
- Loss Coverage Ratio: Measures extent of subordination protection for senior tranches.
- Yield to Maturity (YTM): Reflects returns based on holding to maturity.
Stress Testing:
- Default Scenarios: Assess impact on investor payouts.
- Prepayment Scenarios: Measure yield variability with faster or slower prepayments.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Gauge how rising/falling rates influence tranche performance.
Equity Holders Analysis:
- Residual Cash Flow Distributions: Surplus after debt servicing.
- Profit Distribution Timing: Dictates payout sequencing.
Final Notes on the 20 Year Financial Model Integration
- Interdependencies: Cash flow projections directly influence the income statement and balance sheet through interest income, reserves, and tranche payments.
- Scenario Analysis: Embedded functionality to test various market assumptions like property value depreciation, default rates, and interest rate spikes.
- Investor Reporting: Schedules for interest/principal payouts and performance updates tailored to tranche types.
Combined CMBS ABS Finance Model
This structured model helps CMBS and ABS Investors have a broad market spectrum, offering the right balance between cost, and investment support.
Download Link On Next Page
