Virtualization Software Financial Model
This 10-Year, 3-Statement Virtualization Software Financial Model in Excel includes revenue streams from PAYG project-based services and subscriptions, to one-time set-up fees and consulting. Financial statements to forecast the financial health of your Virtualization business.
Financial Model for a Virtualization Company
These financial models for a virtualization software company includes projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability based on various revenue streams. The key financial statements in the model include:
- Income Statement (Profit & Loss)
- Cash Flow Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Subscription Model Assumptions (6-tier pricing model)
There are 2 Versions of this Excel Template: Both are 10-Year 3 Statement.
Version 1: Financial model with 5 project-based PAYG revenue streams, and reporting of your financials.
Version 2: 6 Tier Subscription and 5 PAYG streams. ‘Managed Service Agreements’. Build your MSA book as quickly as possible.
You would typically sell your services at tiered 12-month agreements that increase in price as SLAs (Service Level Agreement) and monthly consulting hours scale upwards.
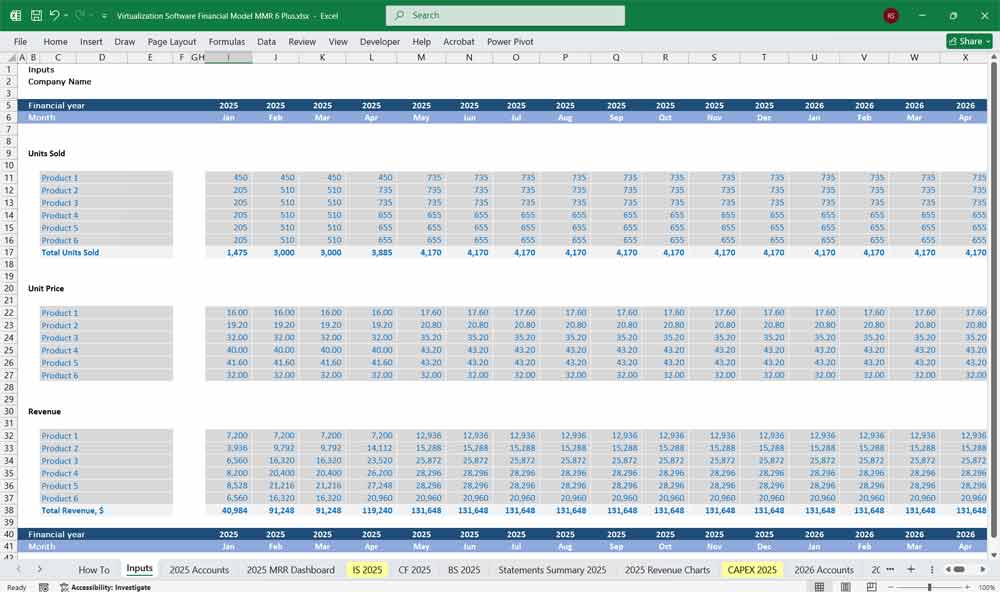
Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
The Income Statement reflects the company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period.
Revenue Streams:
Software License Sales
One-time license fees for perpetual software use.
Subscription Revenue
Monthly/annual SaaS subscriptions for cloud-based virtualization services.
Enterprise Licensing
Bulk licenses for corporations at discounted rates.
Professional Services
Implementation, customization, and consulting fees.
Support & Maintenance
Recurring revenue from customer support and software updates.
Partner & Reseller Revenue
Revenue from strategic alliances, channel partners, and resellers.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):
Hosting Costs
Cloud infrastructure, data centers, and server maintenance.
Software Development & Licensing Fees
Costs associated with third-party software, APIs, and libraries.
Technical Support Expenses
Customer service, troubleshooting, and help desk staffing costs.
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
Operating Expenses:
Research & Development (R&D)
Salaries of software engineers, developers, and testers.
Investment in new features, bug fixes, and security enhancements.
Sales & Marketing (S&M)
Advertising, branding, customer acquisition costs.
Sales team salaries and commissions.
General & Administrative (G&A)
Executive salaries, office rent, utilities, legal, and compliance costs.
Operating Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Other Income & Expenses:
Interest Income/Expense
Interest on loans or investments.
Depreciation & Amortization
Cost allocation for software development and capitalized assets.
Taxes
Corporate tax obligations based on net profit.
Net Profit = Operating Profit – Other Expenses – Taxes
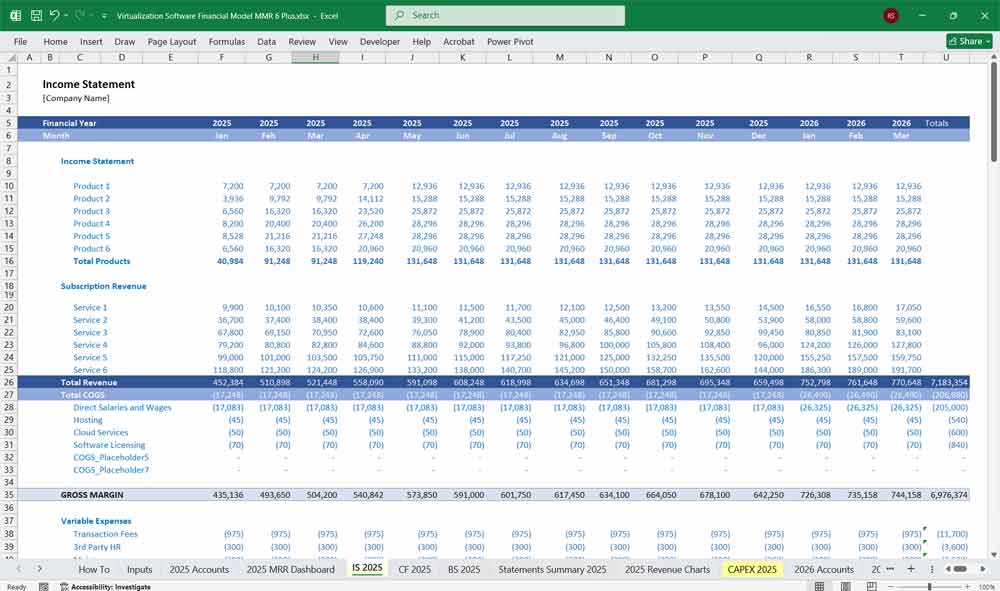
Virtualization Software Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of the business.
Operating Cash Flow:
Net Income (from the Income Statement)
Adjustments for Non-Cash Items:
Depreciation & Amortization
Stock-based compensation
Changes in deferred revenue
Changes in Working Capital:
Accounts Receivable (Cash outflow if increasing)
Accounts Payable (Cash inflow if increasing)
Prepaid Expenses (Cash outflow if increasing)
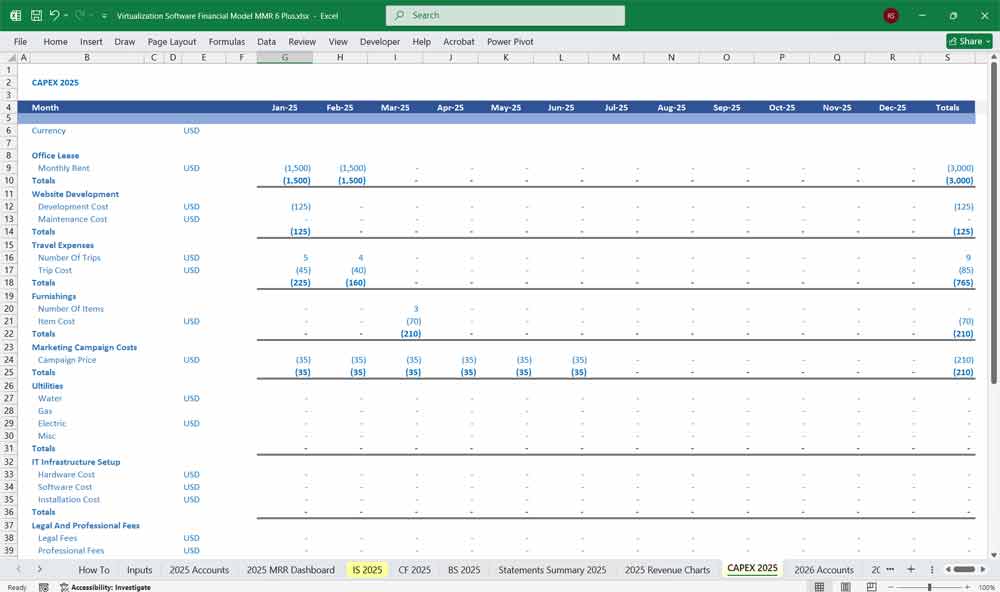
Investing Cash Flow:
Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
Investments in software development, data centers, and R&D.
Acquisitions & Investments
Purchase of other companies or technology assets.
Sale of Assets
Disposal of unused office equipment or old servers.
Financing Cash Flow:
Equity Financing
Cash from issuing new shares to investors.
Debt Financing
Loans or lines of credit from banks or venture capital firms.
Dividend Payments
Cash outflows if dividends are paid to shareholders.
Net Cash Flow = Operating Cash Flow + Investing Cash Flow + Financing Cash Flow
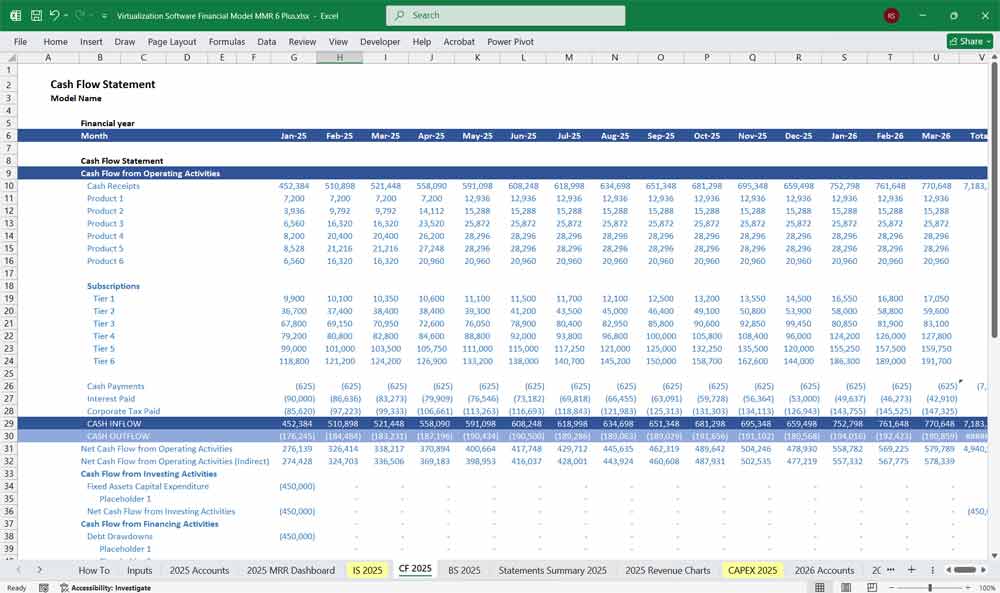
Virtualization Software Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet presents the financial position of the company at a given point in time.
Assets:
Current Assets
Cash & Cash Equivalents: Bank balances, short-term investments.
Accounts Receivable: Outstanding payments from customers.
Prepaid Expenses: Advance payments for software tools, marketing, etc.
Non-Current Assets
Property, Plant & Equipment (PP&E): Servers, data centers, office space.
Intangible Assets: Patents, trademarks, and capitalized software development costs.
Liabilities:
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable: Payments due to vendors and service providers.
Deferred Revenue: Subscription revenue collected in advance.
Short-Term Debt: Credit lines or loans due within a year.
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-Term Debt: Loans or bonds with maturities beyond one year.
Lease Obligations: Office or data center leases.
Shareholders’ Equity:
Common Stock & Paid-in Capital
Retained Earnings (Cumulative net income reinvested in the business)
Balance Sheet Formula:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
Example 6-Tier Subscription Model for a Virtualization Software Company
A Well-structured subscription pricing Model is crucial to help cater to different customer segments—from individual developers to large enterprises. Below is a detailed 6-tier subscription model, including features, pricing, target customers, and key differentiators.
1. Free Tier (Basic) – “Starter Virtualization”
Target Audience: Individual developers, students, small businesses testing virtualization.
Price: $0 (Freemium)
Key Features:
Basic hypervisor functionality (limited to 2 VMs)
4GB RAM & 2 vCPU per VM
Community support only (no SLA)
No high availability (HA) or live migration
Local storage only (no shared storage)
Basic monitoring & logging
Monetization Strategy:
Upsell to paid tiers
Collect user data for product improvement
Build brand loyalty
2. Developer Tier – “Pro Virtualization”
Target Audience: Freelancers, small dev teams, startups.
Price: 29/month(or29/month(or249/year, ~30% discount)
Key Features:
Up to 5 VMs
8GB RAM & 4 vCPU per VM
Basic snapshots & backups
API access for automation
Email support (24-48hr response)
Limited cloud integration (AWS/Azure)
Differentiator:
Affordable for small teams
Better than open-source alternatives (easier management)
3. Business Tier – “Standard Virtualization”
Target Audience: SMBs, mid-sized companies, IT departments.
Price: 99/month(or99/month(or999/year, ~15% discount)
Key Features:
Up to 20 VMs
16GB RAM & 8 vCPU per VM
High availability (HA) for critical VMs
Live migration between hosts
Centralized management dashboard
Priority support (12-24hr response)
Basic security & compliance (RBAC, encryption)
Differentiator:
Balances cost & advanced features
Ideal for growing businesses
4. Enterprise Tier – “Advanced Virtualization”
Target Audience: Large enterprises, MSPs, government agencies.
Price: 499/month(or499/month(or4,999/year, ~15% discount)
Key Features:
Unlimited VMs (with fair usage policy)
32GB RAM & 16 vCPU per VM
Full high availability & disaster recovery
Automated scaling & load balancing
Advanced security (SIEM integration, audit logs)
24/7 premium support (SLA-backed, <4hr response)
Multi-cloud & hybrid cloud support
Differentiator:
Fully scalable for mission-critical workloads
Compliance-ready (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2)
5. Cloud Provider Tier – “Elite Virtualization”
Target Audience: Cloud providers, hyperscalers, large data centers.
Price: Custom pricing (volume-based, $10K+/month)
Key Features:
Bare-metal performance with nested virtualization
Multi-tenant isolation
White-labeling & branding options
API-first architecture for automation
Dedicated account manager & engineering support
Custom SLAs (99.99% uptime guaranteed)
Differentiator:
Built for B2B resellers & cloud platforms
Fully customizable for large-scale deployments
6. Ultra-Tier – “Platinum Virtualization” (Custom Enterprise Solution)
Target Audience: Fortune 500, financial institutions, defense sectors.
Price: $50K+/month (negotiable, multi-year contracts)
Key Features:
Fully dedicated infrastructure (private cloud)
On-premises & air-gapped deployments
Military-grade security (FIPS 140-2, FedRAMP)
Custom feature development (tailored to needs)
Dedicated security & compliance team
Global 24/7 support with on-site engineers
Differentiator:
Highest security & compliance standards
Fully bespoke solution
Key Pricing Strategies Across Tiers
Annual vs. Monthly Discounts (Encourage long-term commitments)
Volume Discounts (For large deployments)
Add-ons (Backup, premium support, training)
Trial-to-Paid Conversion (Free tier → Pro/Enterprise)
Usage-Based Upselling (Auto-scale features)
This 6-tier subscription model ensures that the virtualization software company can serve every market segment—from hobbyists to global enterprises—while maximizing revenue through upselling, customization, and premium support.
Key Financial Metrics to Track
Gross Margin (%) = (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue
Operating Margin (%) = Operating Profit / Revenue
Net Profit Margin (%) = Net Profit / Revenue
ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) = Subscription Revenue x 12
Churn Rate (%) = Customers Lost / Total Customers
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) = Sales & Marketing Costs / New Customers
LTV (Lifetime Value) = Average Revenue per Customer x Customer Lifetime
Burn Rate = Monthly Cash Outflows – Monthly Revenues
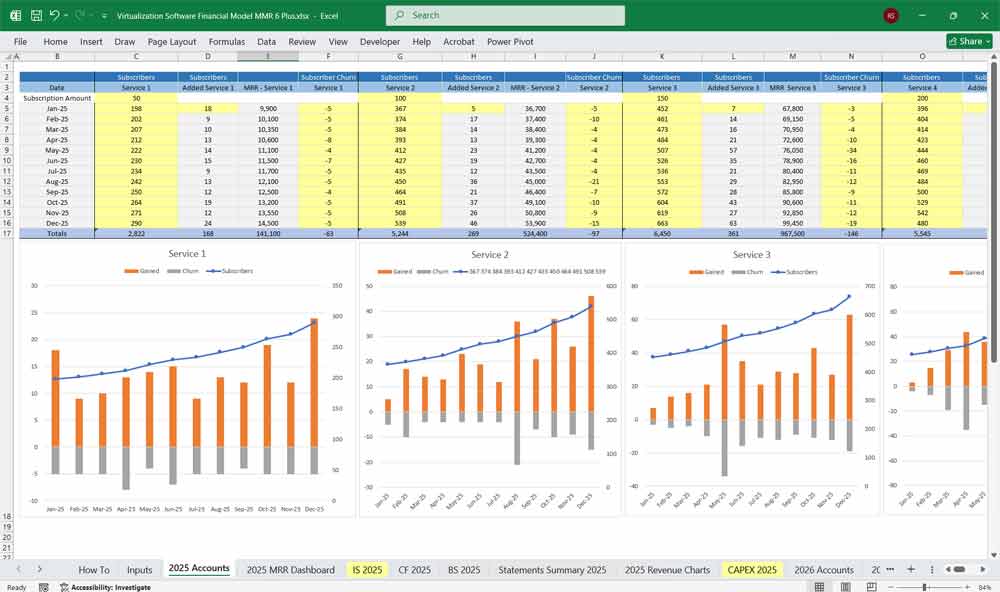
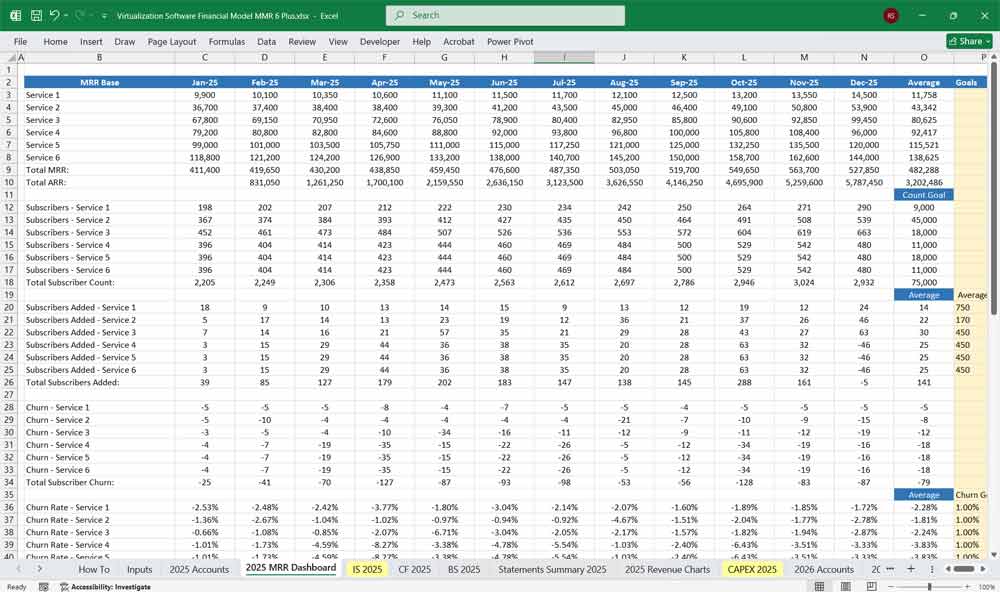
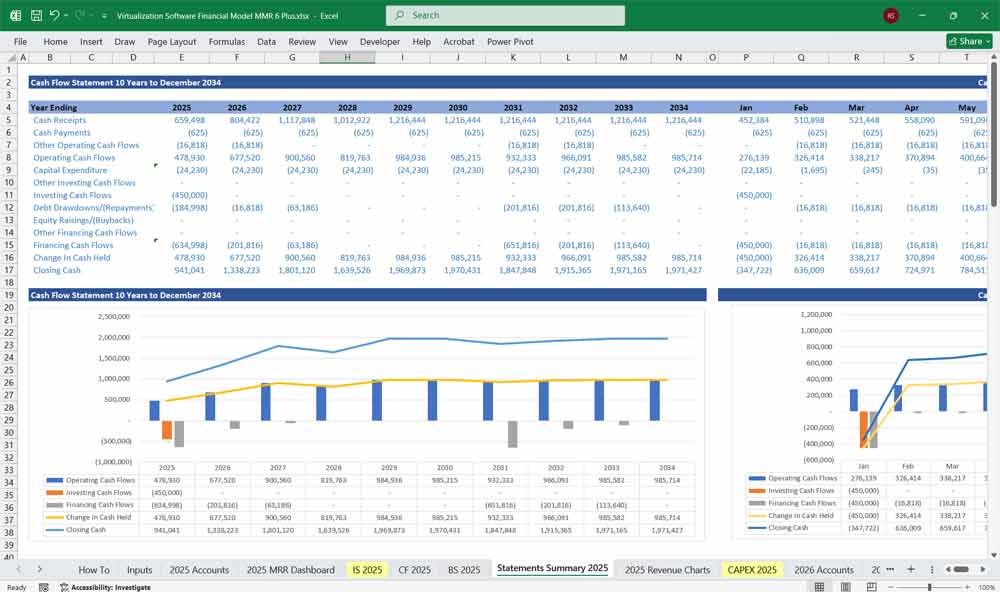
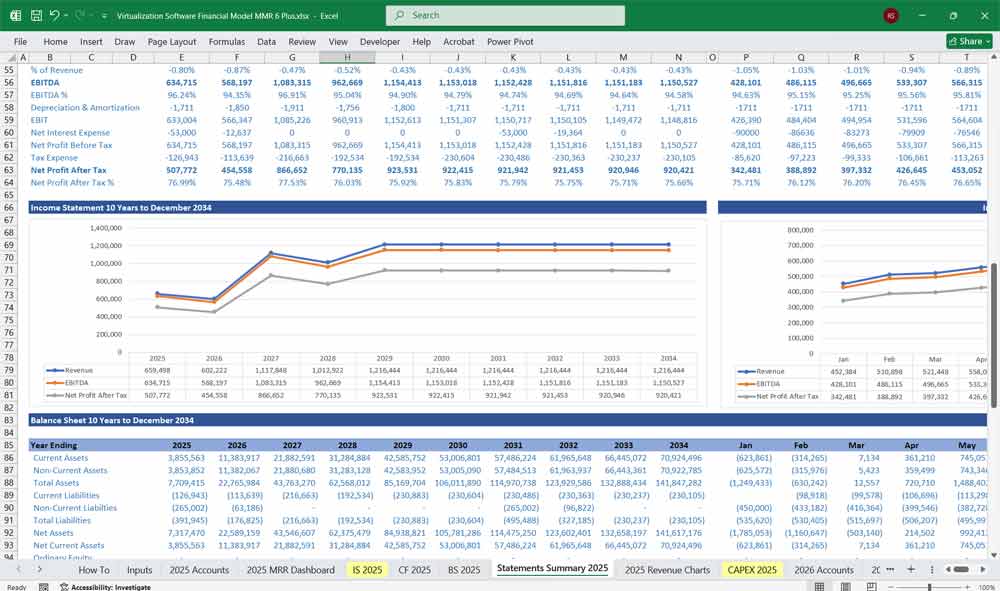
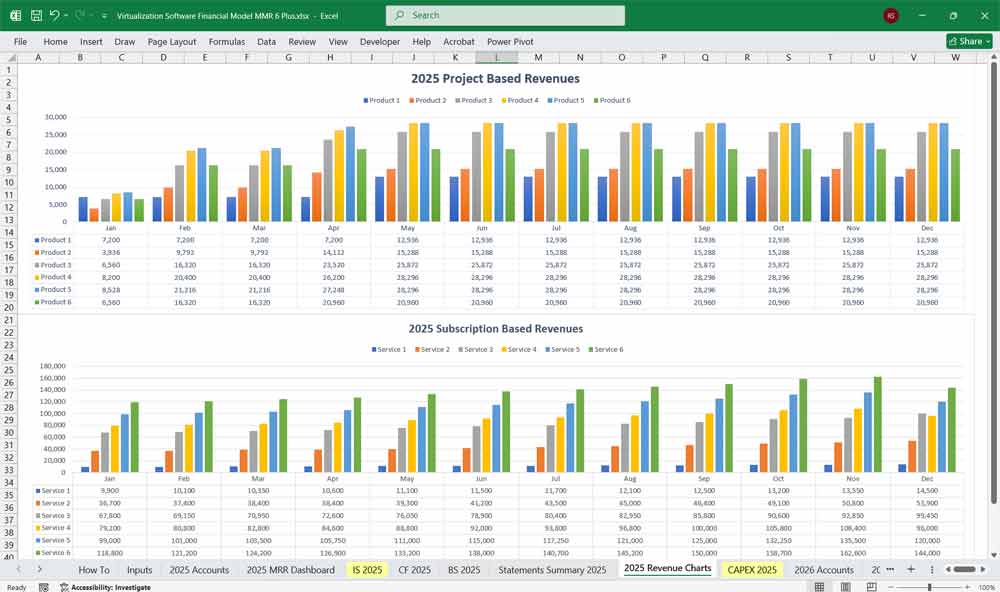
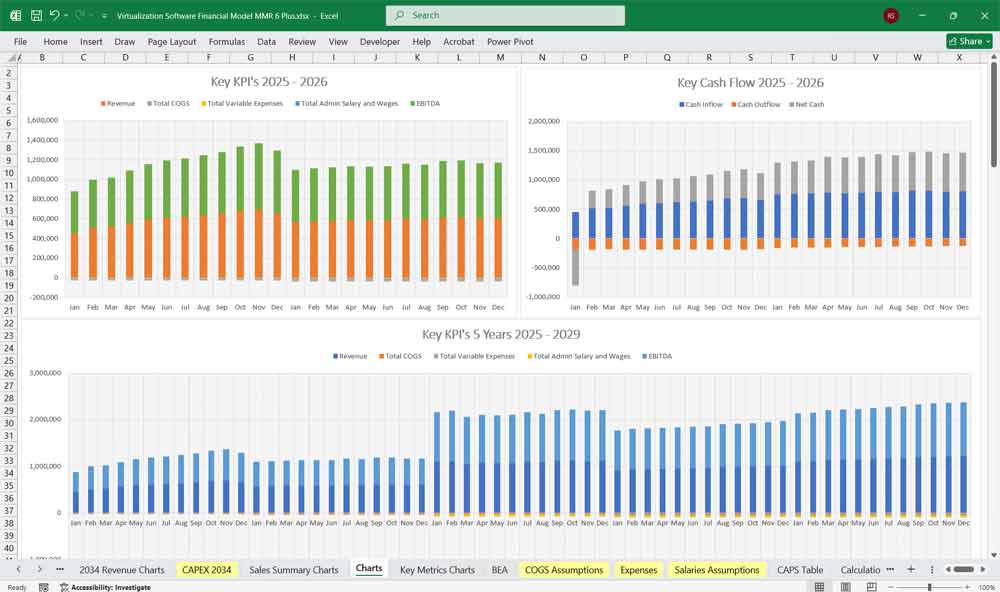
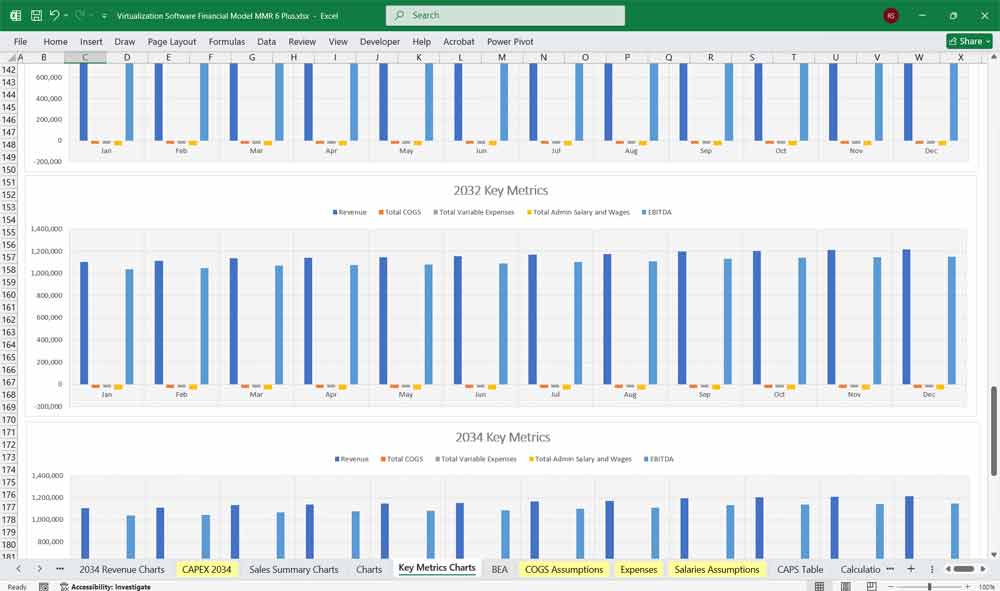
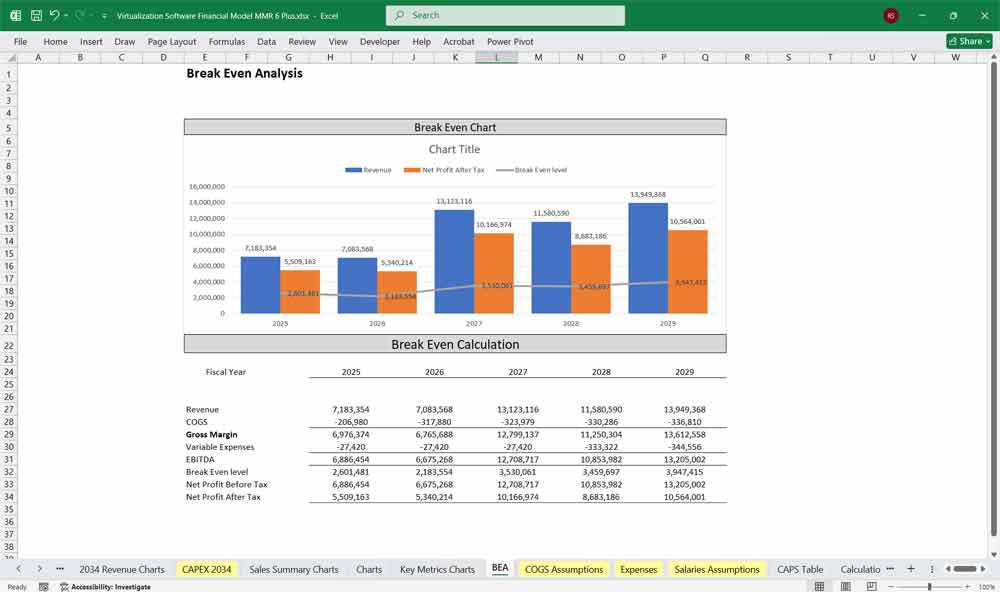
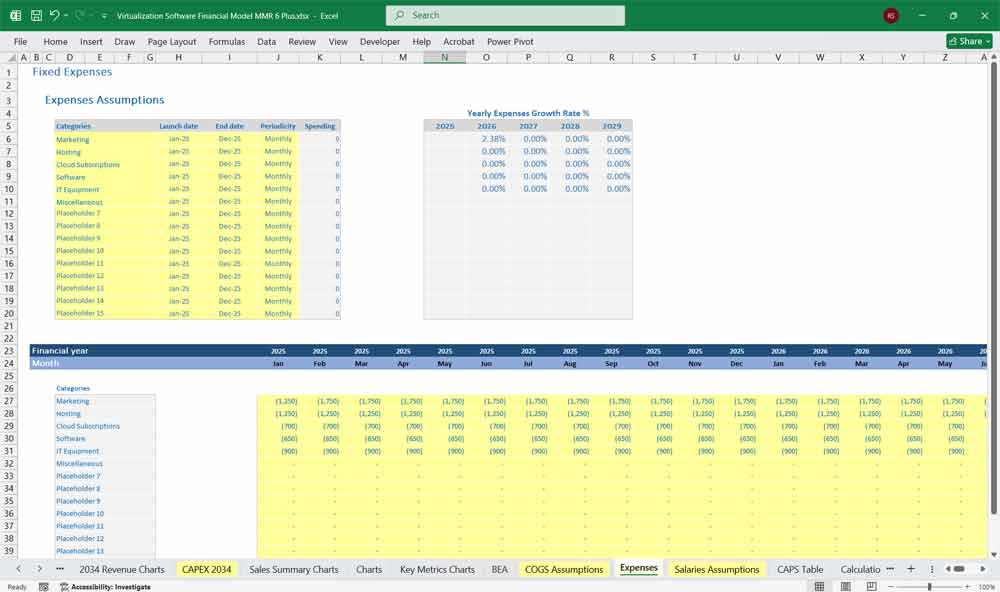
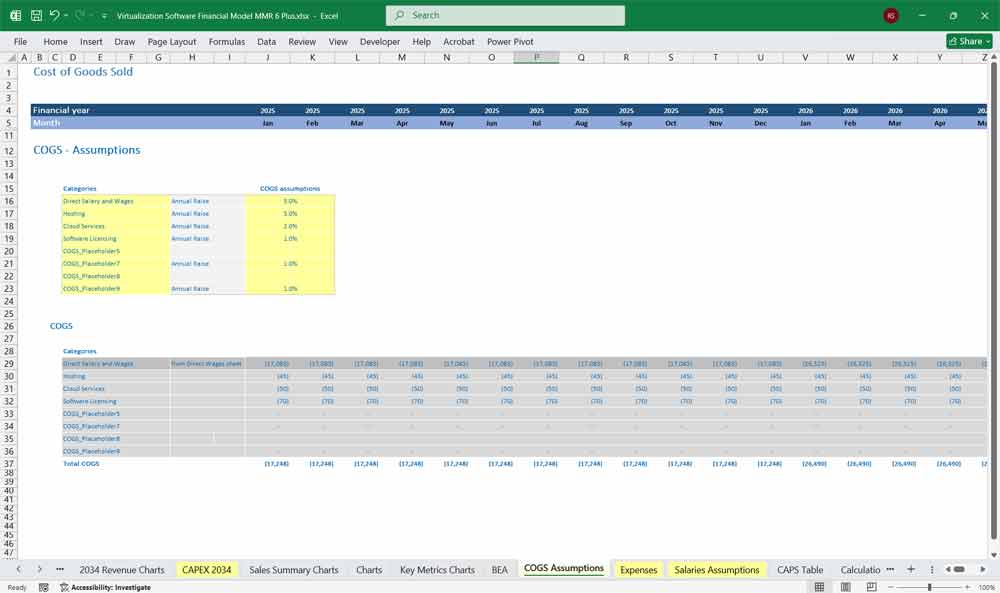
Key Metrics for The Financial Model
- Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) vs. Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
- Churn Rate (customer retention rate)
- Gross & Net Profit Margins
- Burn Rate & Cash Runway (if venture-backed)
Conclusion
This Virtualization Software Financial Model gives a structured approach to analyzing your virtualization software company’s financial health. The 6-tier subscription model ensures flexible pricing for different customer segments while optimizing revenue potential.
Download Link On Next Page
Download Link On Next Page
