How Effective Subscription Churn Analysis Can Reduce Revenue Loss.
Run an effective retention strategy. Study subscription churn analysis and improve your long-term revenue from your subscription-based company.
Deeper Churn Analysis for Subscription Revenue
The churn rate is the percentage of subscribers who cancel their subscription over a given period. Analyzing churn in-depth helps optimize retention strategies and improve long-term revenue.
Types of Churn
There are two main types of churn to analyze:
Voluntary Churn (Customer-Driven)
- Users actively cancel due to:
- High pricing
- Lack of content variety
- Poor user experience
- Switching to competitors
Involuntary Churn (Payment-Related)
- Subscription cancellations due to:
- Payment failures (expired credit cards, insufficient funds)
- Billing issues
Example Churn by Subscription Tier
Different pricing tiers experience different churn rates:
| Tier | Monthly Churn Rate (%) | Key Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Free (Ad-Supported) | 20% | Low engagement, ads annoyance |
| Basic | 8% | Limited features, better alternatives |
| Standard | 5% | Price sensitivity, content library |
| Premium | 3% | Strong retention, better experience |
| Family Plan | 2% | Multi-user advantage |
| Enterprise (B2B) | 1% | Contracts lock in users |
- Lower-tier plans tend to have higher churn.
- Premium and family plans retain users longer due to added value.
Churn Impact on Revenue
Direct Revenue Loss
Immediate Impact: When customers churn, the company loses their recurring revenue. This is especially critical in subscription-based models where revenue is predictable and relies on a steady stream of payments.
Example: If 100 customers paying 50 / month churn, the company loses 50 / month churn, the company loses 5,000 in monthly revenue.
Reduced Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Long-Term Impact: Churn shortens the average customer lifespan, reducing the total revenue a customer generates over their relationship with the company.
Example: If the average customer stays for 12 months and pays 50 / month, their CLV is 50 / month, their CLV is 600. If churn reduces the average lifespan to 6 months, CLV drops to $300.
Increased Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Replacement Cost: Acquiring new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing ones. High churn forces companies to spend more on marketing and sales to replace lost customers.
Example: If the cost to acquire a new customer is 200, losing 50 customers means the company must spend 200, losing 50 customers means the company must spend 10,000 to replace them.
Subscription Churn Effect On Revenue Growth
Net Growth Impact: High churn offsets new customer acquisition, making it harder to grow the customer base and revenue.
Example: A company adds 200 new customers but loses 150 to churn. Net growth is only 50 customers, which may not be enough to meet revenue targets.
Increased Dependency on New Subscription Customers
Sustainability Risk: High churn rates force companies to rely heavily on acquiring new customers to maintain revenue levels. This can be risky, as customer acquisition channels may become saturated or more expensive over time.
Example: If a company relies on paid ads to acquire customers, rising ad costs can make it unsustainable to replace churned customers.
Missed Upselling and Cross-Selling Opportunities
Lost Revenue Potential: Churned customers are lost opportunities for upselling or cross-selling additional products or services. Retained customers are more likely to upgrade or purchase add-ons over time.
Example: A SaaS company loses a customer who might have upgraded to a premium plan or purchased additional features in the future.
Difficulty in Revenue Forecasting
Unpredictability: High churn rates make it harder to predict future revenue accurately. This can lead to poor decision-making, misallocation of resources, and challenges in planning for growth.
Example: If churn rates fluctuate unpredictably, a company may overestimate revenue and overspend on marketing or product development.
Subscription Churn And Brand Reputation
Indirect Revenue Impact: High churn rates can indicate dissatisfaction with the product or service, which can harm the company’s reputation. Negative word-of-mouth from churned customers can deter potential new customers.
Example: If customers leave due to poor service, they may share their negative experiences online, discouraging others from subscribing.
Strategies to Reduce Churn
Retention Strategies
✅ Content Personalization: AI-driven recommendations to increase engagement.
✅ Exclusive Content & Originals: High-quality content that isn’t available elsewhere.
✅ Loyalty Programs: Discounts for long-term subscribers.
Payment Recovery for Involuntary Churn
✅ Automated Payment Retries: Retries for failed transactions.
✅ Card Update Reminders: Notifications for expiring payment methods.
Engagement Tactics
✅ Win-Back Campaigns: Email campaigns offering discounts to churned users.
✅ Surveys & Exit Polls: Understand cancellation reasons and address pain points.
✅ Personalize Communication: Tailor interactions to build stronger relationships with customers.
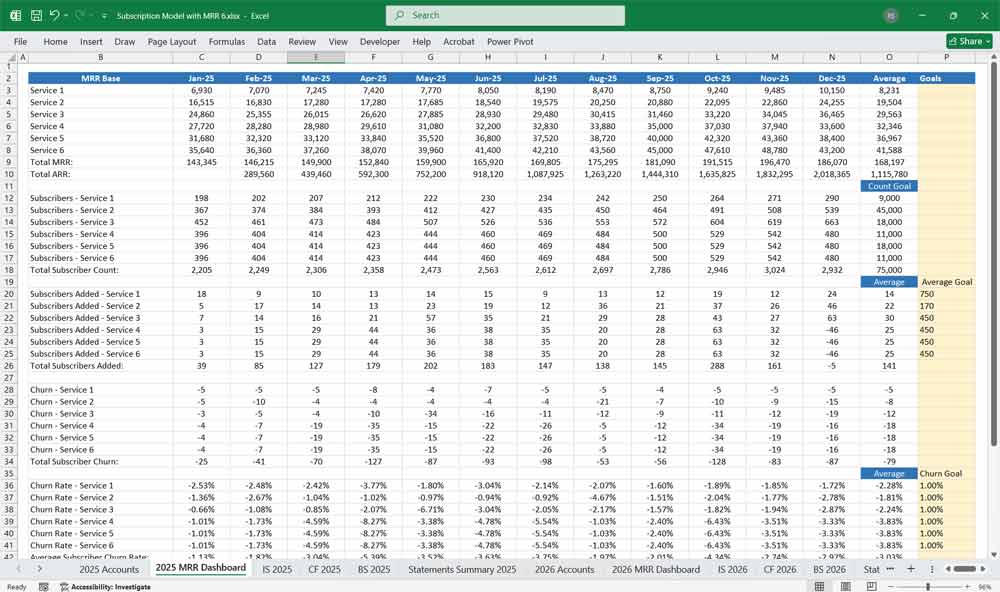
Build a Dynamic Subscription Churn Prediction Model
Define the Problem:
Objective: Predict the probability of a user churning based on their behavior.
Target Variable: Binary (1 = churned, 0 = not churned).
Collect and Prepare Subscription Data:
Gather historical data on user behaviour, such as:
✅ Usage frequency (e.g., logins, sessions, transactions). Engagement metrics (e.g., time spent, features used).
✅ Payment history (e.g., missed payments, subscription plan).
✅Customer support interactions (e.g., tickets raised, complaints).
✅Demographic data (e.g., age, location).
✅Ensure the dataset includes a column indicating whether the user churned (target variable).
Feature Subscription Revenue Engineering:
Create meaningful features from raw data, such as:
✅ Average usage over the last 7, 30, or 90 days.
✅ Changes in usage patterns (e.g., decline in logins).
✅ Payment delinquency (e.g., number of missed payments).
✅ Customer support interactions (e.g., number of tickets raised).
✅ Normalize or scale numerical features.
Split the Subscription Revenue Data:
✅Divide the dataset into training and testing sets (e.g., 80% training, 20% testing).
Choose a Subscription Churn Forecast Model:
Use a machine learning algorithm suitable for binary classification, such as:
✅ Logistic Regression
✅ Random Forest
✅ Gradient Boosting (e.g., XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost)
✅ Neural Networks (for more complex datasets)
Train the Subscription Churn Forecast Model:
✅ Train the model on the training dataset.
✅ Use techniques like cross-validation to optimize hyperparameters.
Evaluate the Subscription Churn Forecast Model:
Evaluate the model’s performance using metrics like:
✅ Accuracy
✅ Precision, Recall, F1-Score
✅ ROC-AUC (Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve)
Deploying the Subscription Churn Forecast Model:
✅ Deploy the model to dynamically predict churn based on real-time or recent user behavior.
✅ Continuously update the model with new data to improve accuracy.
Key Considerations for Dynamic Subscription Churn Prediction
Real-Time Data Integration:
✅ Use APIs or data pipelines to feed real-time user behavior data into the model.
✅ Example: Update features like dynamically averaging logins over the last 7 days.
Model Retraining:
✅ Regularly retrain the model with new data to ensure it adapts to changing user behavior.
Explainability:
✅ Use techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) to explain model predictions and identify key drivers of churn.
Threshold Tuning:
✅ Adjust the probability threshold for churn predictions based on business goals (e.g., prioritize reducing false negatives).
Monitoring:
✅ Continuously monitor model performance and update features as needed.
By implementing any of these models, you can dynamically predict subscription churn and take proactive measures to retain at-risk customers, ultimately reducing revenue loss.
For further Blog posts.
