Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Financial Model Excel
This 20-Year, 3-Statement Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Financial Model Excel includes editabe revenue streams from Recycled Sintered Magnets, Magnet Alloy Powders, Rare Earth Oxides, Rare Earth Carbonates to Government Grants, cost structures, and financial statements to forecast the financial health of your rare earth magnet recycling, REM facility.
20-Year Financial Model for a Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Facility
This very extensive 20 Year REM Model involves detailed revenue projections, cost structures, capital expenditures, and financing needs. This model provides a thorough understanding of the financial viability, profitability, and cash flow position of your recycling facility. Includes: 20x Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, Balance Sheets, CAPEX sheets, OPEX Sheets, Statement Summary Sheets, and Revenue Forecasting Charts with the revenue streams, BEA charts, sales summary charts, employee salary tabs and expenses sheets. Over 120 Spreadsheets in 1 Excel Workbook.
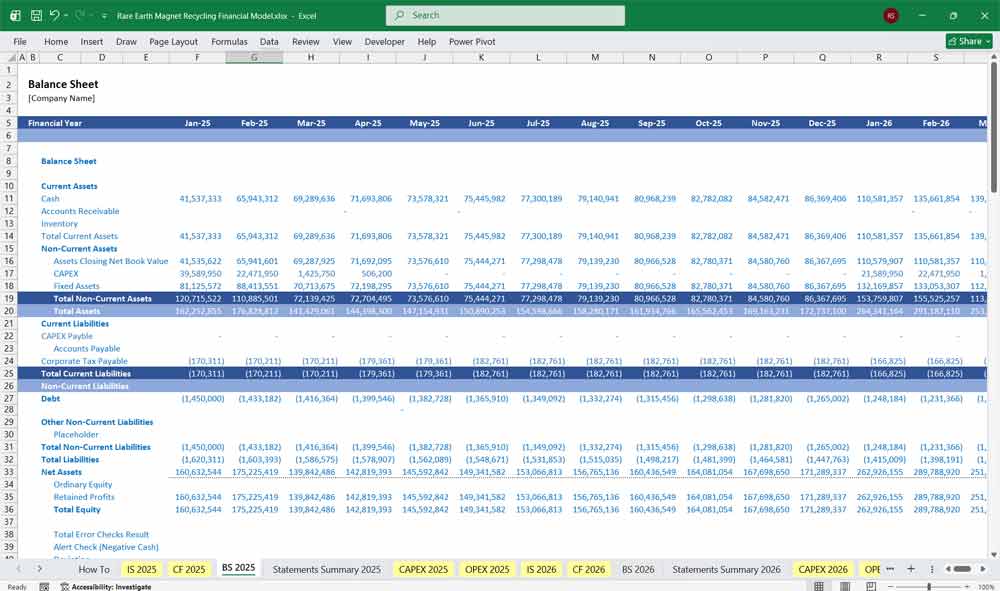
Income Statement (Profit & Loss)
The Income Statement measures operational profitability over time.
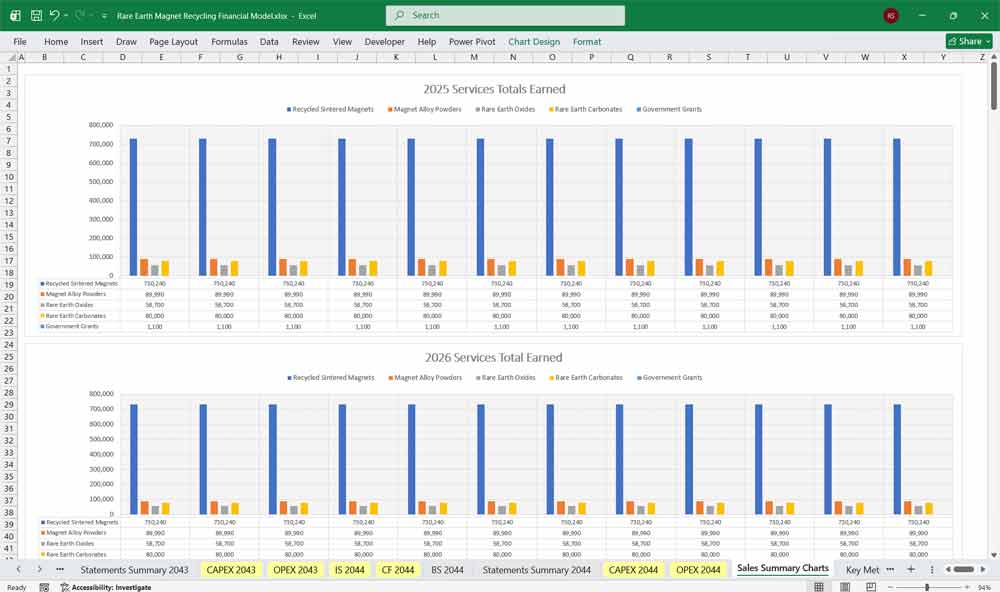
Revenue
Revenue is typically modeled bottom-up:
Recovered Nd oxide sales
Recovered Pr oxide sales
Heavy rare earths (Dy, Tb)
By-product revenue (iron, boron residues, tolling services)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Direct costs tied to production.
Key COGS Components
Feedstock procurement costs
Chemicals and reagents
Energy (electricity, gas)
Consumables (filters, membranes)
Direct labor (operators, technicians)
Waste treatment and disposal
Maintenance materials
COGS is often split into:
Variable costs (scale with throughput)
Semi-fixed costs (minimum operating levels)
Gross Profit
Margins are highly dependent on
Key Components
Feedstock cost vs recovered REE price
Process yield stability
Energy pricing
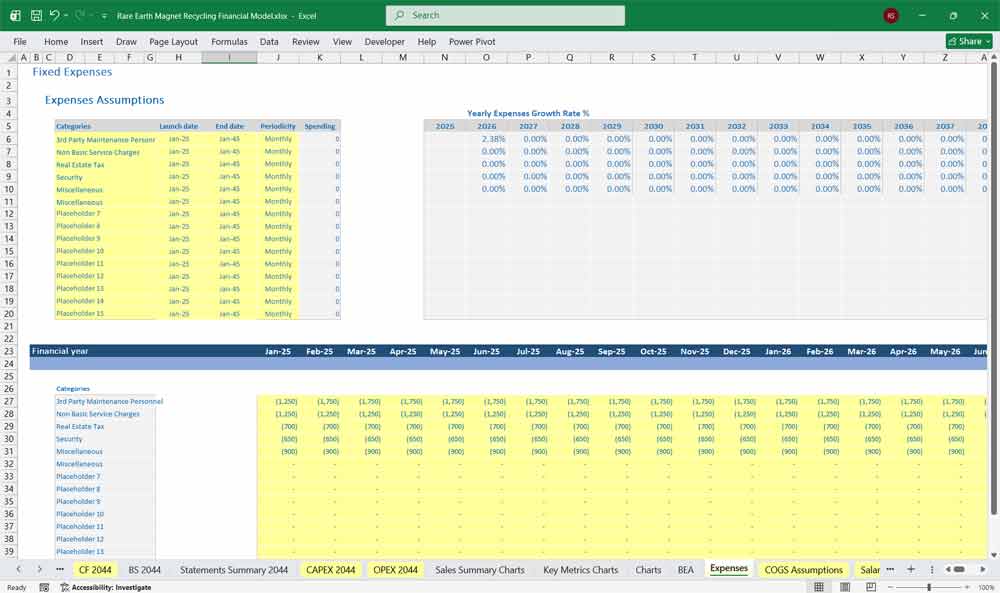
Operating Expenses (OPEX)
Indirect costs not directly tied to throughput.
OPEX Categories
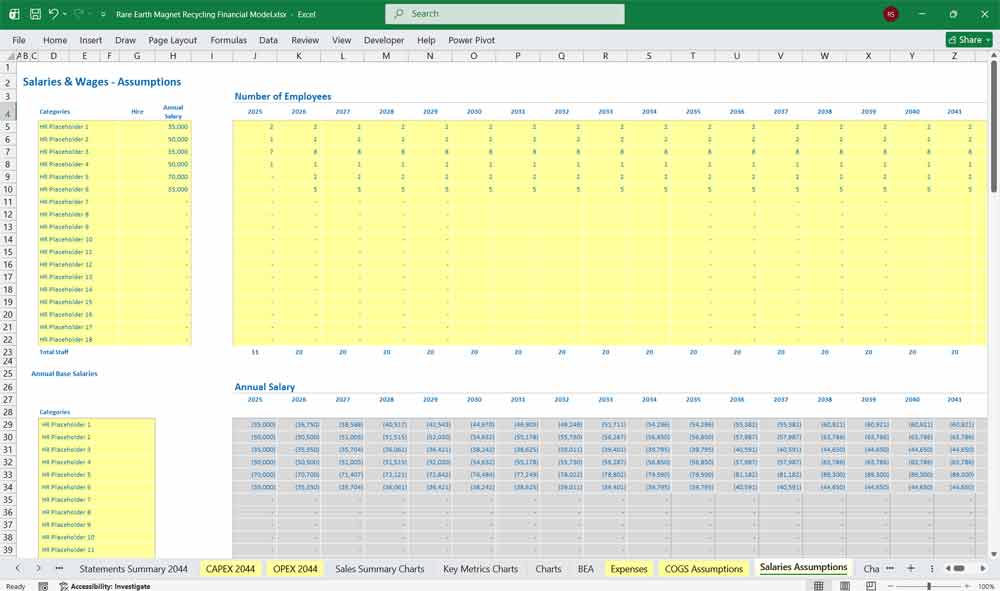
Salaries (management, admin, R&D)
Site overhead
Insurance
Environmental monitoring & compliance
Corporate G&A
Digital and Technology Costs
- Material Handling System Improvement
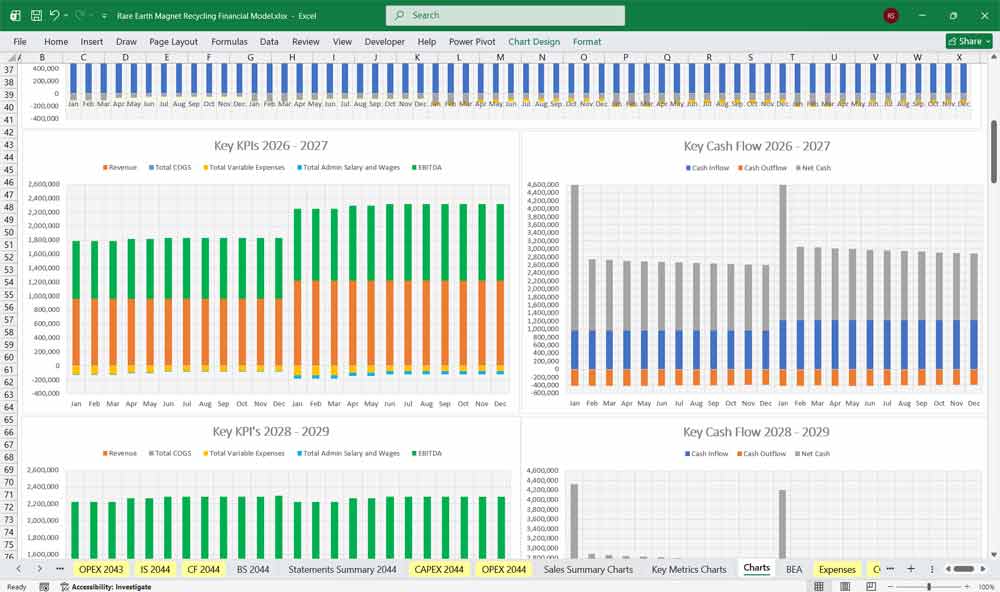
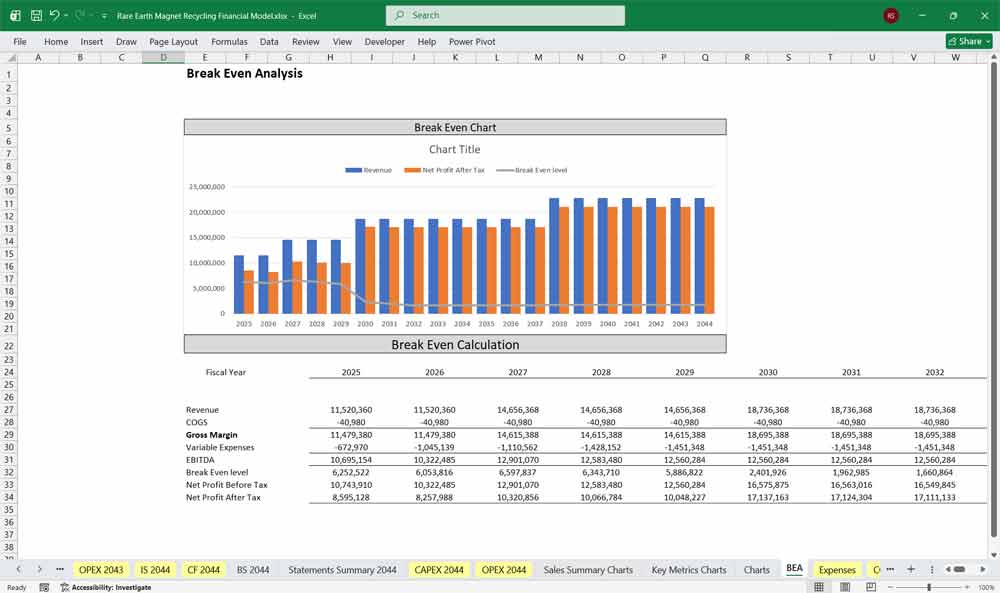
EBITDA
A critical metric for infrastructure and recycling projects.
Used For
Debt sizing
Valuation multiples
- Cash flow analysis
Interest Expense
Project debt interest
Working capital facilities
Taxes
Corporate income tax
Loss carryforwards modeled explicitly
Investment tax credits or recycling incentives (if applicable)
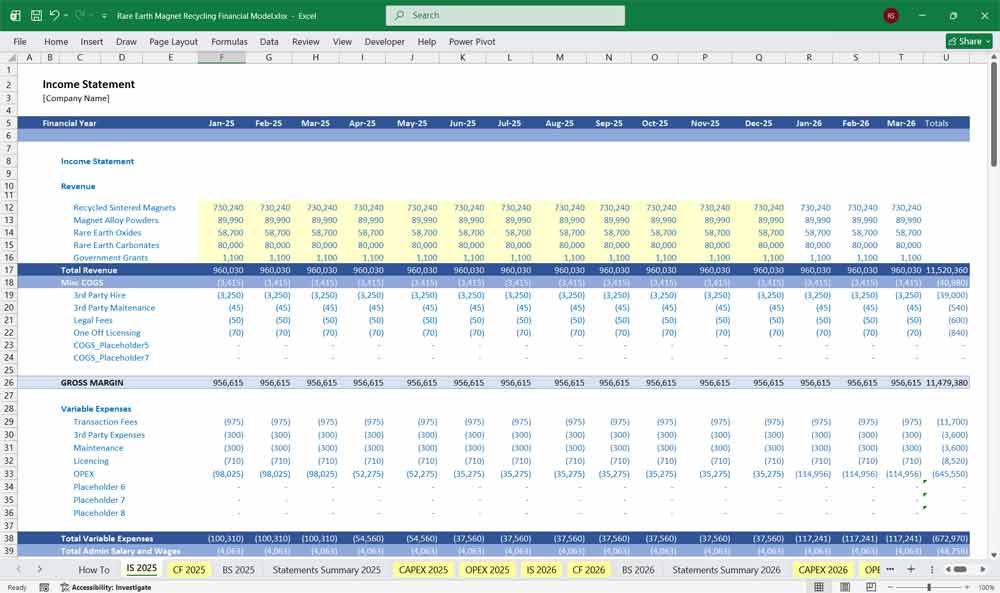
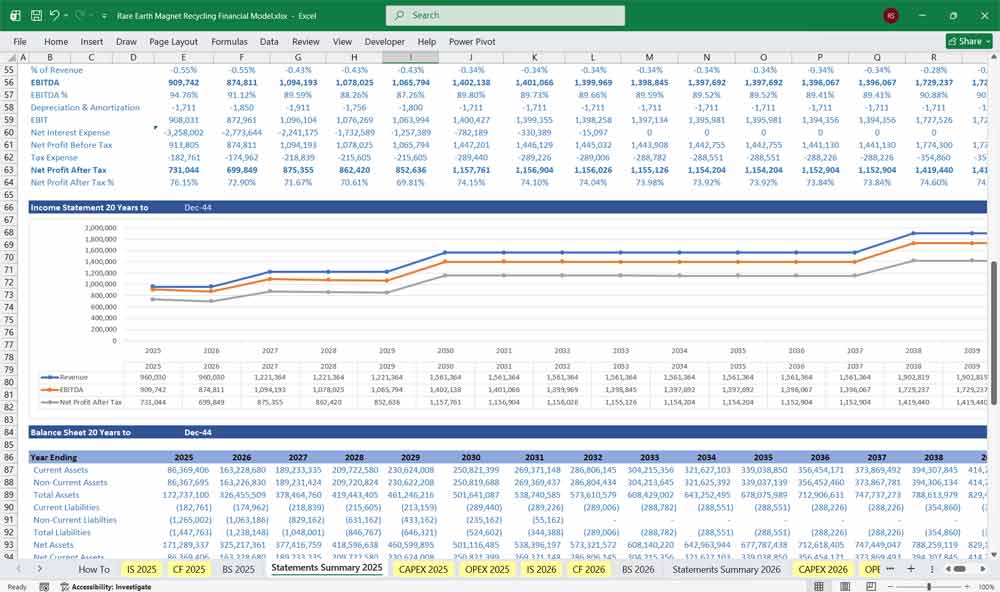
Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Cash Flow Statement
Shows cash movements, integrating operations, investment, and financing.
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Starts from Net Income and adjusts for non-cash items.
Add-backs / Adjustments
Depreciation & amortization
Deferred taxes
Changes in working capital:
Inventory
Accounts receivable
Accounts payable
This section reflects the facility’s true cash-generating ability.
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Captures long-term asset investments.
Key Items
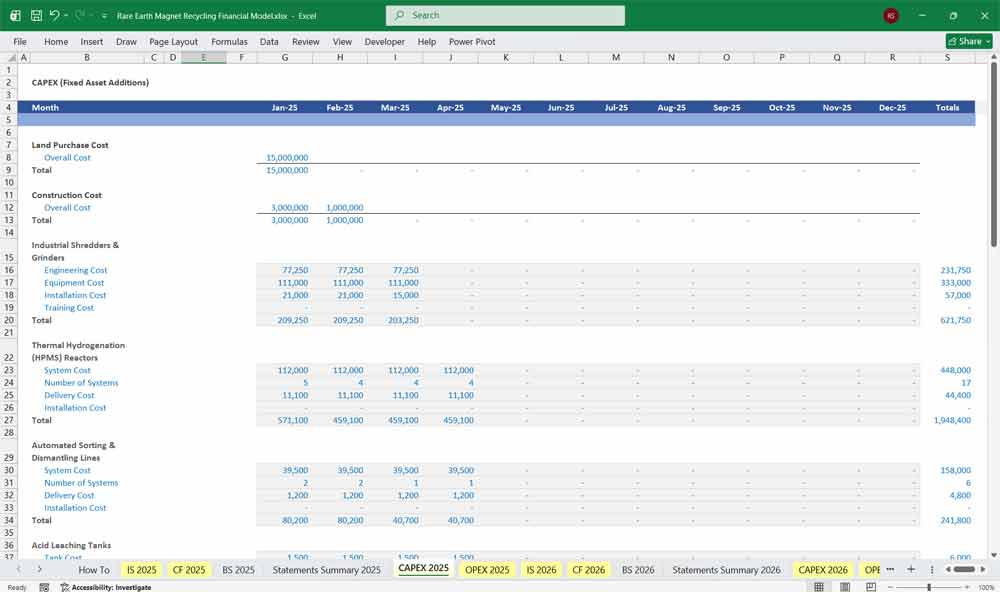
Initial plant construction (CAPEX)
Replacement CAPEX
Capacity expansion
Technology upgrades
Typically front-loaded in early years.
Cash Flow from Financing Activities
Tracks how the project is funded.
Financing Sources
Equity contributions
Project debt drawdowns
Government grants or subsidies
Uses
Debt repayment (principal)
Interest payments
Dividends (if applicable)
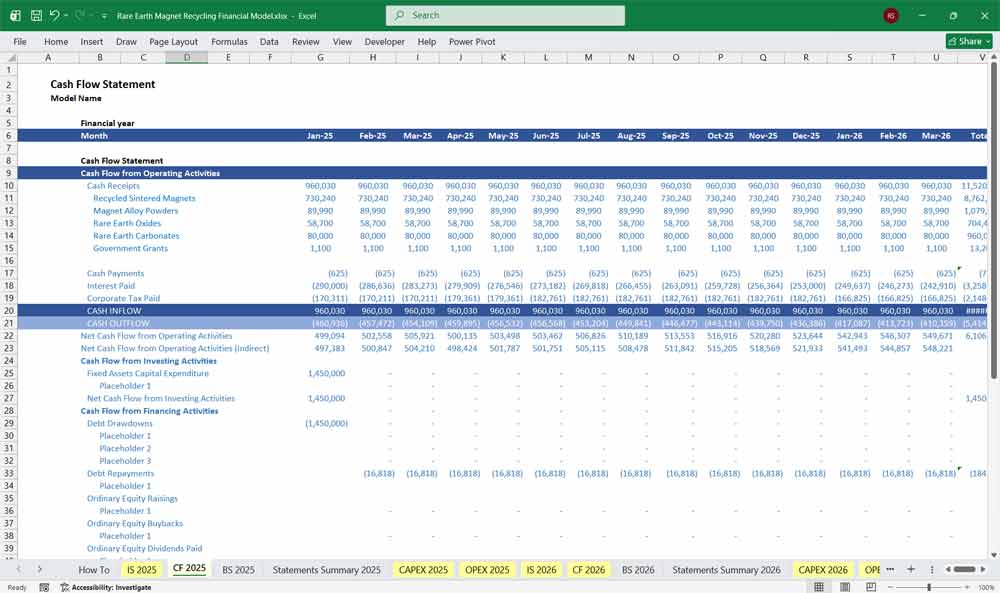
Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Balance Sheet
Snapshot of the company’s financial position at a point in time.
Assets
Current Assets
Cash & cash equivalents
Accounts receivable
Inventory:
Feedstock
Work-in-process
Finished goods
Non-Current Assets
Property, plant & equipment (net of depreciation)
Capitalized development costs
Environmental bonds or deposits
Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts payable
Accrued expenses
Short-term debt
Current portion of long-term debt
Long-Term Liabilities
Project finance debt
Decommissioning or reclamation provisions
Deferred tax liabilities
Key Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Facility Considerations
High Fixed Cost Base: Equipment-heavy industry with high depreciation.
R&D Intensity: Critical for staying competitive.
Quality & Certification: Failure costs can be catastrophic (scrap, rework).
20-Year Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Financial Model Advantages
A 20-year financial model gives a REM Facility the ability to plan around long product lifecycles and extended contract horizons. Contracts can span 20 years, and equipment lifespans often exceed two decades. A long-term model ensures that capital investment decisions—like building new Thermal Hydrogenation (HPMS) Reactors and Solvent Extraction (SX) Batteries—are aligned with the revenue and cash flow timelines they are meant to serve.
Closer View Of Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Investments
A 20-year model allows management to capture the full return on R&D and innovation investments. In the composite sector, new material systems or recycling processes can take years to develop and commercialize. A 20-year horizon shows not only the upfront development costs but also the long-term payoff in reduced recycling costs, and reflects a higher market share over time.
REM Recycling 20 Year Dept Financing
A 20-year debt financing structure for a rare earth magnet recycling facility offers significant advantages by aligning long-term capital with the asset’s extended operating life. Longer tenor debt reduces annual debt service, improves cash flow stability during ramp-up years, and enhances debt service coverage ratios, making the project more resilient to commodity price volatility.
20 Years Of Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Facility Projections
Twenty-year financial and operational projections for a rare earth magnet recycling facility provide a long-term view that aligns with the asset’s durable infrastructure, evolving feedstock availability, and multi-cycle commodity dynamics. Extended projections capture full ramp-up, steady-state operations, and reinvestment cycles, improving the accuracy of cash flow forecasting, debt sizing, and lifecycle returns while demonstrating resilience across rare earth price fluctuations and policy-driven demand growth.
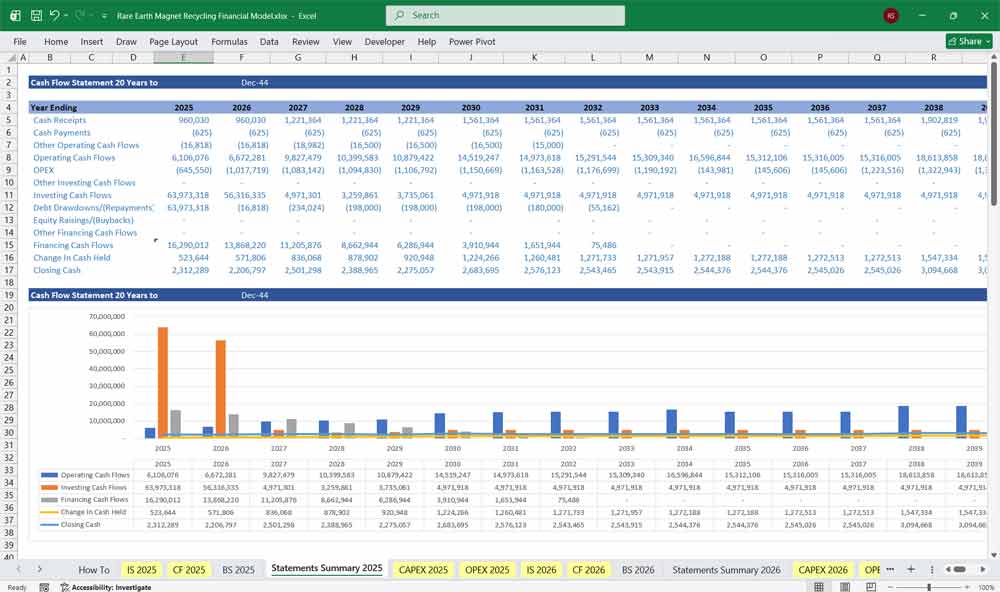
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This 20-Year, 3 Statement Rare Earth Magnet Recycling Financial Model in Excel focuses on balancing capital expenditures with steady revenue growth. By optimizing operational costs, and power efficiency, and maximizing high-margin services, the models ensure sustainable profitability and cash flow stability.
