Industrial Development Financial Model
Financial Model for an Industrial Building Development
Editable Cost Sections Examples
Each has its own Workbook Tab, and each tab has 10 editable named sections, some of which have their details listed below.
1. Civil Works – Entrance & Access Infrastructure
Editable Input Examples: Site clearing, entrance roads, security gates, drainage, curbs, sidewalks, and guard booths.
Focuses on foundational access works, ensuring safe and efficient vehicle and personnel movement on-site.
2. Building Construction
This section outlines the complete structural development of the facility, broken down into detailed, editable sub-categories:
Final Design & Engineering
Fabrication of Steel Components
Plot Preparation & Foundation Work
Erection of Primary Steel Frame
Secondary Framing Installation
Roof & Wall Cladding
Flooring System (If Applicable)
Crane & Heavy Equipment Integration
Quality Checks & Inspections
Handover & Maintenance Planning
All items in this section are editable to reflect design specifications, engineering complexity, material selection, and contractor pricing.
3. Electrical Works
Editable Inputs: External & internal power distribution, lighting systems, fire alarms, power backup (generators, UPS), compliance testing.
Adaptable to suit load requirements, safety regulations, and tenant-specific operational needs.
- The main worksheet below categorises all the tabs into one main spreadsheet for easy viewing. The tabs are (although all fully editable) Civil Work, Building Construction, Electrical Works, Interiors, Landscaping, Plant and Tool Hire, and HR Costs
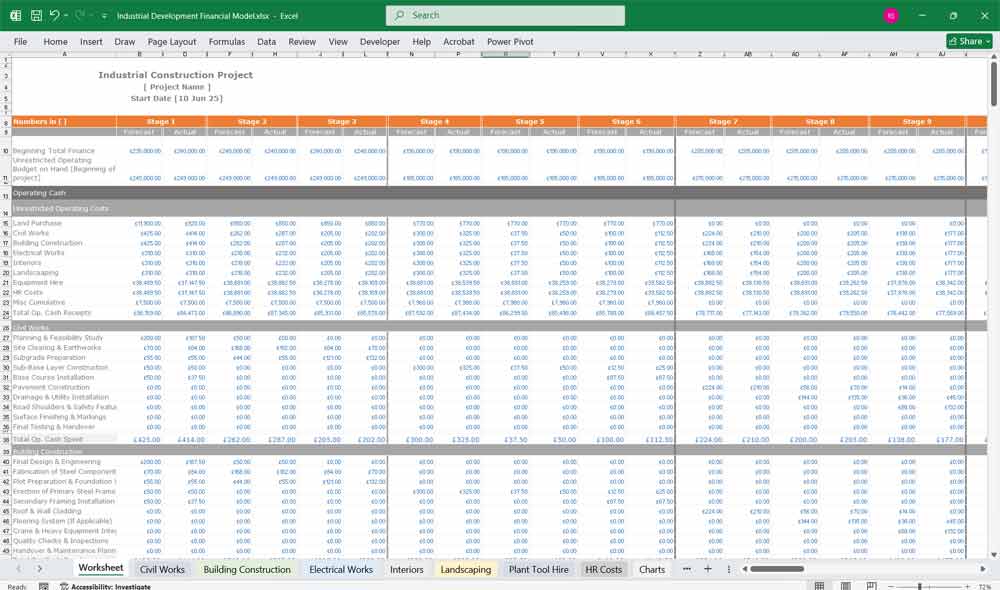
Tabs In the Financial Model
Each section of the Industrial Building Development has its own tab (7 In Total).
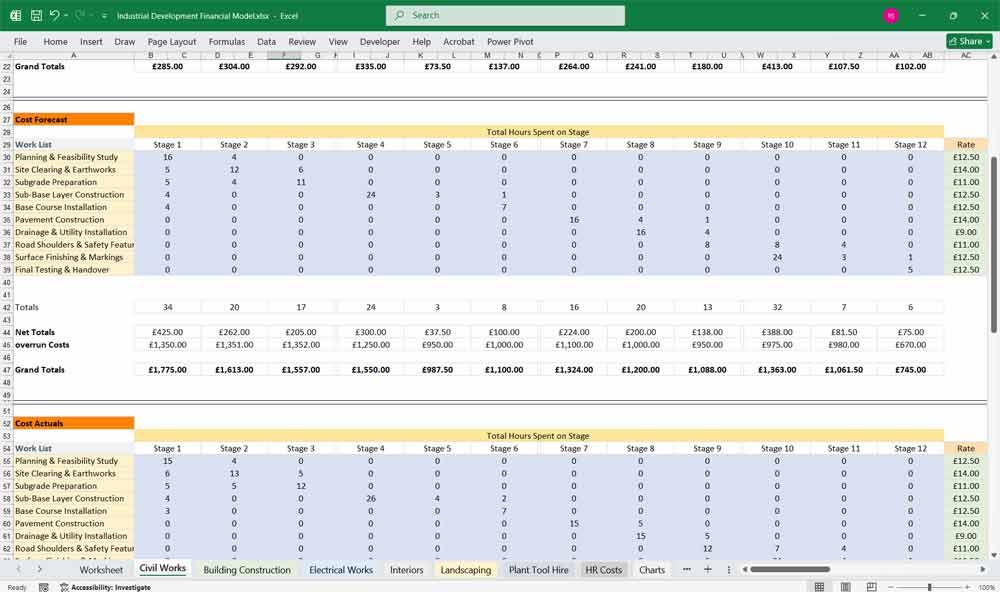
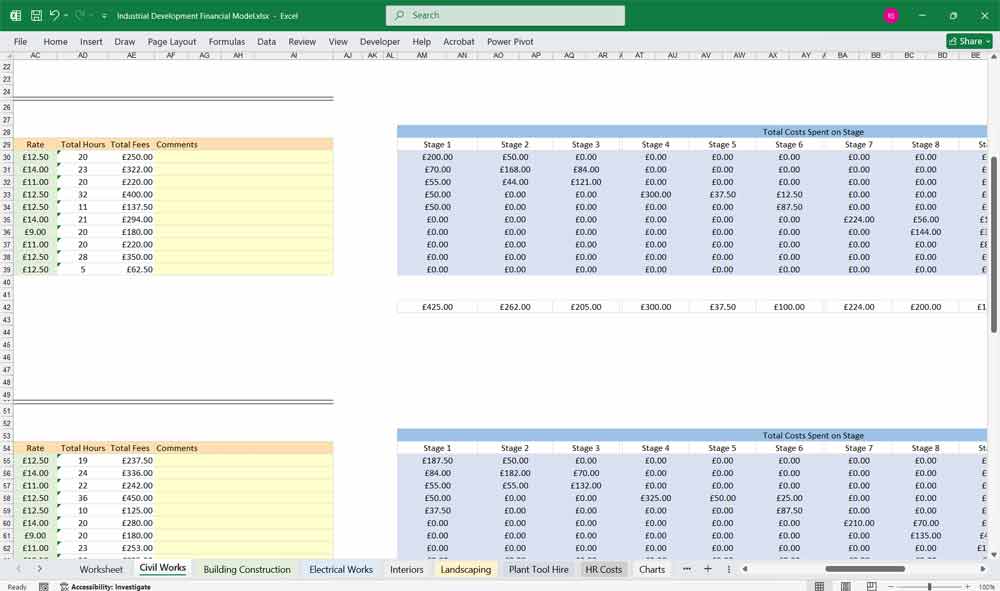
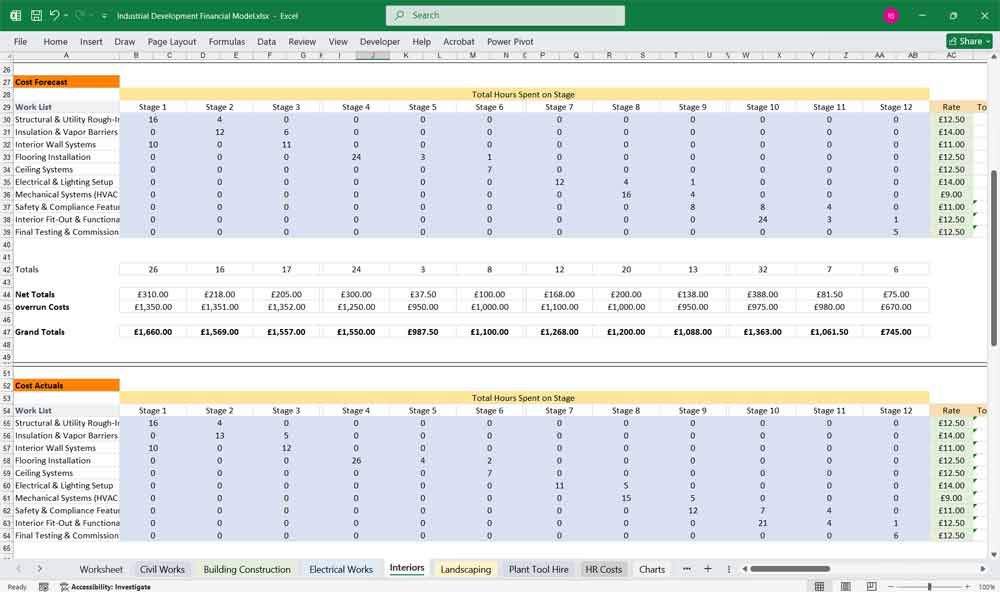
The tabs are currently set to “Stage 1” etc Just change the name to Day or Month on the “Civil Works” tab, and all tabs are updated. Enter the hours forecasted on task, enter the rate, and the totals are calculated, view them by scrolling right on the same tab (Picture 2 below)
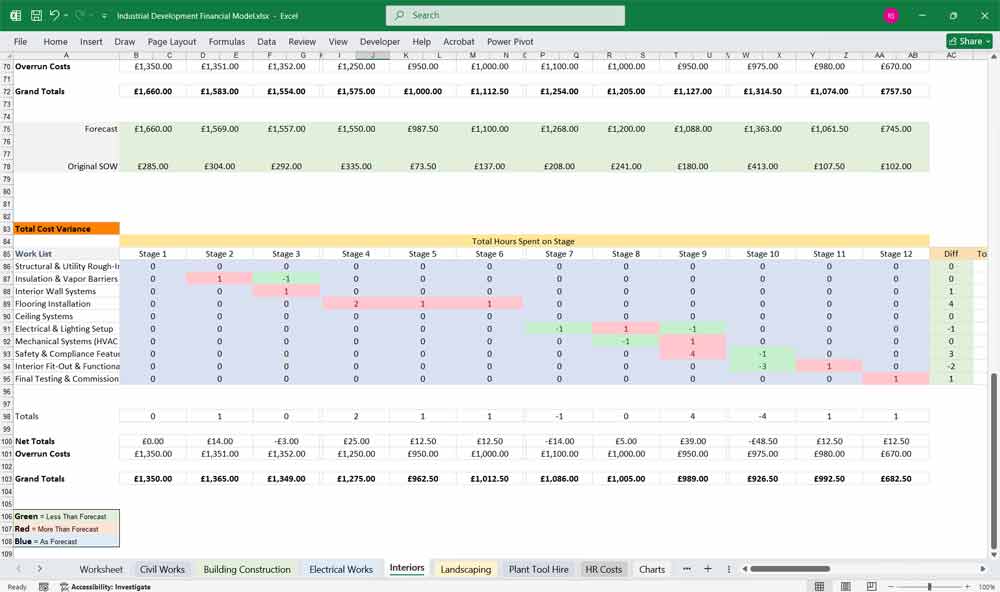
Forecast vs Actuals and the Variance Spreadsheet.
Easily view cost variances of projections and actuals with color-coded cells. Track overspending on tasks, Plant Hire and even HR, and avoid future overspends. (Picture 3 below)
4. Interiors
This section covers interior build-out and functional fit-out with editable sub-components:
Structural & Utility Rough-Ins
Insulation & Vapor Barriers
Interior Wall Systems
Flooring Installation
Ceiling Systems
Electrical & Lighting Setup
Mechanical Systems (HVAC & Ventilation)
Safety & Compliance Features
Interior Fit-Out & Functional Zones
Final Testing & Commissioning
Each line item is editable to accommodate variations in space utilization (e.g., office vs warehouse), materials, and finishes.
5. Landscaping
Editable Inputs: Grading, topsoil, planting, irrigation systems, fencing, lighting, signage, and aesthetic enhancements.
Customizable to reflect local planning authority requirements and corporate branding preferences.
6. Plant and Tool Hire
Details the temporary equipment required for construction, with editable cost inputs per unit/time period:
Generator
Concrete Paver
Excavators
Graders
Aerial Platform Lift Truck
Roller
Light Tower
Power Tools
Cabling
Surveying Equipment
This section enables adjustment based on construction duration, procurement strategy, or local rental rates
7. HR Costs
Editable Inputs: Project managers, engineers, site supervisors, skilled labor, safety officers, administrative support.
Supports flexible modeling of salary structures, labor hours, benefit costs, and team scaling over the project timeline.
Financial Model Features
Modular, user-friendly interface with cost categories
Monthly, Weekly, or project-phase budgeting
Built-in contingency, inflation, and cash flow forecasting
Integration-ready with funding schedules and project timelines
PowerPoint Features
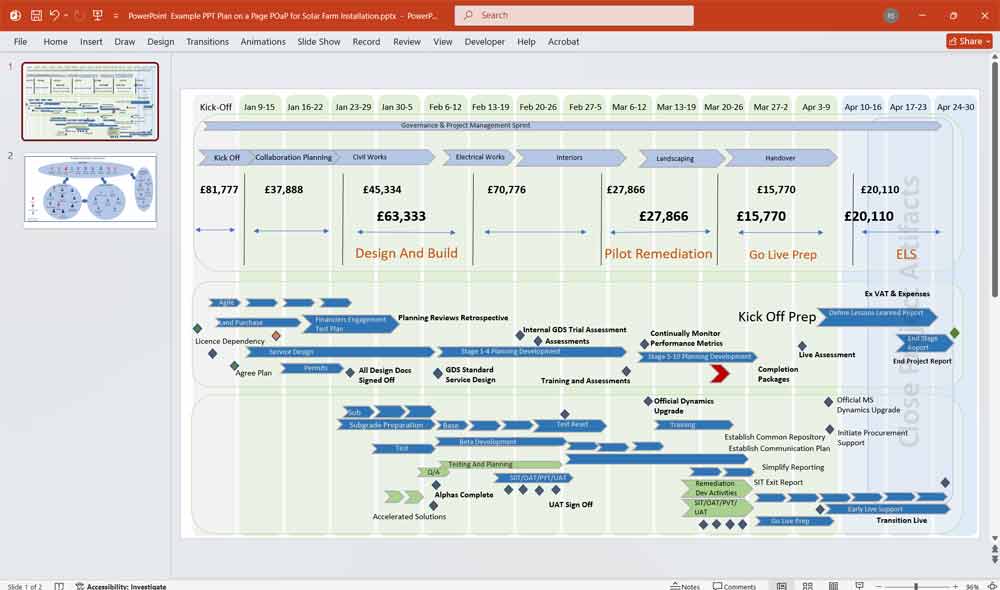
- 2 Slide presentation covering the timeline of the construction and the proposed team structure
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This 12-Stage Financial Model for an Industrial Building Development focuses on balancing capital expenditures with steady production, easily optimising operational costs, and efficiency, and minimising high expenditures.
