Heavy Equipment Manufacturer Financial Model
This 20-Year, 3-Statement 80 Product Line Excel Heavy Equipment Manufacturer Financial Model includes revenue streams from Product Sales, Spare Part Sales, Machine Servicing and Repair Services. Cost structures, Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) with Terminal Value, Sensitivity Analysis, WACC, and financial statements to forecast the financial health of your Heavy Equipment Manufacturing.
20-year Financial Model for a Heavy Equipment Manufacturer
This very extensive 20 Year Heavy Equipment Manufacturer Model involves detailed revenue projections, cost structures, capital expenditures, and financing breakdowns. This model provides a thorough understanding of the financial viability, profitability, and cash flow position of the equipment manufacturing. Including: 20x Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, Balance Sheets, CAPEX sheets, OPEX Sheets, Statement Summary Sheets, and Revenue Forecasting Charts with the specified revenue streams, BEA charts, sales summary charts, employee salary tabs and expenses sheets. This model also takes into account “Equipment as a Service” (EaaS) with a 6-Tier Subscription, as many heavy machine manufacturers are allowing their customers to access machinery for a monthly or annual fee, rather than making a large upfront purchase.
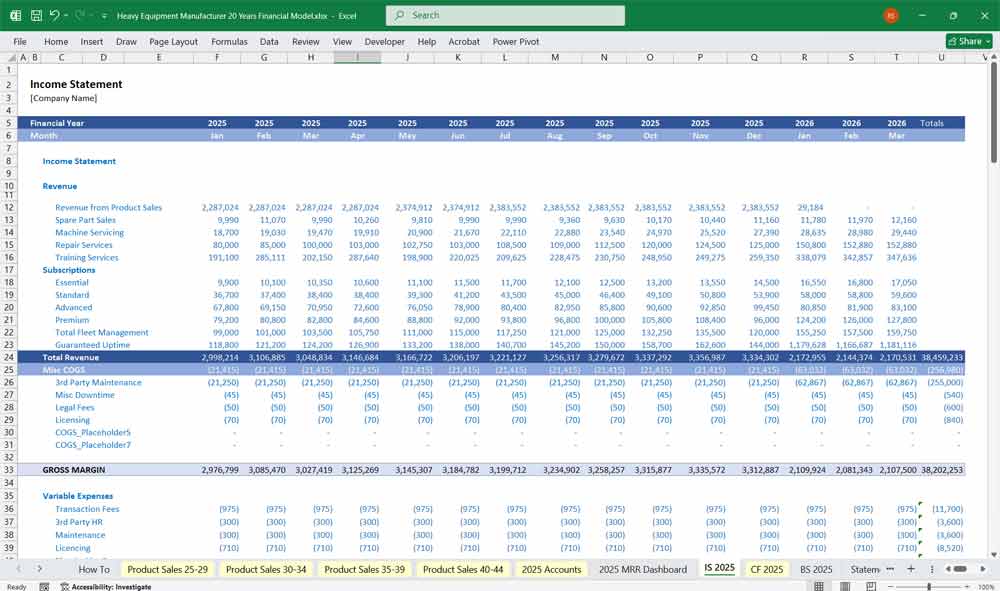
Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
The Income Statement outlines the revenues, costs, and profitability of the Equipment Manufacturer.
Editable Revenue Streams
You might generate revenue from:
Heavy Equipment Sales (Primary Revenue)
Spare Parts Sales
Machine Servicing & Maintenance Contracts
Repair Services (On-site & Workshop)
Training Services (Operator & Technician Training)
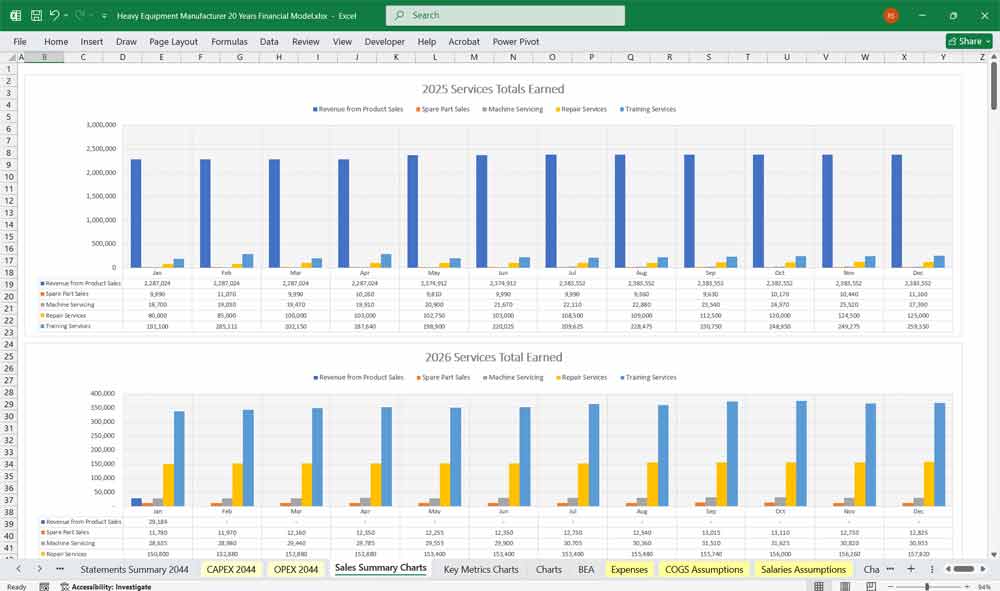
Revenue Breakdown by Product Line (80 Lines)
Each product line (e.g., Excavators, Bulldozers, Cranes) will have:
Unit Sales Volume (Annual)
Average Selling Price (ASP)
Revenue = Unit Sales × ASP
Spare Parts Attach Rate (% of equipment sales)
Service Contract Penetration Rate (% of equipment under service agreements)
Revenue
Product Sales Revenue
New Equipment Sales
Used/Refurbished Equipment Sales
Spare Parts Revenue
Service & Repair Revenue
Scheduled Maintenance
Emergency Repairs
Training Revenue
Operator Certification Programs
Technical Training Workshops
B. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Direct Manufacturing Costs
Raw Materials (Steel, Electronics, Hydraulics)
Labor (Assembly Line Workers)
Factory Overhead (Utilities, Depreciation)
Spare Parts COGS
Service & Repair COGS
Technician Labor
Replacement Parts
Training COGS
Instructor Costs
Training Material Costs
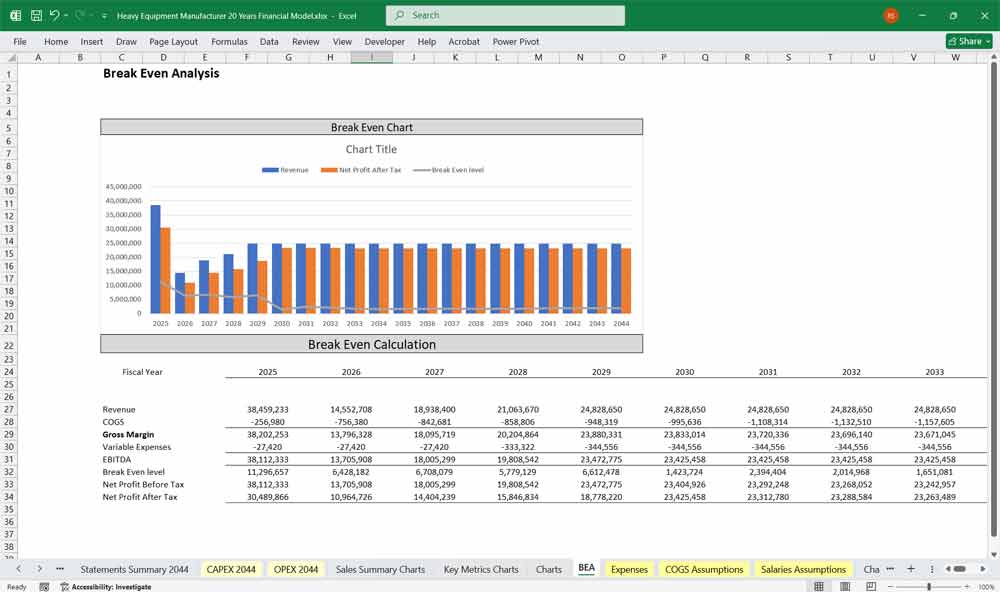
C. Gross Profit
Gross Profit = Total Revenue – COGS
Gross Margin % = (Gross Profit / Revenue) × 100
D. Operating Expenses (OPEX)
Sales & Marketing
Trade Shows, Advertising, Sales Commissions
Research & Development (R&D)
New Product Development
Engineering Costs
General & Administrative (G&A)
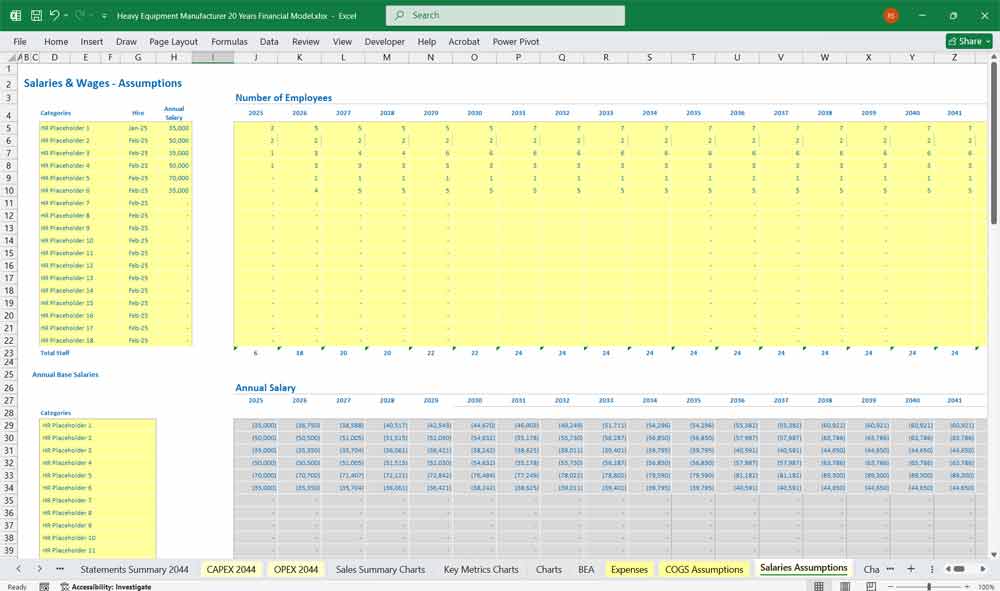
Salaries (Management, HR, Finance)
Office Rent, IT, Legal Fees
Warranty & Post-Sales Support
Warranty Claims
Customer Service
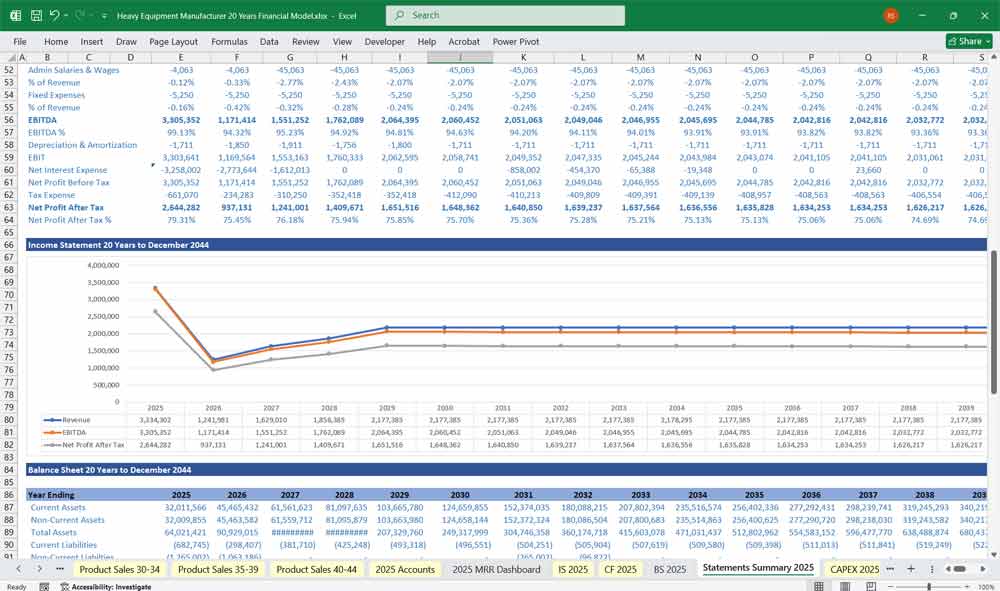
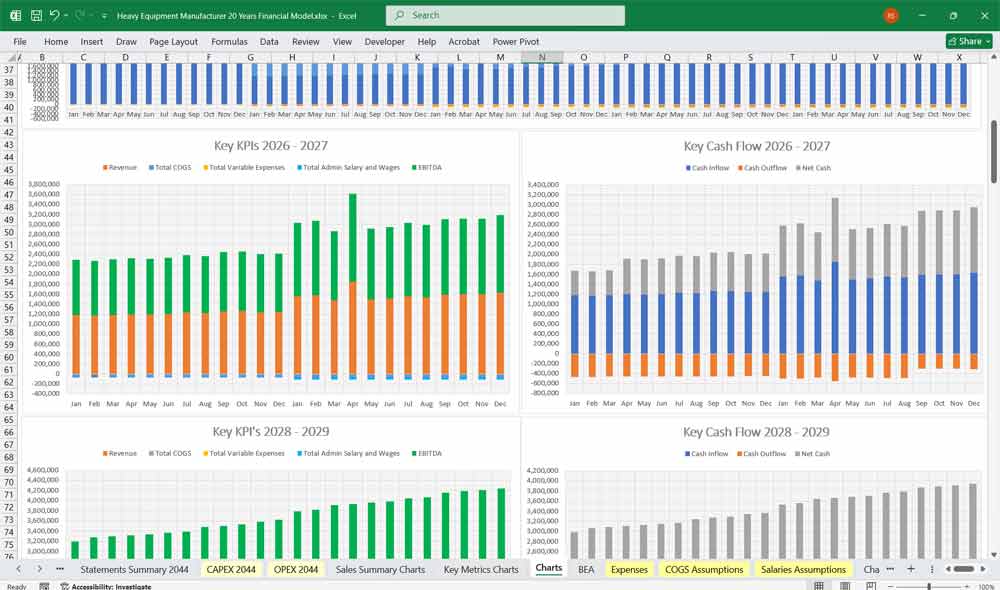
E. EBITDA & Net Profit
EBITDA = Gross Profit – OPEX
Depreciation & Amortization (Factory Equipment, Software)
Interest Expense (Loans, Leases)
Taxes (Corporate Income Tax)
Net Profit = EBITDA – Depreciation – Interest – Taxes
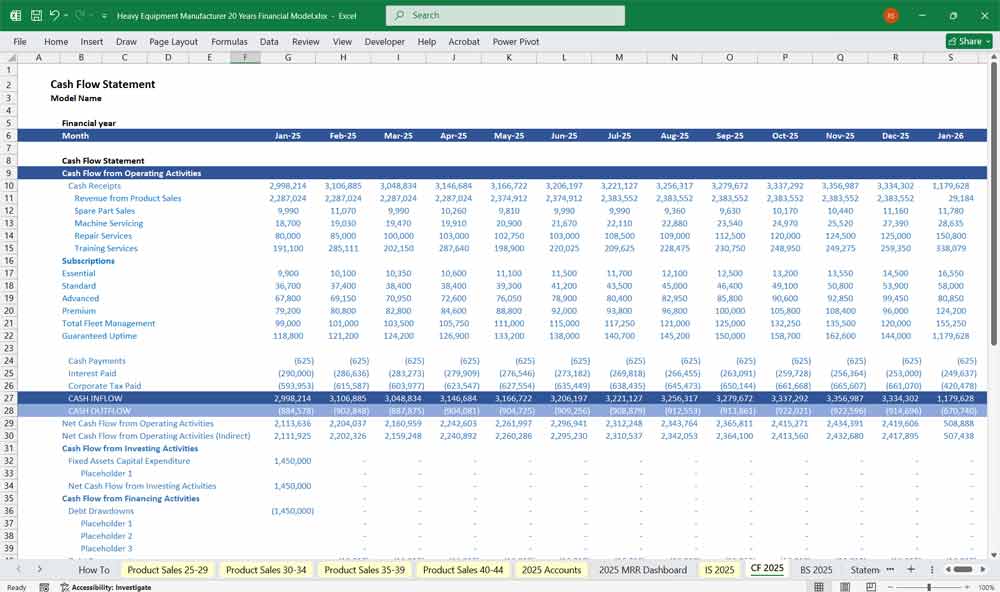
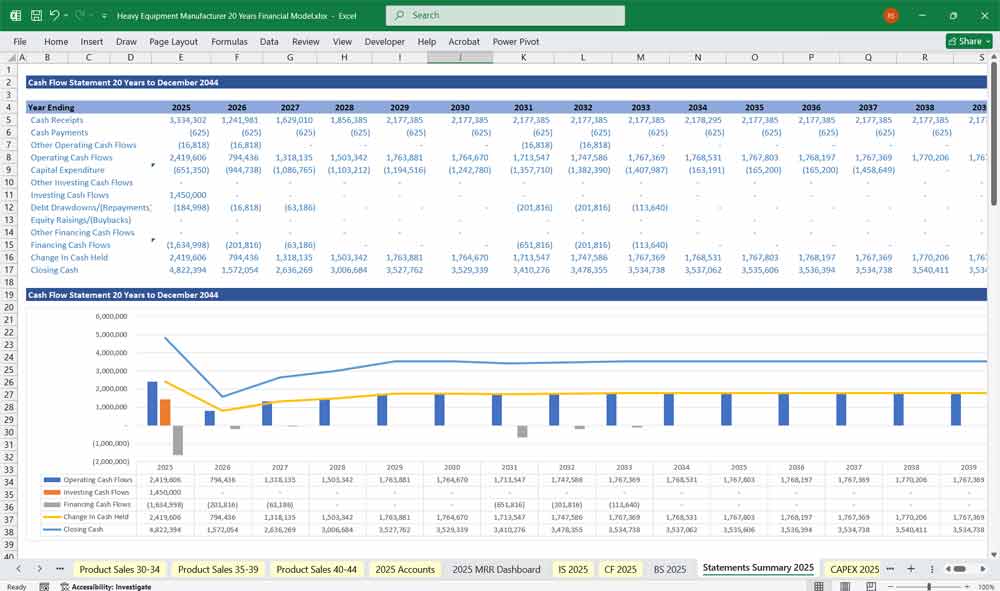
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer Cash Flow Statement
A. Operating Cash Flow
Cash from Sales (Equipment, Parts, Services)
Cash Paid to Suppliers (Raw Materials, Spare Parts)
Salaries & Wages
Tax Payments
B. Investing Cash Flow
Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
Machinery Purchases
Facility Expansion
R&D Investments
C. Financing Cash Flow
Debt Financing (Loans, Bonds)
Equity Financing (Investments, Share Issuance)
Dividend Payments
Net Cash Flow = Operating + Investing + Financing
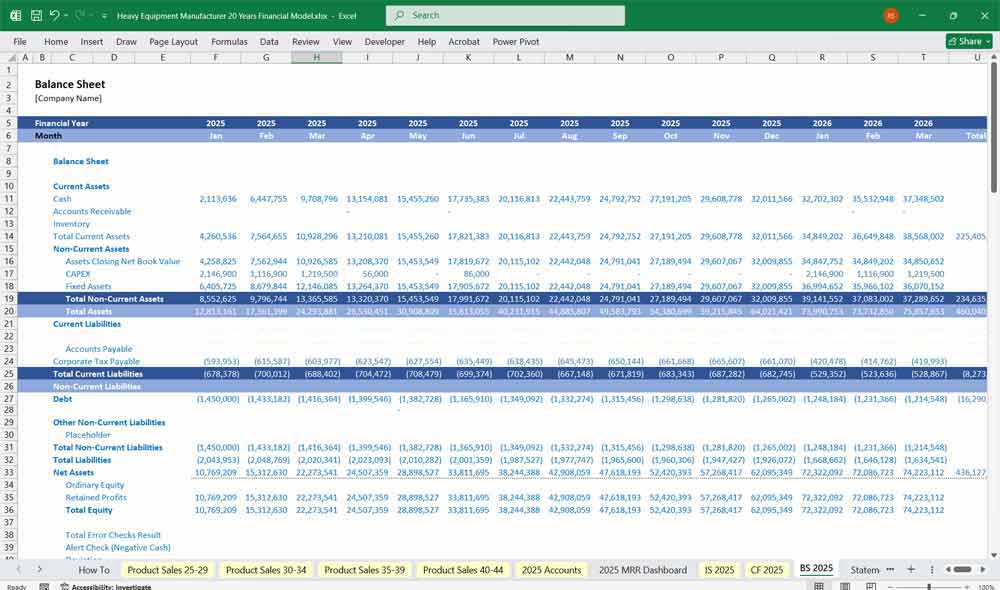
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer Balance Sheet
A. Assets
Current Assets
Cash & Equivalents
Accounts Receivable (Customer Payments Due)
Inventory (Finished Goods, Work-in-Progress, Raw Materials)
Non-Current Assets
Property, Plant & Equipment (PP&E)
Intangible Assets (Patents, Software)
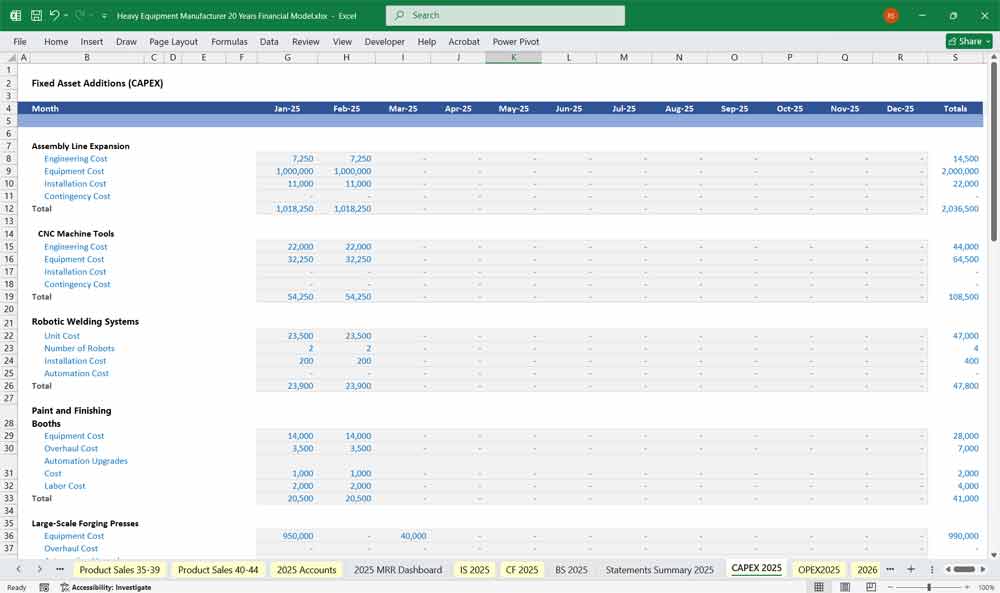
B. CAPEX
Fixed Asset Additions
Assembly Line Expansion
CNC Machine Tools
Robotic Welding Systems
- New Paint and Finishing Booths
- Large-Scale Forging Presses
- Foundry Modernization
C. OPEX
OPEX Liabilities
Personnel Costs
Maintenance and Repair
Transportation and Logistics
- Supplies and Materials
D. Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable (Suppliers)
Short-Term Debt
Warranty Reserves
Long-Term Liabilities
Bank Loans
Lease Obligations
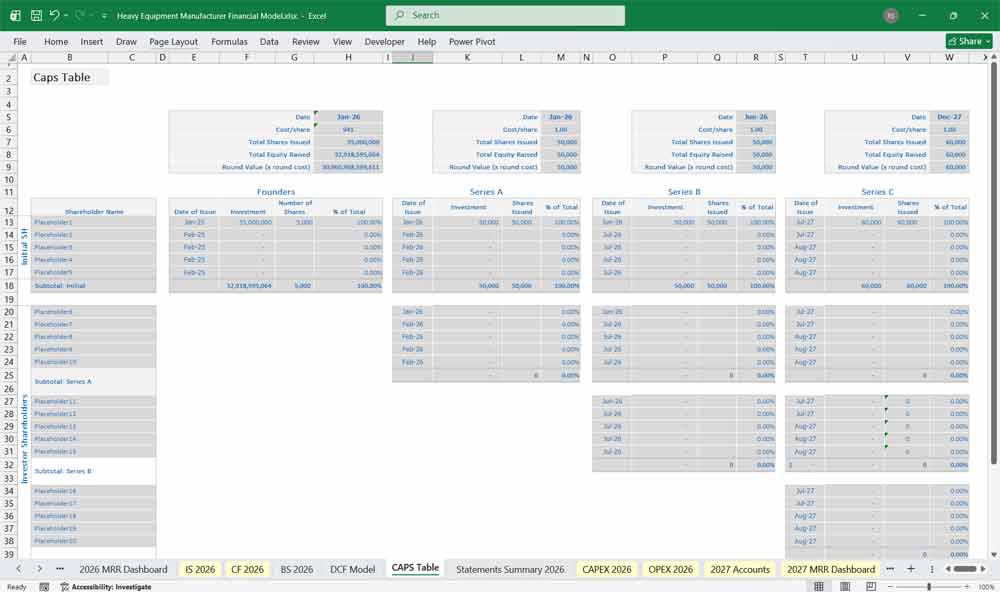
E. Shareholders’ Equity
Common Stock
Retained Earnings
Balance Sheet Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Key Financial Metrics for a Heavy Equipment Manufacturer with Up To 80 Product Lines Allow You To:
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer – Product Innovation Strategy
Launch eco-friendly diesel-electric hybrid machines
Incorporate AI for predictive maintenance
Introduce modular equipment designs
Develop noise-reducing technologies
Partner with R&D labs for material innovations
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer – Revenue Diversification
Expand into spare parts and consumables
Offer subscription-based maintenance services
Introduce training-as-a-service for operators
Monetize data analytics from smart equipment
License proprietary technology to OEMs
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer – Aftermarket Services (This Can Be Part Of A Subscription Revenue Service)
Offer maintenance contracts
Launch mobile servicing units
Enable on-site diagnostics with handheld tools
Develop a customer portal for service history
Bundle service with extended warranty plans
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer – Training & Certification Programs
Launch operator training academies
Create virtual simulators for new equipment
Certify mechanics through online modules
Partner with trade schools
Offer re-certification every 2 years
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer – CapEx Planning
Budget for new assembly lines
Invest in automation equipment
Prioritize high-yield R&D projects
Build warehousing capacity near key markets
Model NPV of all major capital projects
Heavy Equipment Manufacturer – Data Analytics & Reporting (Also Part Of A Subscription Tier)
Analyze machine usage trends remotely
Forecast part failures using AI models
Track KPI dashboards in real time
Monitor factory OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
Segment customer retention by region and sector
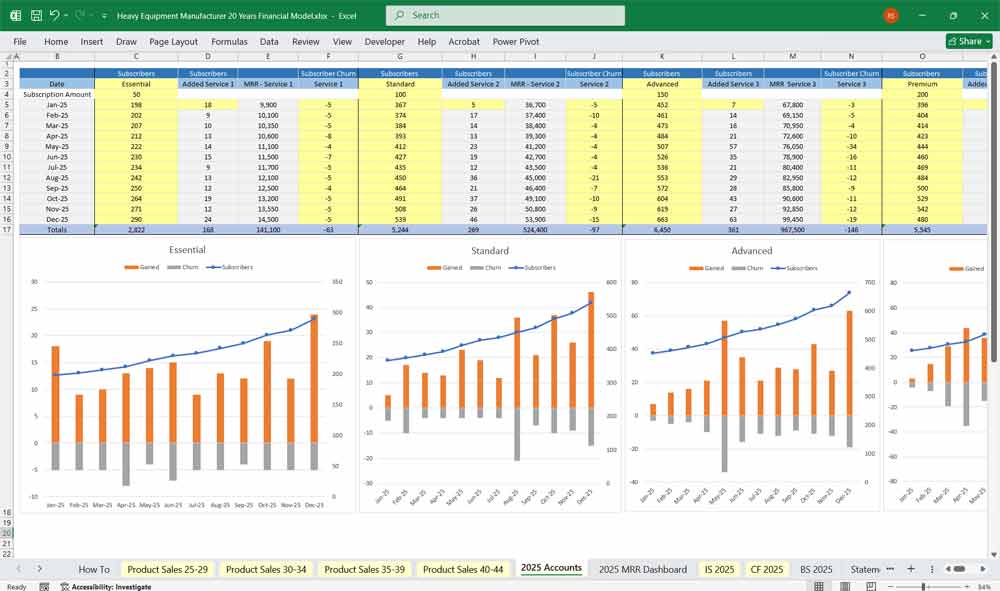
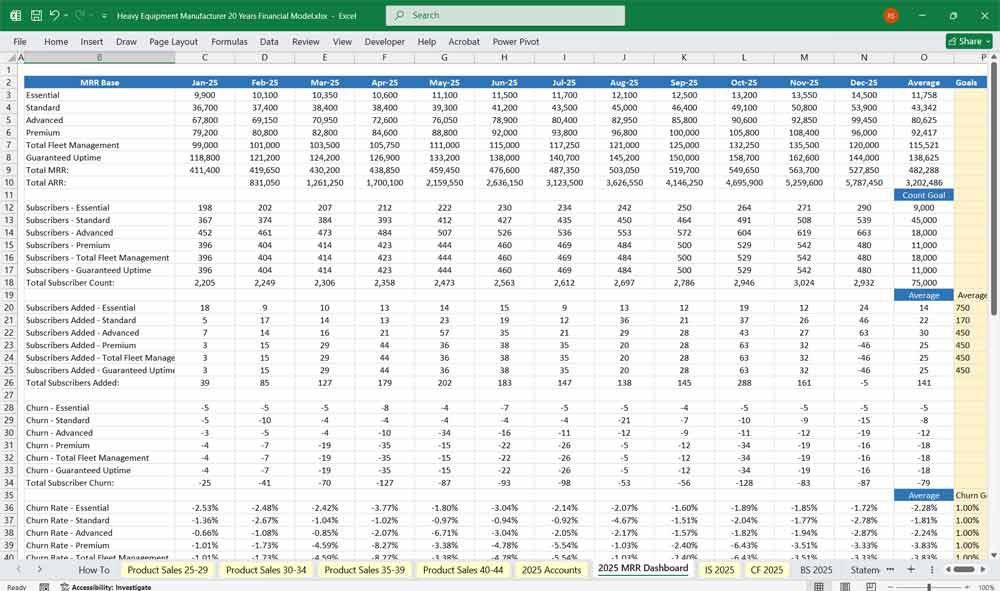
Six-tier subscription service for a heavy Equipment manufacturer “Equipment as a Service” (EaaS)
Tier 1: “Essential Heavy Equipment”
This basic tier would likely be included with the purchase of a new machine or available for a low monthly fee. It would provide customers with access to a digital parts catalog and a basic service manual. Think of it as a foundational resource for the owner-operator. 🛠️
Tier 2: “Standard Heavy Equipment“
Building on the Essential tier, this level introduces scheduled maintenance reminders and diagnostic code lookup. It helps the customer stay on top of routine service, preventing potential issues before they become major problems.
Tier 3: “Advanced Heavy Equipment”
This is where preventive maintenance becomes a key feature. Subscribers would get access to predictive analytics based on machine usage data. The system could alert them to potential component failures (e.g., a bearing showing early signs of wear) before they happen. This tier would also include remote monitoring, allowing the manufacturer to access machine data for troubleshooting.
Tier 4: “Premium Heavy Equipment”
The Premium tier adds significant value by including on-site technical support and a loaner machine program. If a critical piece of equipment breaks down, a technician would be dispatched, and the customer could get a temporary replacement to minimize downtime. It is a comprehensive solution designed to keep operations running smoothly.
Tier 5: “Total Heavy Equipment Fleet Management”
This tier is geared towards customers with multiple machines. It includes everything from the previous tiers, plus data analytics that provide insights into fleet performance, fuel consumption, and operator efficiency. The manufacturer would offer consulting services to help the customer optimize their entire operation.
Tier 6: “Heavy Equipment Guaranteed Uptime”
This top-tier subscription is a commitment from the manufacturer. It includes all the features of the other tiers and guarantees a certain level of machine uptime (e.g., 98%). If the machine falls below the agreed-upon uptime, the manufacturer would provide financial compensation or other remedies. This is a complete risk-management solution.
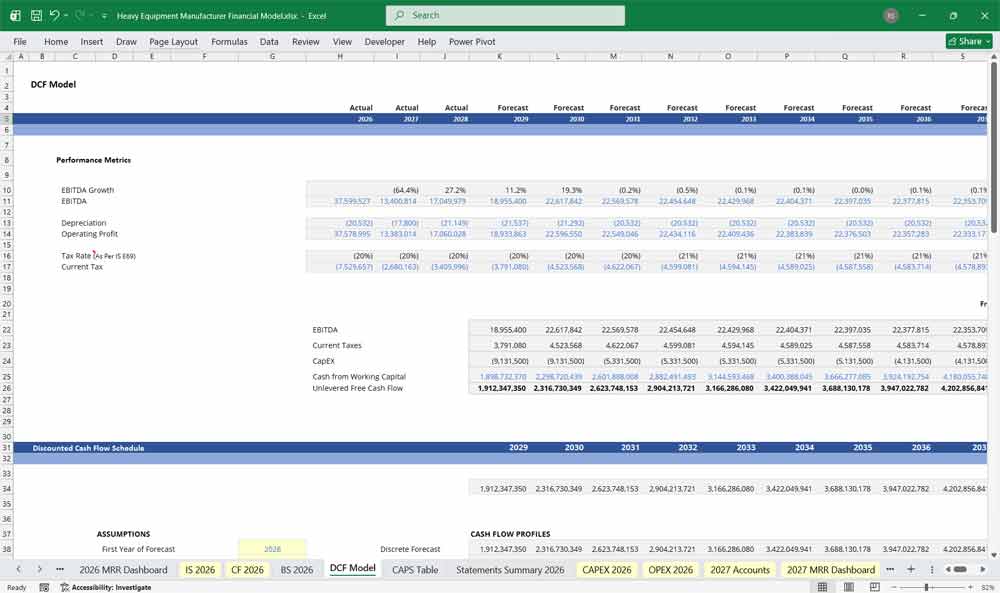
Valuing a heavy equipment manufacturer With A Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
DCF: Valuing the Cycle and the “Aftermarket Tail”
This 20-year Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis for a heavy equipment manufacturer captures the rhythmic “replacement cycles” of global fleets in mining, construction, and agriculture. The model balances the high-margin, highly cyclical sales of new “heavy iron” against a remarkably stable aftermarket tail—the recurring revenue from parts and services that often carries the business through economic downturns. Because these manufacturers are currently pivoting toward autonomous and electric machinery, the DCF must meticulously model the R&D-heavy transition phase, ensuring the terminal value reflects a company that has successfully traded diesel engines for next-generation propulsion and software-as-a-service (SaaS) integration.
WACC: Pricing Industrial Volatility and Captive Finance
The Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) for a heavy equipment manufacturer typically reflects a “high-beta” risk profile, as its fortunes are tightly tethered to global GDP and commodity prices. A unique factor in this calculation is the presence of captive finance arms; these subsidiaries allow the manufacturer to carry significant debt to fund customer purchases, which can lower the overall WACC but introduce “credit risk” to the balance sheet. The discount rate must price in the double-edged sword of interest rates: a rise increases the company’s cost of capital while simultaneously dampening customer demand by making equipment leases more expensive. This hurdle rate ensures that the multi-decade cash flows are appropriately “punished” for the inherent volatility of the heavy machinery sector.
Sensitivity Analysis: Stress-Testing Steel and Order Backlogs
For a heavy equipment manufacturer, Sensitivity Analysis is the primary tool for measuring operating leverage—the way a small change in sales volume triggers a massive swing in profit. Analysts use sensitivity tables to see how a 10% spike in specialized steel prices or a shift in global labor costs impacts the “unit margin” of a bulldozer or excavator. Perhaps most critically in a 20-year model, the analysis stress-tests “backlog conversion” rates, identifying how sensitive the valuation is to customers cancelling orders during a sudden cyclical slump. By testing the impact of fluctuating exchange rates on global sales, the sensitivity analysis reveals the manufacturer’s resilience to a “strong dollar” or a prolonged downturn in the mining and infrastructure sectors.
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This 20 Year Heavy Equipment Manufacturer Financial Model focuses on balancing capital expenditures with steady revenue growth from diversified 80 product line sales and subscription-based services. By optimizing OPEX and CAPEX and maximizing high-margin services like heavy machinery sales and servicing offerings, the model ensures sustainable profitability and cash flow stability.
Download Link On Next Page
