EV Charger Factory Financial Model
This 20-Year, 3-Statement EV Charger Factory Financial Model includes revenue streams, cost structures, and financial statements to forecast the economic health of your EV Charger Factory. Track revenues generated through 80 product lines, and subscription sales.
20x Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, Balance Sheets, OPEX Sheets, CAPEX sheets, Statement Summary Sheets, and Revenue Forecasting Charts, BEA charts, sales summary charts, employee salary tabs and expenses sheets. Over 130 Tabs of financial data to monitor.
Financial Model For An EV Charger Factory
This financial model for an EV Charger factory is built to assess profitability, cash flow, and financial health. It accounts for production costs, sales projections, operational expenses, capital investment, and financing. It includes detailed scenarios for up to 80 SKUs and a 6-tier subscription model Add-On.
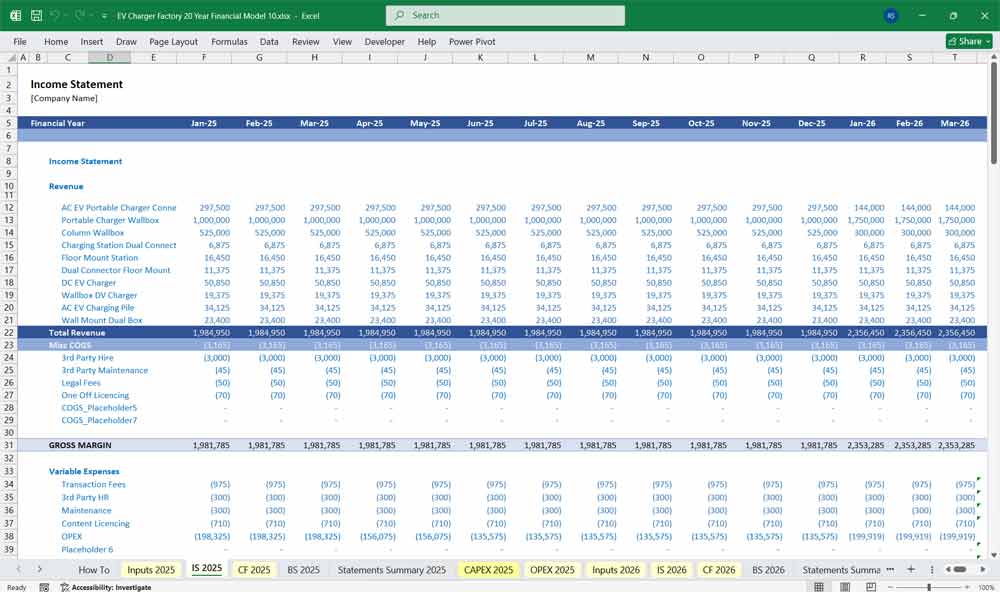
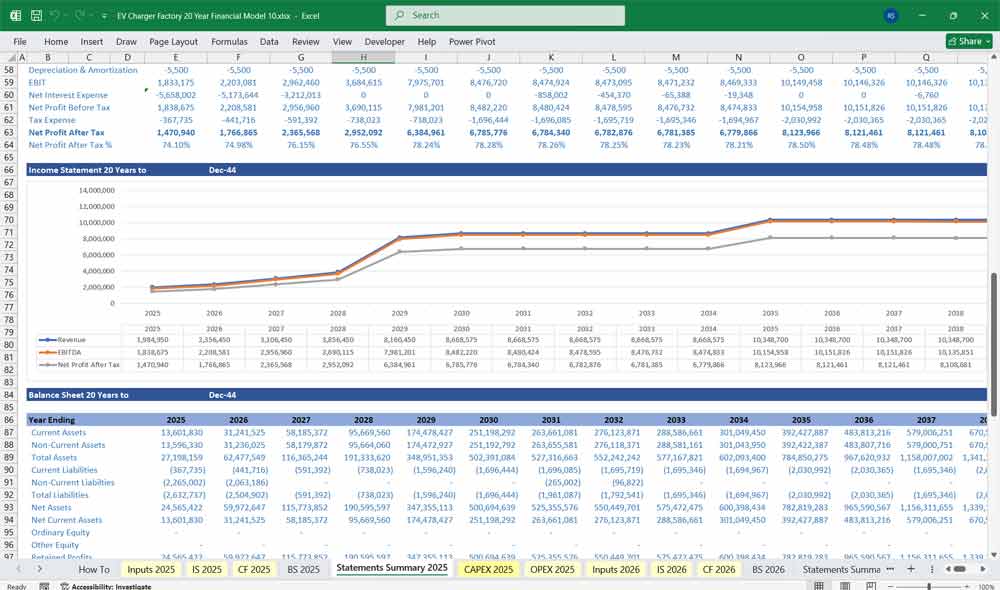
Income Statement (P&L)
The Income Statement is projected monthly (for years 1–2) and annually thereafter. Key sections:
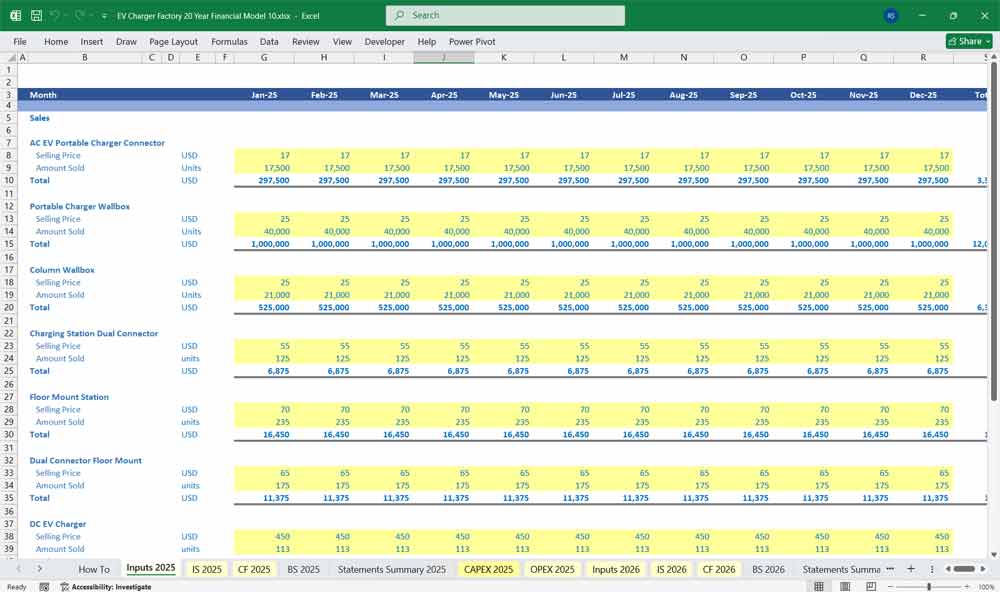
Revenue
Product Sales (by group and total)
Service & Software Subscriptions
Parts & Accessories Sales
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Materials
Labor
Factory Overheads
Freight
Warranty
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
Margin analysis by product line
Operating Expenses (OPEX)
R&D
SG&A
Depreciation & Amortization
Operating Income (EBIT)
Interest Expense (on loans)
Pre-Tax Income
Income Tax
Net Income
EBITDA, EBIT, and Net Margin ratios
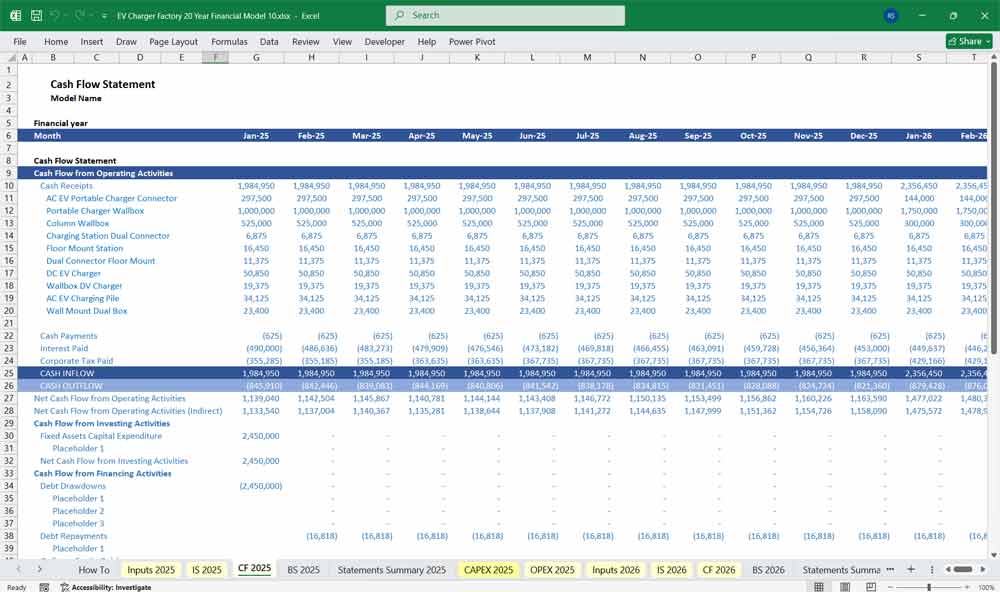
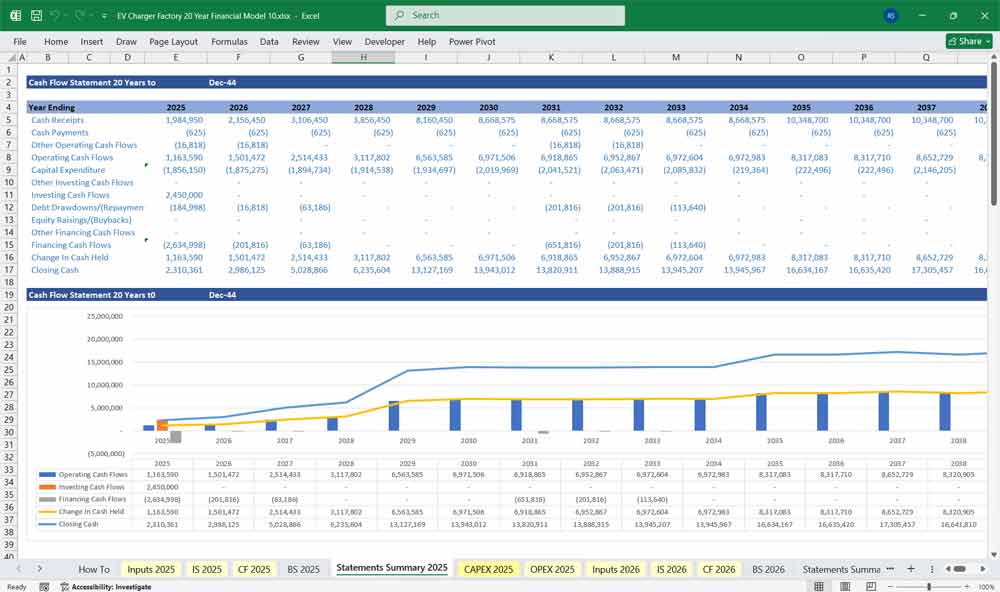
EV Charger Factory Cash Flow Statement
Modeled using the Indirect Method:
Operating Cash Flow
Start with Net Income
Add: Depreciation & Amortization
Add/Subtract: Working Capital changes
Less: Taxes paid
= Net Cash from Operations
Investing Cash Flow
Capital Expenditures (negative)
Proceeds from asset sales
R&D capitalization (if any)
= Net Cash from Investing
Financing Cash Flow
New Debt Issuance / Repayment
Equity Injections / Buybacks
Dividend Payments
= Net Cash from Financing
Net Change in Cash
Sum of all above sections.
The cash balance at the end of each period flows directly into the Balance Sheet.
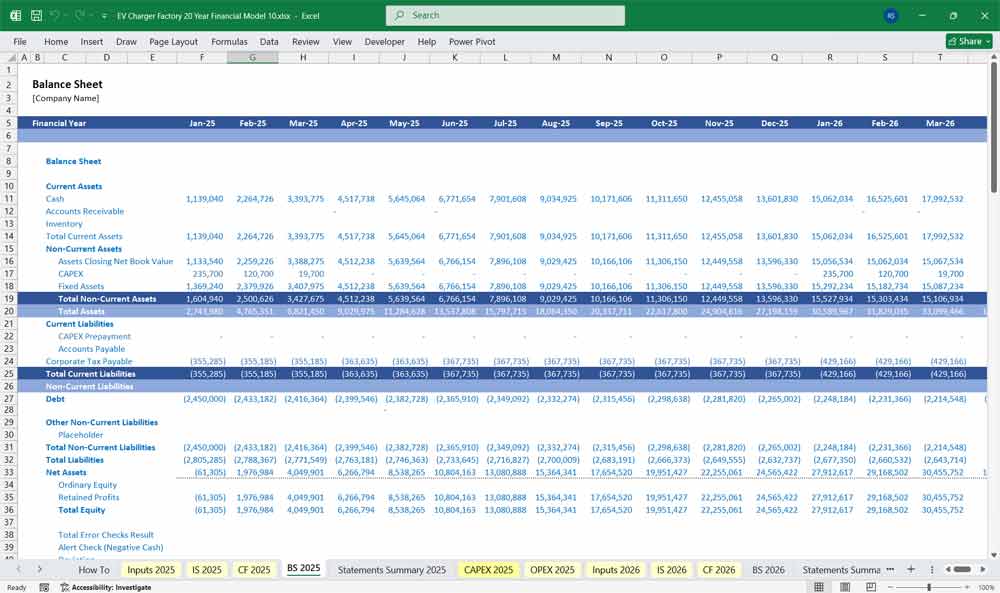
EV Charger Factory Balance Sheet
Assets
Current Assets
Cash & Cash Equivalents
Accounts Receivable
Inventory (raw, WIP, finished)
Prepaid Expenses
Non-Current Assets
Property, Plant & Equipment (net of depreciation)
Intangible Assets (software, patents)
Deferred Tax Assets
Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable
Accrued Expenses
Short-term Debt
Current Portion of Long-term Debt
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-term Loans
Deferred Tax Liabilities
Shareholders’ Equity
Paid-in Capital
Retained Earnings
Other Comprehensive Income
The Balance Sheet always balances:
Total Assets = Total Liabilities + Equity
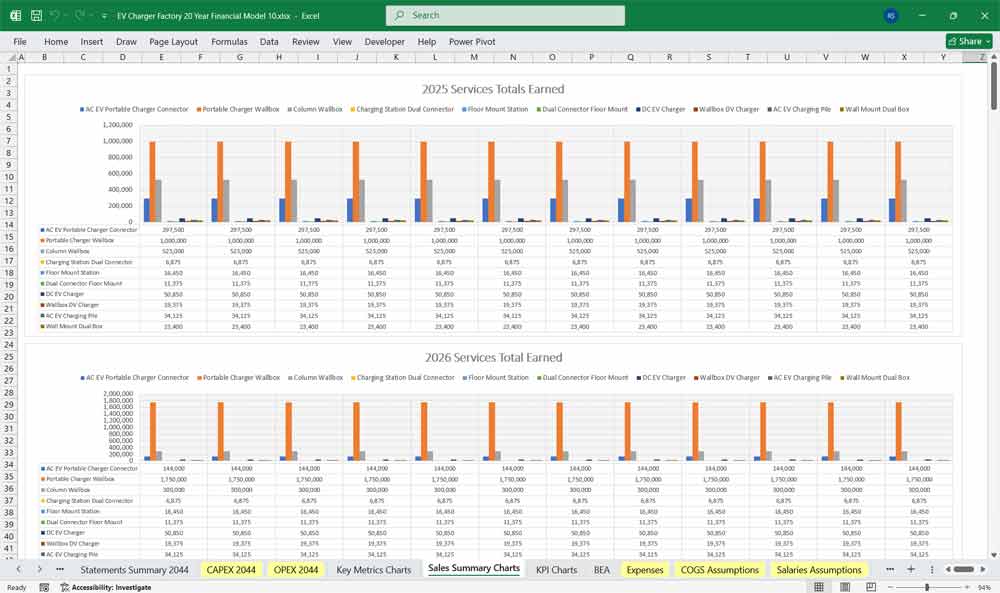
Key Financial Metrics for an EV Charger Factory
This financial model represents the operations of an Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger Manufacturing Factory, which designs, produces, and sells both complete charging systems and associated parts and components. The model projects 5–10 years of financial performance, based on production capacity, product mix, pricing strategy, market growth, and capital structure.
The model is divided into several key modules:
Revenue Module (80 Product Lines + Turnkey Systems)
Cost Structure (COGS, labor, overhead, materials, logistics)
Operating Expenses (R&D, SG&A, marketing, etc.)
Depreciation and CapEx schedule
Working Capital
Financing (Debt & Equity)
Taxation
Output Statements:
Income Statement
Cash Flow Statement
Balance Sheet
KPIs and Ratios
Revenue Module
Product Line Example Structure (80 SKUs)
The model incorporates 80 separate product lines, grouped into categories:
DC Fast Chargers (10 models) — 50 kW, 100 kW, 150 kW, 350 kW variants
AC Chargers (15 models) — residential, fleet, and workplace units
Charging Modules (10 models) — power electronics modules, converters
Cables and Connectors (8 models) — Type 1, Type 2, CCS, CHAdeMO, etc.
Payment & Control Systems (7 models) — smart control panels, metering systems
Software Licenses (5 models) — cloud management, billing, analytics tools
Replacement Parts (15 models) — fuses, boards, transformers, internal wiring, relays
Accessories (10 models) — mounting kits, housings, pedestals, branding panels
Each SKU line includes:
Unit price (wholesale, retail)
Monthly/annual sales volume
Production cost per unit
Gross margin per SKU
SKU contribution to total sales
Expected annual growth rate
Product life cycle (launch–maturity–decline)
Regional split (domestic/export)
Warranty/return rates
Spare part attachment rate
A consolidation sheet aggregates SKU-level revenue and cost data into total product group revenues.
Revenue Drivers
Sales Volume is driven by factory capacity utilization, industry demand forecasts, and market penetration assumptions.
Average Selling Price (ASP) is modeled to decline slightly each year due to competition and scale effects.
Parts Sales grow in proportion to installed base of chargers (e.g., 3–5% of cumulative chargers sold require replacement parts per year).
Aftermarket Service Revenue grows as the installed base expands.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS is calculated per product family:
Raw Materials: Metal enclosures, copper cabling, semiconductors, transformers, cooling systems, printed circuit boards.
Direct Labor: Assembly, testing, quality control.
Factory Overhead: Utilities, maintenance, indirect staff, consumables.
Freight & Packaging: Outbound logistics and protective packaging.
Warranty Expense: Percentage of sales (1–2%) set aside for replacements or service.
The COGS schedule ties to production volumes and cost efficiency improvements over time (e.g., 2–3% annual cost reduction via economies of scale).
Operating Expenses
R&D Expense
Ongoing design and innovation, modeled as a percentage of revenue (typically 4–6%), front-loaded in early years for new charger designs.
Sales & Marketing
Sales commissions, trade shows, digital marketing, distributor support — modeled as a fixed + variable cost based on revenue.
General & Administrative (G&A)
Includes salaries for management, accounting, legal, and HR, plus insurance, rent, IT systems, and professional services.
Depreciation & Amortization
Linked to CapEx schedule and intangible assets (e.g., software IP, patents).
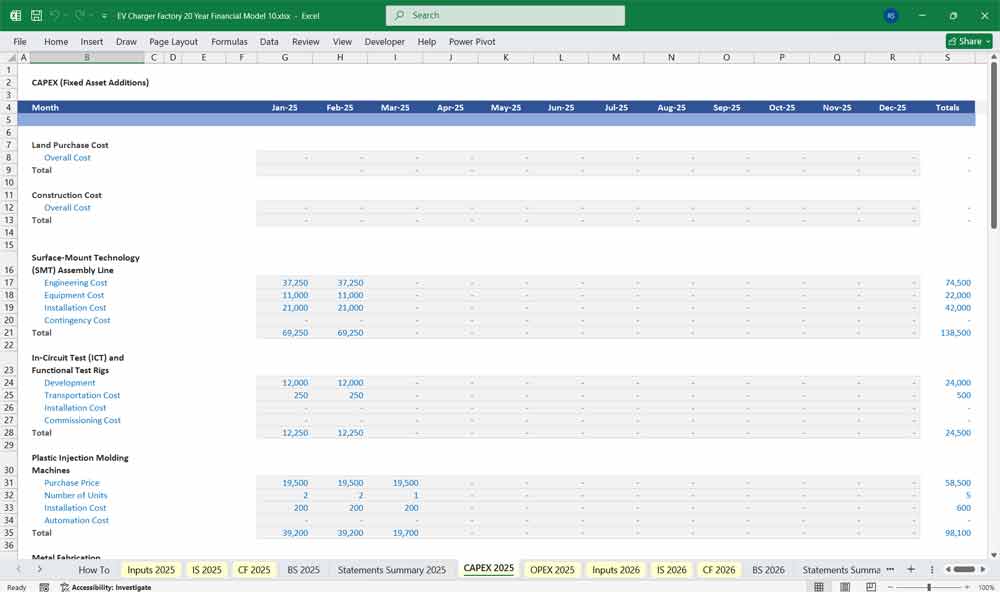
Capital Expenditures (CapEx)
The CapEx schedule includes:
Factory Setup: Buildings, assembly lines, robotics, QC systems.
Machinery & Equipment: Soldering stations, testing rigs, automation.
Tooling & Molds: For housings and connectors.
Software Development: Production monitoring, ERP integration.
Expansion Phases: Additional lines added as capacity utilization exceeds 85%.
CapEx drives depreciation (straight-line or accelerated) over useful lives:
Buildings: 20 years
Equipment: 10 years
Tooling: 5 years
Software: 3–5 years
Financing & Taxation
Debt
Model includes long-term loans for factory buildout and equipment, with interest expense tied to principal balance and amortization schedules.
Equity
Equity injections fund initial CapEx; dividends can be modeled as a payout ratio of net income.
Taxes
Effective tax rate modeled (e.g., 25%) after accounting for depreciation, interest, and R&D credits.
6 Tier Subscription Model For An EV Charger Factory
Tier 1: Basic Hardware Warranty & Support
Target Customer: Home users, small businesses buying individual chargers. The “out-of-the-box” standard offering, often included for free for 1-3 years to enable the initial sale.
Core Offering:
Hardware Warranty: Covers repair or replacement of the charger unit for manufacturing defects.
Basic Technical Support: Access to a support portal, email support, and standard business hours phone support with limited SLAs (e.g., 48-hour response time).
User Manual & Documentation: Standard online resources.
Revenue Model: Typically included in the hardware purchase price. Can be a paid extension after the initial warranty period expires (e.g., $99/year).
Value Proposition for Customer: Peace of mind against hardware failure.
Value Proposition for Factory: Reduces support costs by channeling users to self-service, builds a baseline customer database.
Tier 2: Proactive Monitoring & Maintenance
Target Customer: Fleet operators, commercial property owners, public charging site hosts.
Core Offering:
Everything in Tier 1.
24/7 Remote Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of charger status, connectivity, and health.
Proactive Alerts: Automated notifications for faults, offline status, or performance degradation sent to both the site manager and the factory’s support team.
Basic Diagnostics & Troubleshooting: Remote diagnostics to resolve software issues without a site visit.
Firmware Updates: Guaranteed, automated over-the-air (OTA) security and feature updates.
Revenue Model: Monthly or annual subscription fee per charger (e.g., $15-$30/month/port).
Value Proposition for Customer: Maximizes charger uptime, reduces operational headaches, ensures the charger is always secure and up-to-date.
Value Proposition for Factory: Creates a predictable revenue stream and a direct, ongoing relationship with the operator.
Tier 3: Advanced Software & Management Platform
Target Customer: Businesses with multiple chargers (workplaces, apartments, retail), Charge Point Operators (CPOs).
Core Offering:
Everything in Tier 2.
Central Management Software (CMS): A web-based dashboard to manage a network of chargers.
User Access Control: Set pricing, create access groups (employees, guests, residents), and manage RFID cards or app-based authentication.
Billing & Payment Processing: Automated billing, session data, and payment processing for paid charging.
Usage Reporting & Analytics: Detailed reports on energy consumption, usage patterns, and revenue.
Revenue Model: Higher monthly/annual fee per charger or a percentage of processing fees (e.g., 2-5% of transaction revenue) on top of a base fee.
Value Proposition for Customer: Turns a cost center into a potential revenue stream, provides deep insights into usage, enables controlled access.
Value Proposition for Factory: Locks customers into a proprietary software ecosystem, creates a high-margin revenue stream from software.
Tier 4: Premium Service Level Agreement (SLA) & On-Site Support
Target Customer: High-traffic public charging hubs, large fleet depots, mission-critical logistics centers.
Core Offering:
Everything in Tier 3.
Guaranteed Uptime SLA: A contractual guarantee of network and charger availability (e.g., 99.9% uptime).
Priority 24/7 Support: Dedicated phone line with sub-1-hour response time.
Advanced Parts Replacement: Guaranteed spare parts dispatch within a specified time window (e.g., 4 hours or next-day).
On-Site Technician Dispatch: Includes a certain number of on-site service hours per year for repairs and preventative maintenance.
Revenue Model: Premium annual subscription with a high fee per site or per port, often with a custom quote.
Value Proposition for Customer: Minimizes financial risk from charger downtime, ensuring business continuity for their EV operations.
Value Proposition for Factory: High-margin service contracts, strengthens relationships with most valuable customers.
Tier 5: Energy Management & Grid Services Integration
Target Customer: Sites with high energy costs, CPOs participating in demand response, fleets transitioning to electric.
Core Offering:
Everything in Tier 4.
Smart Load Management: Dynamic power balancing across multiple chargers to avoid expensive peak demand charges and stay within site power limits.
Solar & Battery Storage Integration: Software to intelligently use on-site solar generation and battery storage to charge vehicles, maximizing green energy and minimizing grid draw.
V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) Enablement: Hardware and software to manage bi-directional charging, allowing fleet vehicles to sell energy back to the grid during peak times.
Grid Services Portal: Enables participation in utility demand response programs, creating a new revenue stream for the site host.
Revenue Model: High subscription fee + a share of the revenue generated from grid services.
Value Proposition for Customer: Significant reduction in electricity costs, new revenue opportunities, enhanced sustainability credentials.
Value Proposition for Factory: Positions the factory as a technology leader in the energy transition, creates a deeply integrated and “sticky” product suite.
Tier 6: Fully Managed “Charging as a Service” (CaaS)
Target Customer: A customer who wants a complete, turnkey charging solution with zero operational burden. This is the ultimate “white-glove” service.
Core Offering:
No Upfront CAPEX: The factory owns, installs, and maintains all the hardware on the customer’s site.
Comprehensive Service: Includes *all features from Tiers 1-5*.
End-to-End Operations: The factory’s team handles everything: 24/7 monitoring, maintenance, customer support for drivers, billing, and revenue collection.
Guaranteed Performance/KPI: The factory guarantees a certain level of performance, uptime, or even revenue generation for the site host.
Revenue Model: The customer pays a fixed monthly “service fee” per port or a share of the gross revenue generated from the chargers (e.g., a 70/30 split).
Value Proposition for Customer: Zero risk, zero operational overhead. They provide the location and parking, the factory provides a fully functional, revenue-generating asset.
Value Proposition for Factory: Maximizes long-term Customer Lifetime Value (LTV), creates a vast, owned network of chargers, and provides ultimate control over the user experience and data. This is the pinnacle of the subscription model.
This tiered structure allows the EV Charger Factory to serve a diverse customer base, from simple home users to large sophisticated enterprises, while systematically increasing its recurring revenue and strategic importance to its clients.
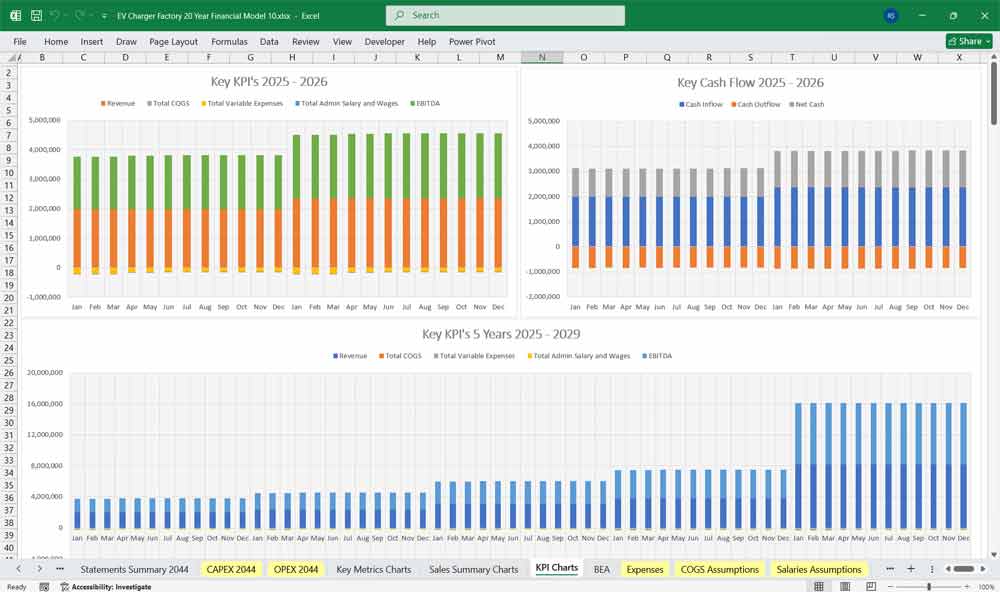
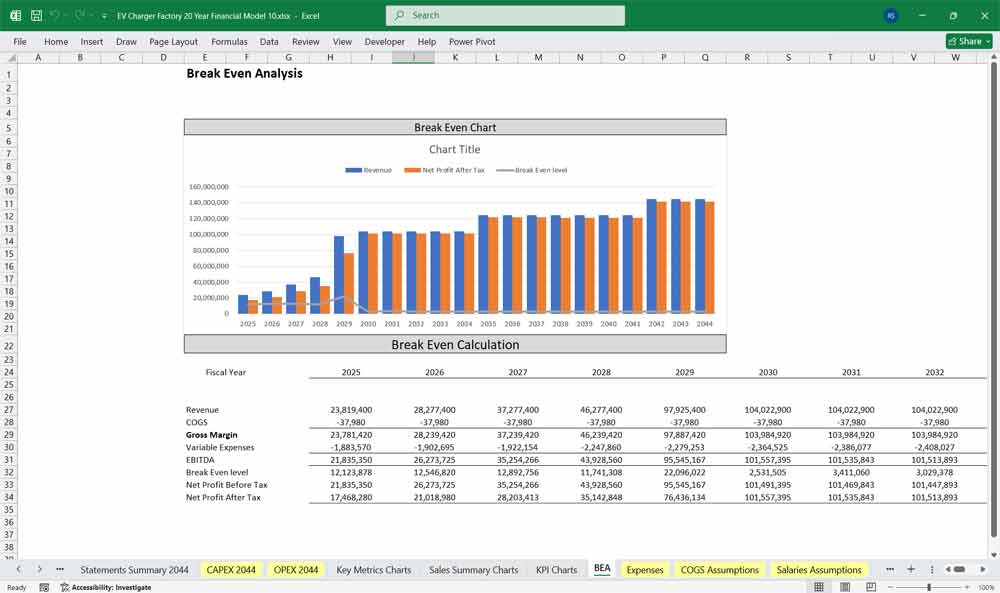
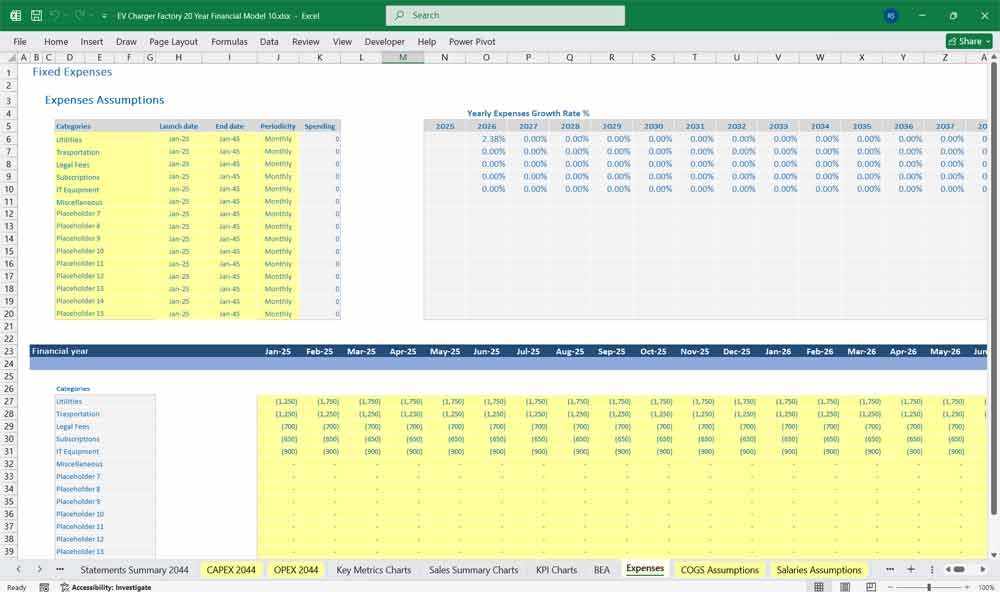
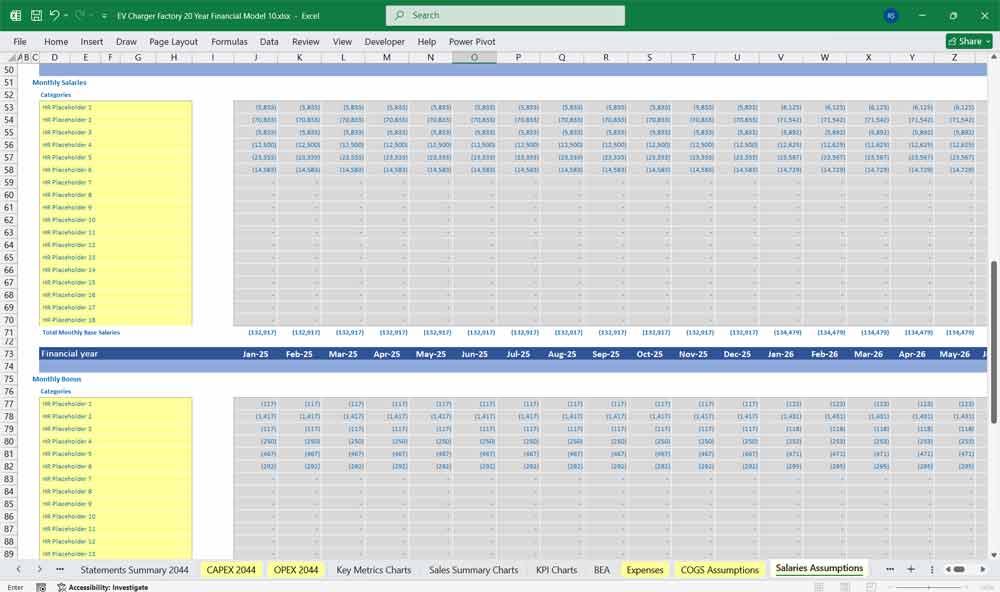
Key Financial Ratios & Metrics
- Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue
- Operating Margin = Operating Profit / Revenue
- EBITDA Margin = (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) / Revenue
- Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Shareholder’s Equity
- Return on Investment (ROI) = Net Profit / Investment Cost
Scenario Analysis
- Best Case: High subscription retention, strong retail demand, cost efficiency.
- Base Case: Steady sales growth with manageable costs.
- Worst Case: Supply chain disruptions, high churn, increased competition.
Conclusion
These Excel financial models for an EV Charger Factory must balance product variety, cost structure, and revenue channels. By incorporating retail sales, bulk distribution, and a 6-tier subscription model, the business can stabilize cash flow and achieve long-term growth
Download Link On Next Page, view the template description.
