Clothing Store Financial Model
Financial Model for a Clothing Store
Financial model for a clothing store forecasting and tracking key financial metrics, inventory performance, and operating expenses over set monthly periods. Includes Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Balance Sheet, and Inventory Discount Analysis Sheets.
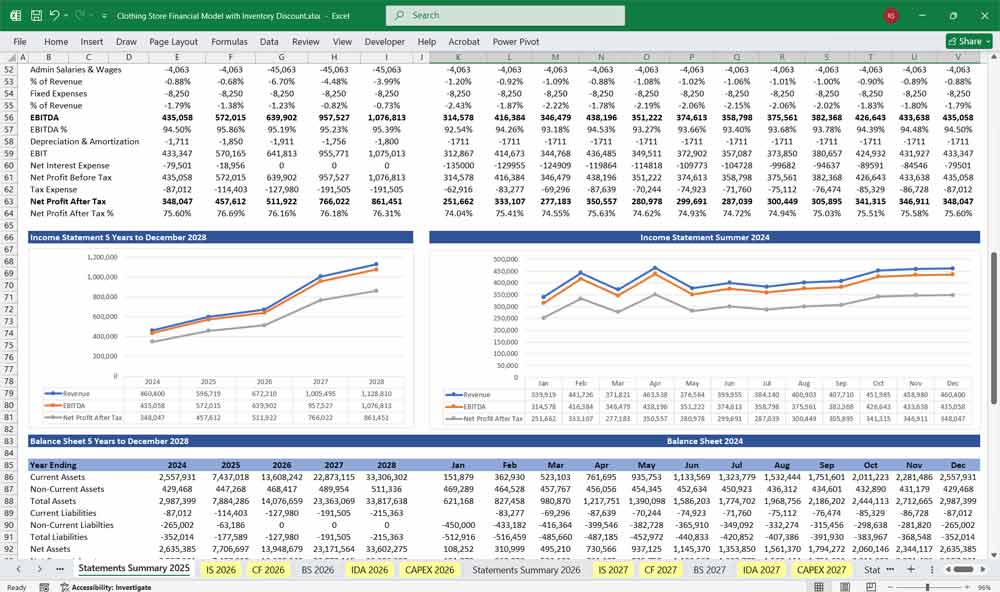
Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement)
This statement summarizes the clothing store’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a period, showing profitability.
A. Revenue
Retail Sales Revenue
In-store sales
Online sales
Wholesale Revenue (if applicable)
Other Revenue
Tailoring services
Consignment sales
Gift card breakage
Revenue = Units Sold × Average Selling Price (ASP)
B. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Opening Inventory
Purchases (including shipping and handling)
Closing Inventory
OR: Units Sold × Cost per Unit
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
C. Operating Expenses
Rent and Utilities
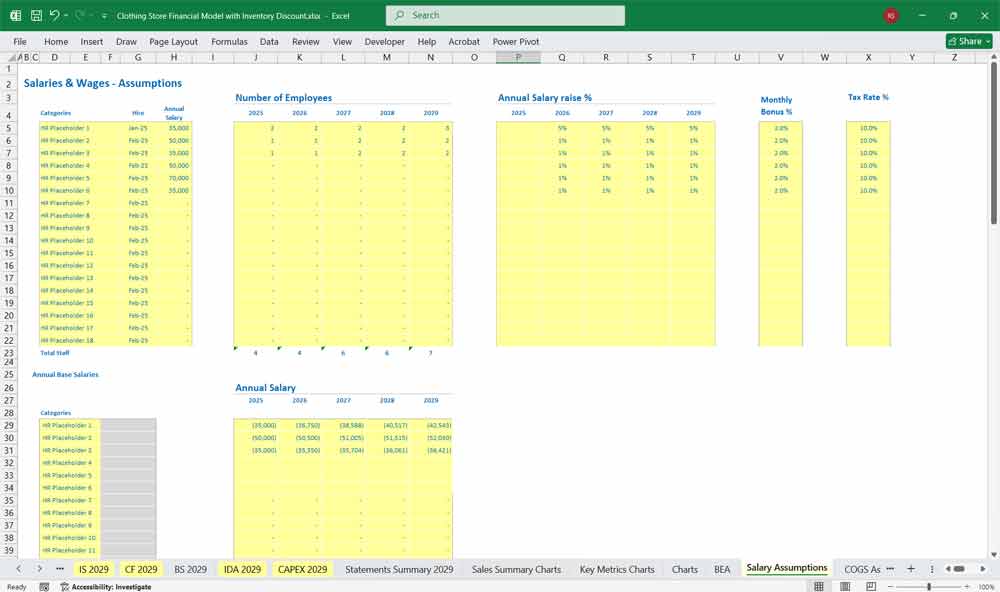
Salaries and Wages
Marketing and Advertising (social media, flyers, promotions)
Point of Sale (POS) system fees
Depreciation (for store fixtures, computers)
Supplies (bags, hangers, etc.)
Insurance
Professional Fees (accounting, legal)
Operating Profit (EBIT) = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
D. Interest and Taxes
Interest on Loans
Taxes (based on local rates)
Net Profit = EBIT – Interest – Taxes
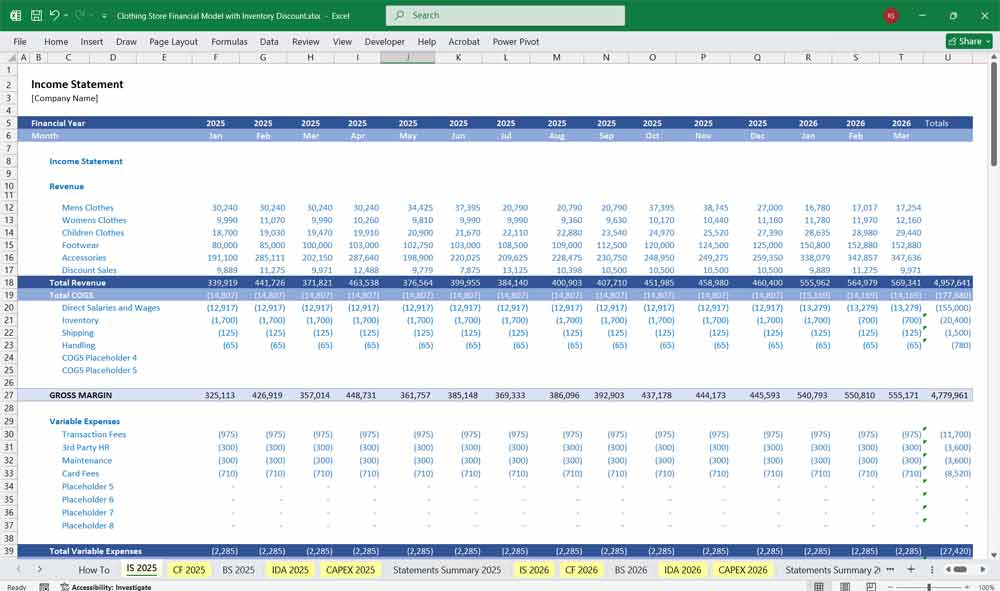
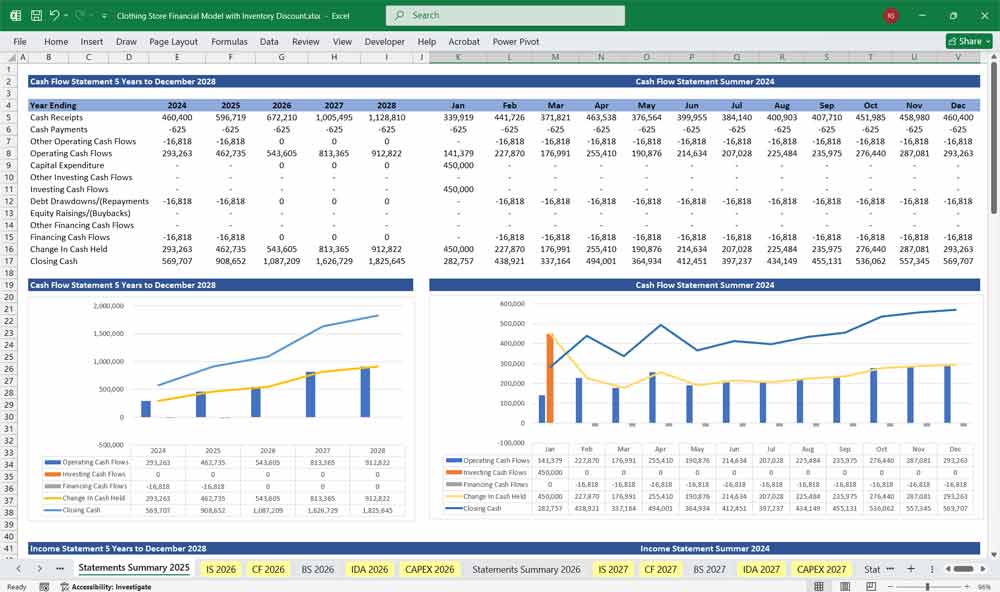
Cash Flow Statement for A Clothing Store
Tracks how much cash is coming in and going out. It’s broken down into Operating, Investing, and Financing activities.
A. Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Net Profit (from Income Statement)
Depreciation/Amortization
Increase in Accounts Receivable
Increase in Inventory
Increase in Accounts Payable
Prepaid Expenses
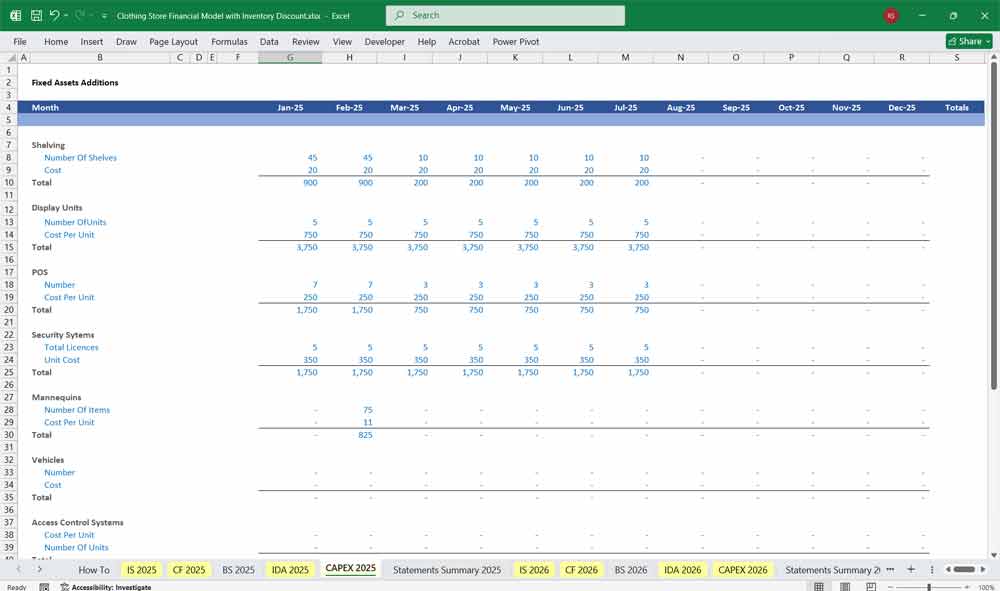
B. Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Purchase of Store Fixtures or Equipment
Purchase of Vehicles (for delivery)
Sale of Old Assets (if any)
C. Cash Flow from Financing Activities
Owner Contributions or Loans
Loan Repayments
Dividend Distributions (if applicable)
Net Change in Cash = Cash from Operating + Investing + Financing
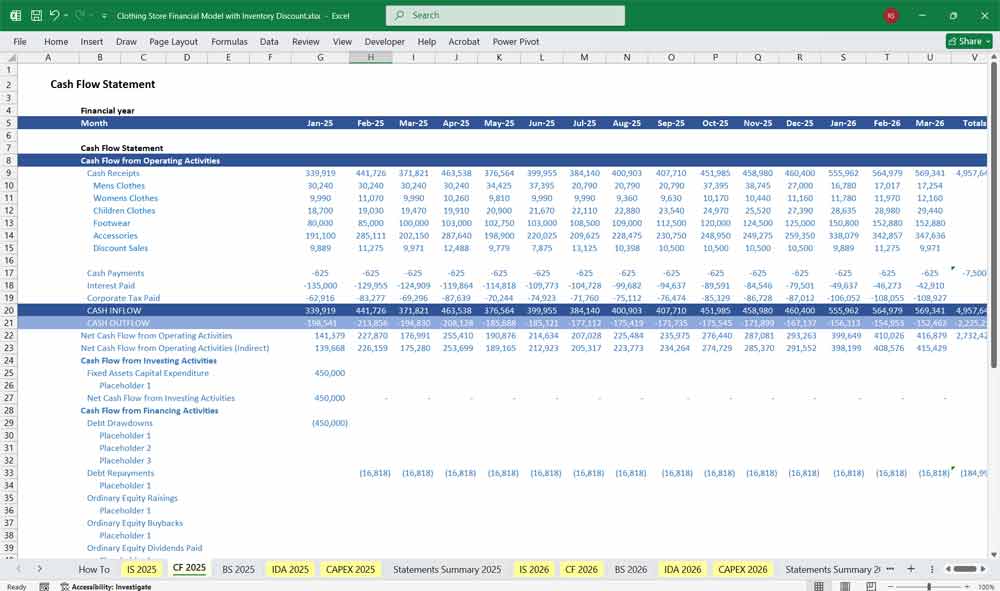
Balance Sheet For A Clothing Store
Provides a snapshot of the business’s financial position at a given date.
A. Assets
Current Assets
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Accounts Receivable
Inventory (raw and finished goods)
Prepaid Expenses
Non-Current Assets
Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E)
Leasehold Improvements
Accumulated Depreciation
B. Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable (to suppliers)
Credit Card Payables
Short-term Loans
Accrued Expenses (wages, utilities)
Long-term Liabilities
Bank Loans
Lease Liabilities
C. Equity
Owner’s Equity / Capital
Retained Earnings
Current Year Net Income
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
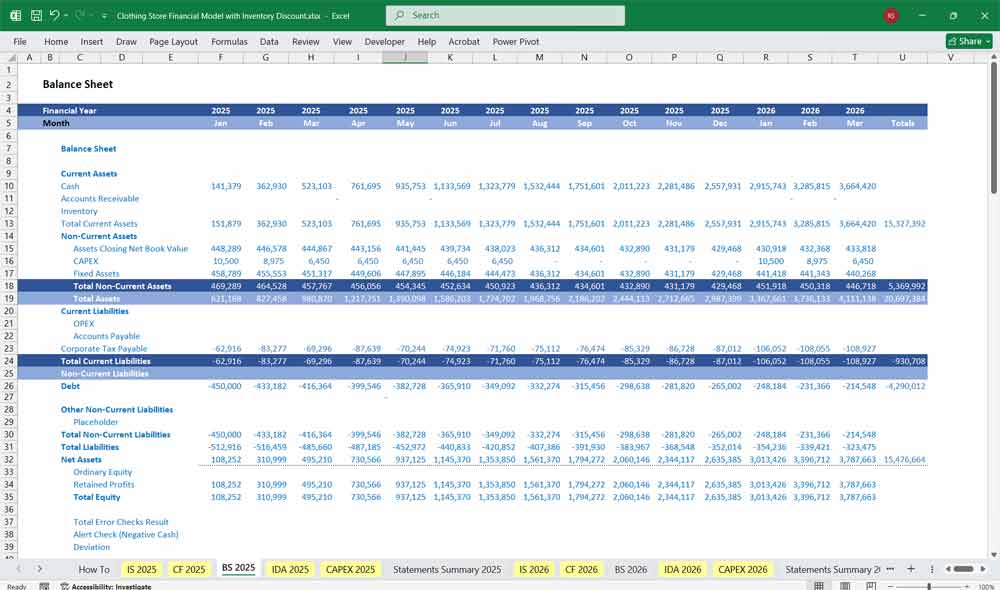
Clothing Store Financial Model With Inventory Discount Analysis Sheet
Tracks how discounting affects inventory turnover and gross margins. Useful for clearance strategies and end-of-season sales.
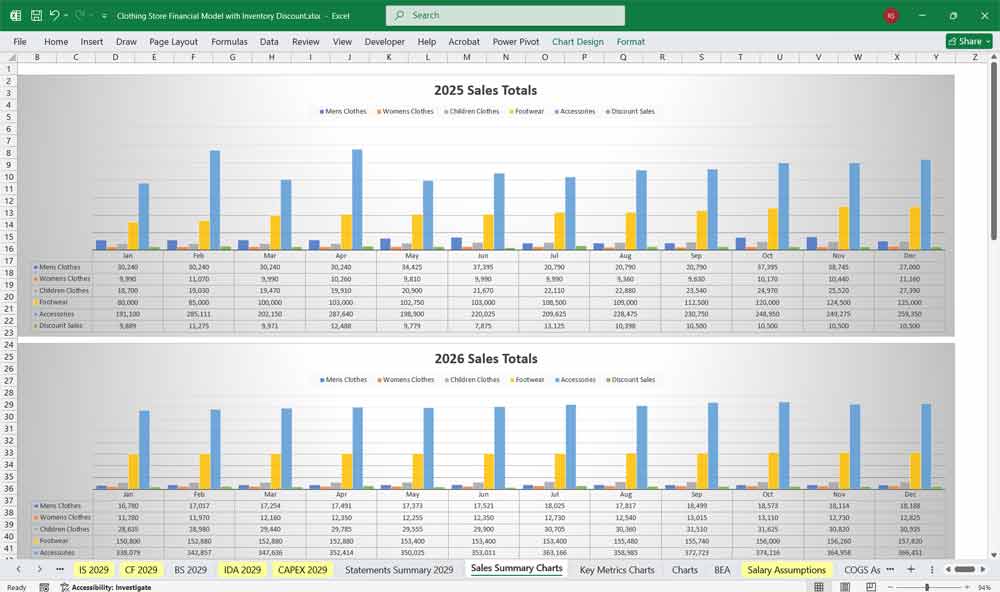
A. Inventory Overview
Beginning Inventory (by SKU)
Purchases (units & cost)
Sales (units & ASP)
Ending Inventory
B. Discount Tiers
Available Units
Amount Sold
Price
Percentage Off
- Sales Totals
C. Key Metrics
Sell-Through Rate = Units Sold / Total Available
Average Discount = ∑ (Units × Discount %) / Total Units
Inventory Turnover Ratio = COGS / Average Inventory
Gross Margin After Discount = ∑ (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue
D. Recommendations
Identify slow-moving SKUs
Analyze profitability of discounts
Optimize markdown timing (e.g., start clearance at 25%, not 50%)
Integration of Sheets
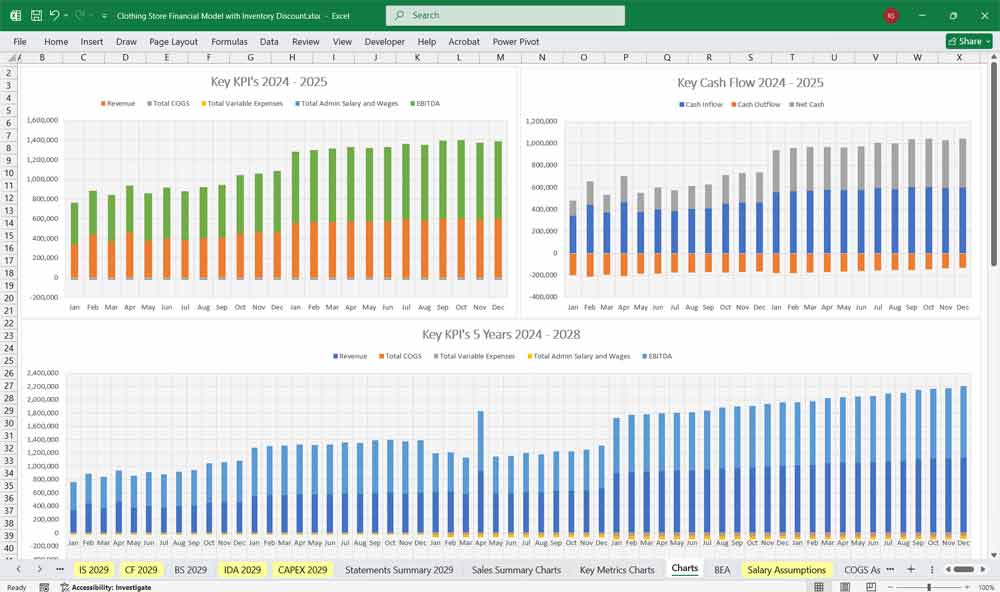
Interlinked pages via formulas in Excel spreadsheets:
Sales data drives revenue and COGS in the Income Statement
Cash inflows/outflows in Cash Flow Statement come from operating, investing, and financing activities
Closing balances of Cash, Inventory, and Payables feed into the Balance Sheet
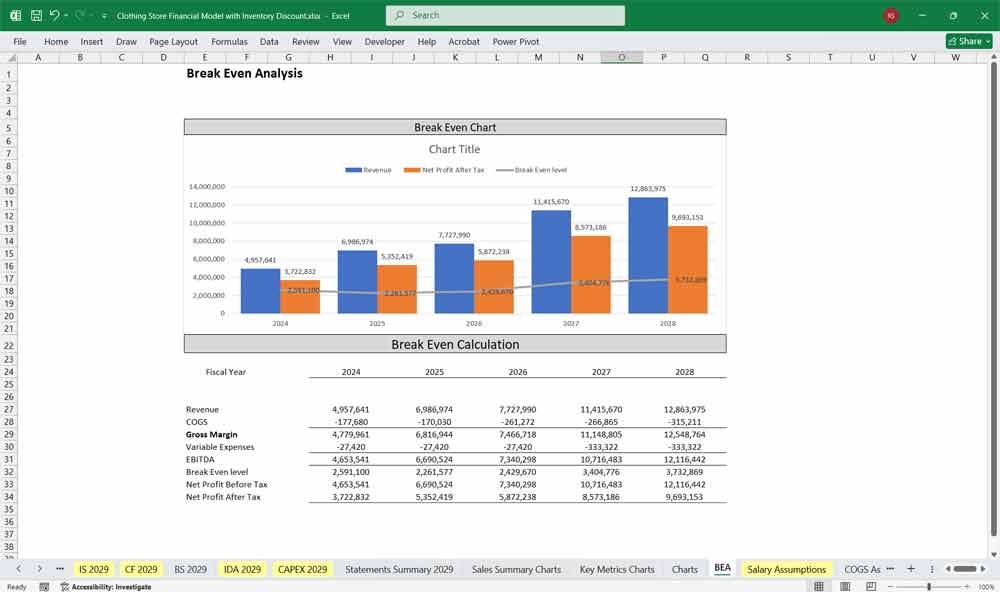
Inventory Discount Analysis provides insights that influence purchasing, pricing, and discounting strategy, reflected in all other sheets.
Final Notes on the Financial Model
This 5 Year Clothing Store Financial Model must focus on balancing capital expenditures with steady revenue growth from diversified services. By optimizing operational costs, power efficiency, and maximizing high-margin services the model ensures sustainable profitability and cash flow stability.
Download Link On Next Page
